Processing method for reusing unqualified chamfered silicon briquette
A processing method and technology for silicon blocks, which are applied in stone processing equipment, fine working devices, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of scrapping, slurry interruption, and increase in manufacturing costs, and achieve unique processing methods, reduce raw material waste, and reduce waste. The effect of improving utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
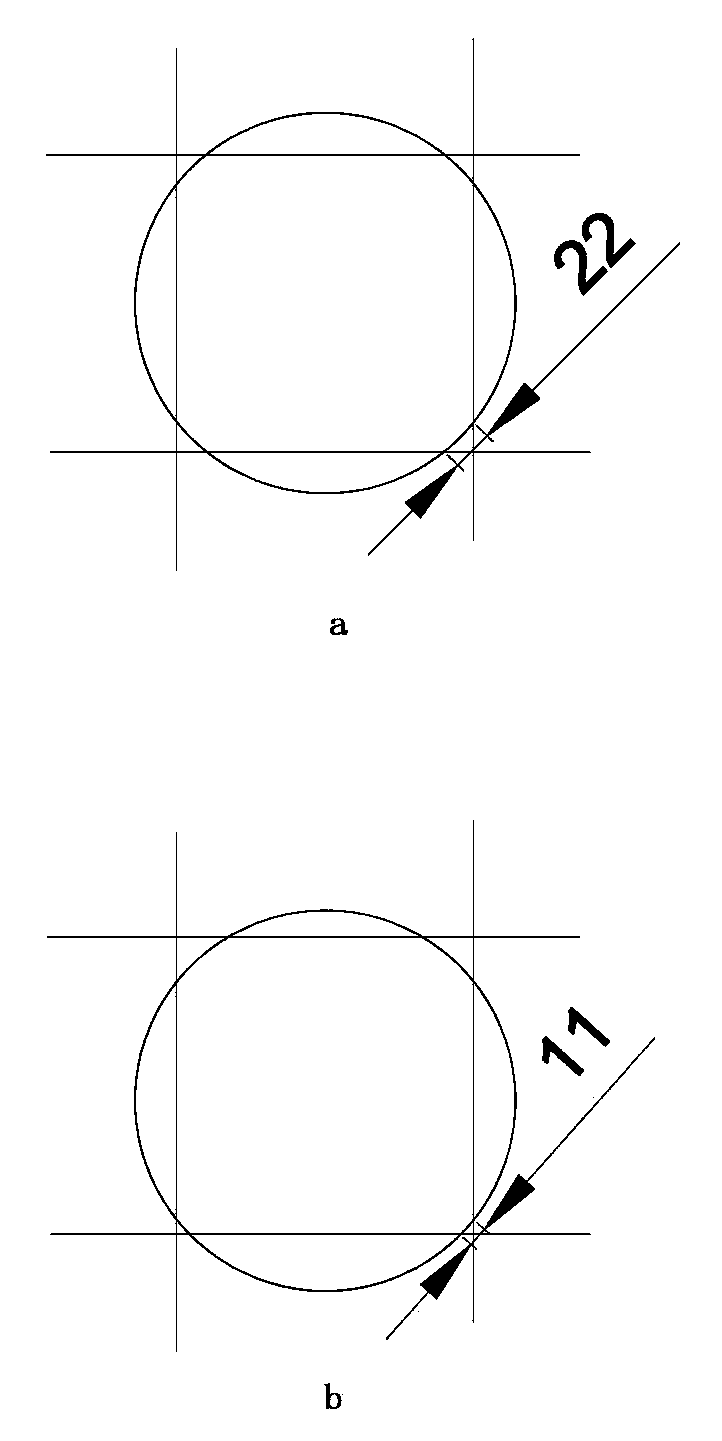
[0026] like figure 1 As shown, the circle represents the outer circle of the single crystal silicon rod, the straight line represents the steel wire, figure 1 a is the end face of the silicon rod that is qualified for normal cutting and chamfering. At this time, the four chamfers are equal, and the radians are all 22. figure 1 b is the end face of the silicon rod with unqualified chamfer. Due to the overall offset of the silicon rod, the dimensions of the four chamfers on the end face are inconsistent. In the prior art, figure 1 The cut and unqualified silicon blocks shown in b can only be scrapped, which will cause serious waste of raw materials and increase the cost of qualified silicon blocks.
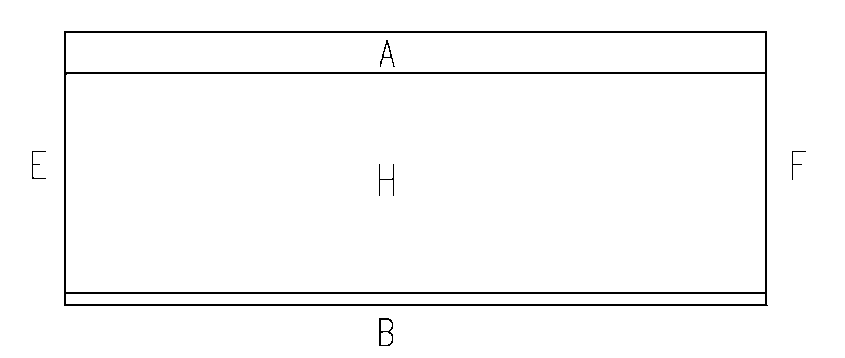
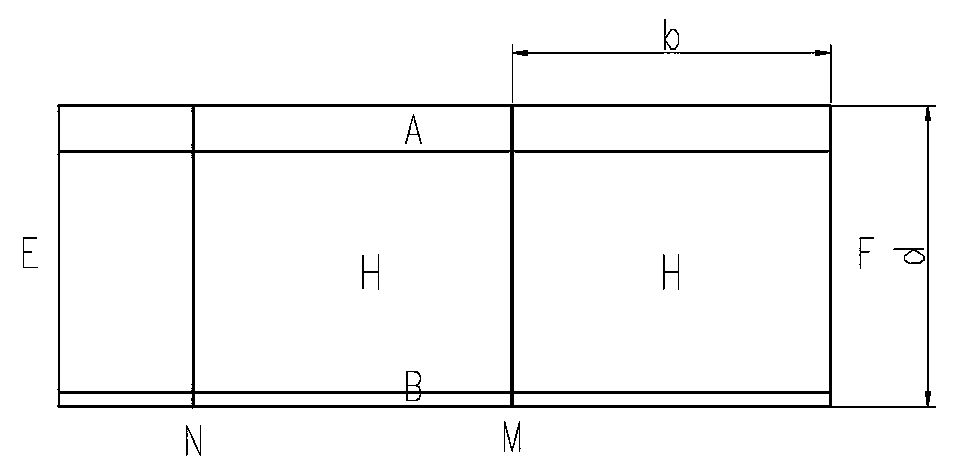
[0027] figure 2 Shown is the structural schematic diagram of the unqualified silicon wafer, figure 1 Shown is the structure viewed from the end face of the ingot, figure 2 For the structure viewed from the side of the ingot, image 3 for figure 2 left view of , in figure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com