Offshore nuclear emergency radiation monitor based on cylindrical buoy
A radiation monitoring and monitoring instrument technology, applied in radiation measurement, X/γ/cosmic radiation measurement, X-ray energy spectrum distribution measurement, etc. Use and other issues to achieve the effect of improving the monitoring speed and efficiency, reducing the occupation of resources, and reducing the difficulty of guaranteeing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
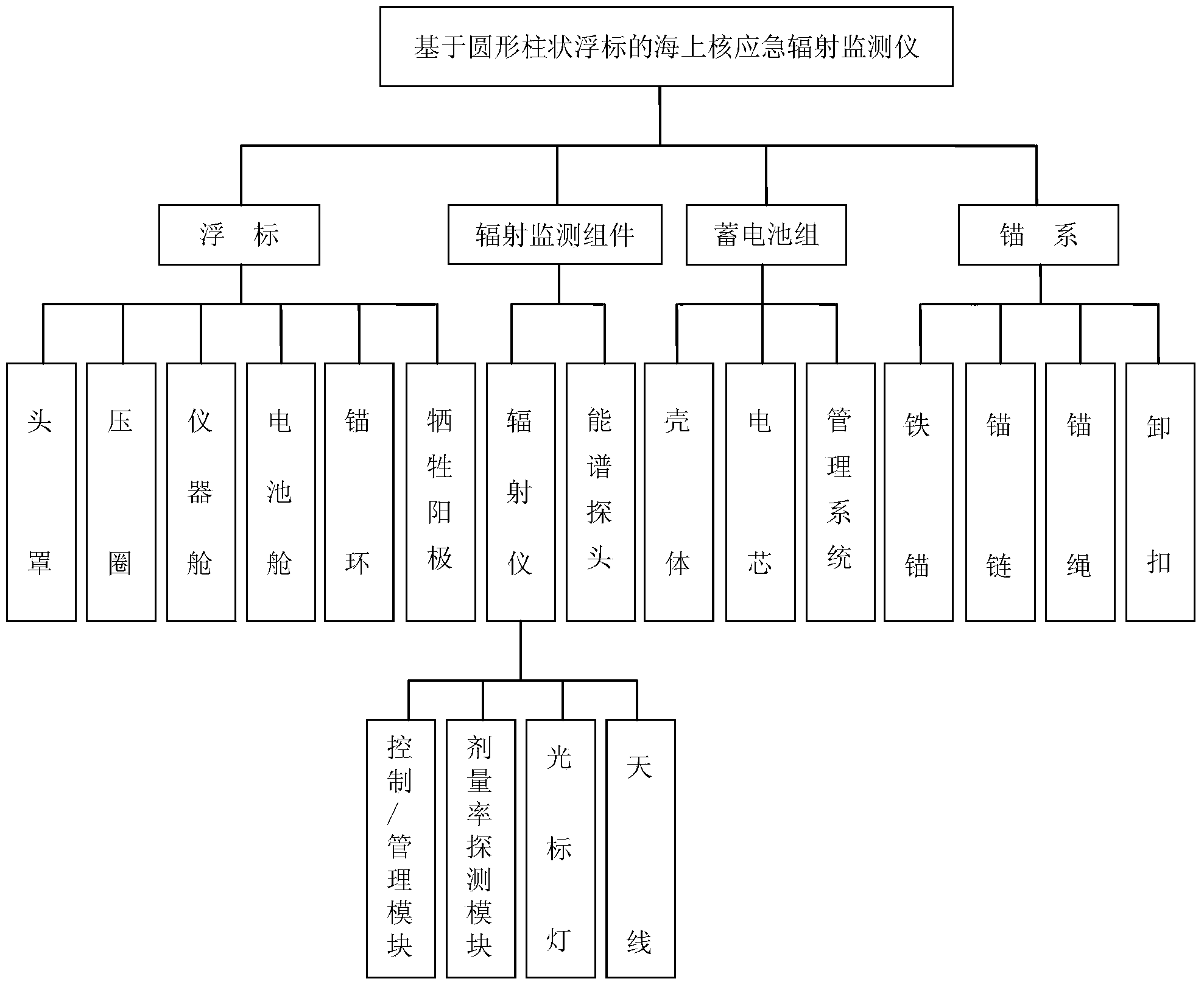
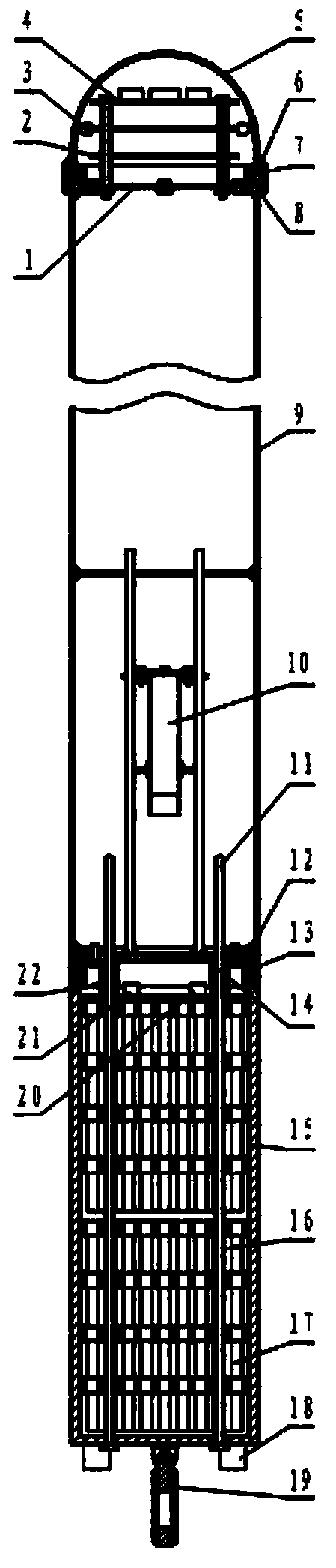
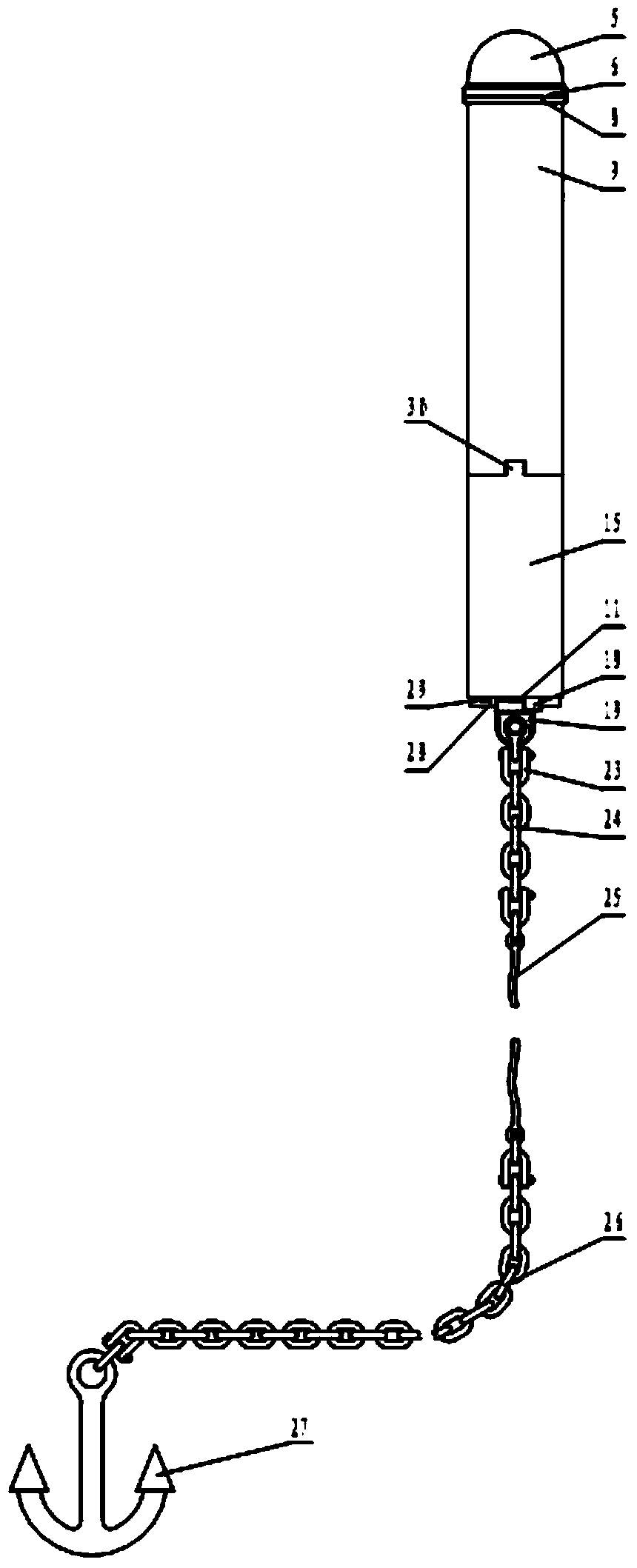
[0040] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention is based on the marine nuclear emergency radiation monitor of circular cylindrical buoys, including radiation monitoring components, buoys, battery packs 17 and mooring systems; the radiation monitoring components are composed of radiometers and energy spectrum probes 10; the buoys It is a cylindrical structure, which is composed of a hood 5, an instrument compartment 9, and a battery compartment 15, and the battery compartment 15 is located below the instrument compartment 9; the radiometer is installed on the upper end of the instrument compartment 9, and the energy spectrum probe 10 is installed on the instrument The lower end of the cabin 9, the battery pack 17 is installed in the battery cabin 15 (that is, the radiometer, the energy spectrum probe 10 and the battery p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com