Interlaminar toughening of thermoplastics
A thermoplastic, thermoplastic matrix technology, applied in the direction of layered products, thin material processing, metal layered products, etc., can solve problems such as expanding damage area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
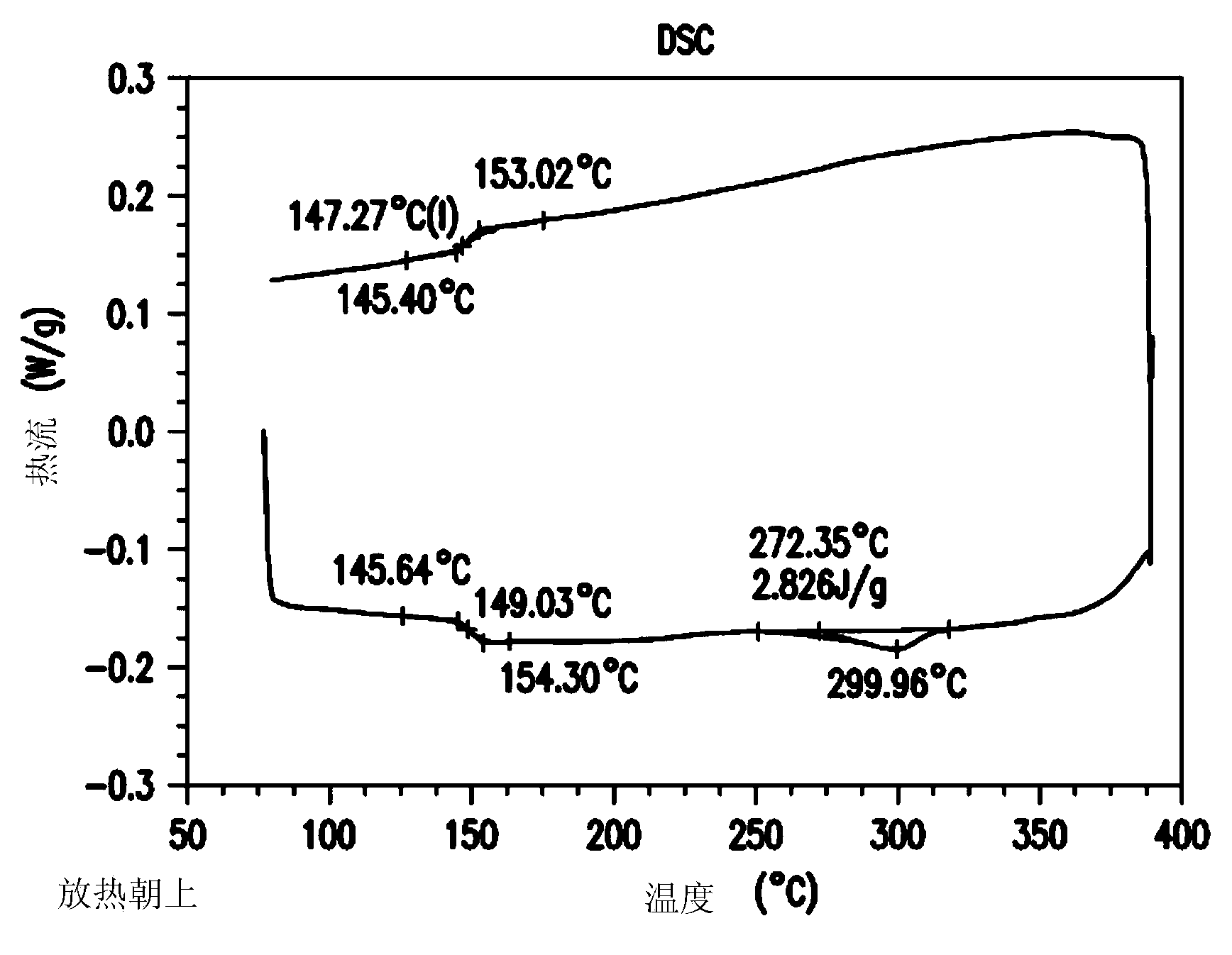
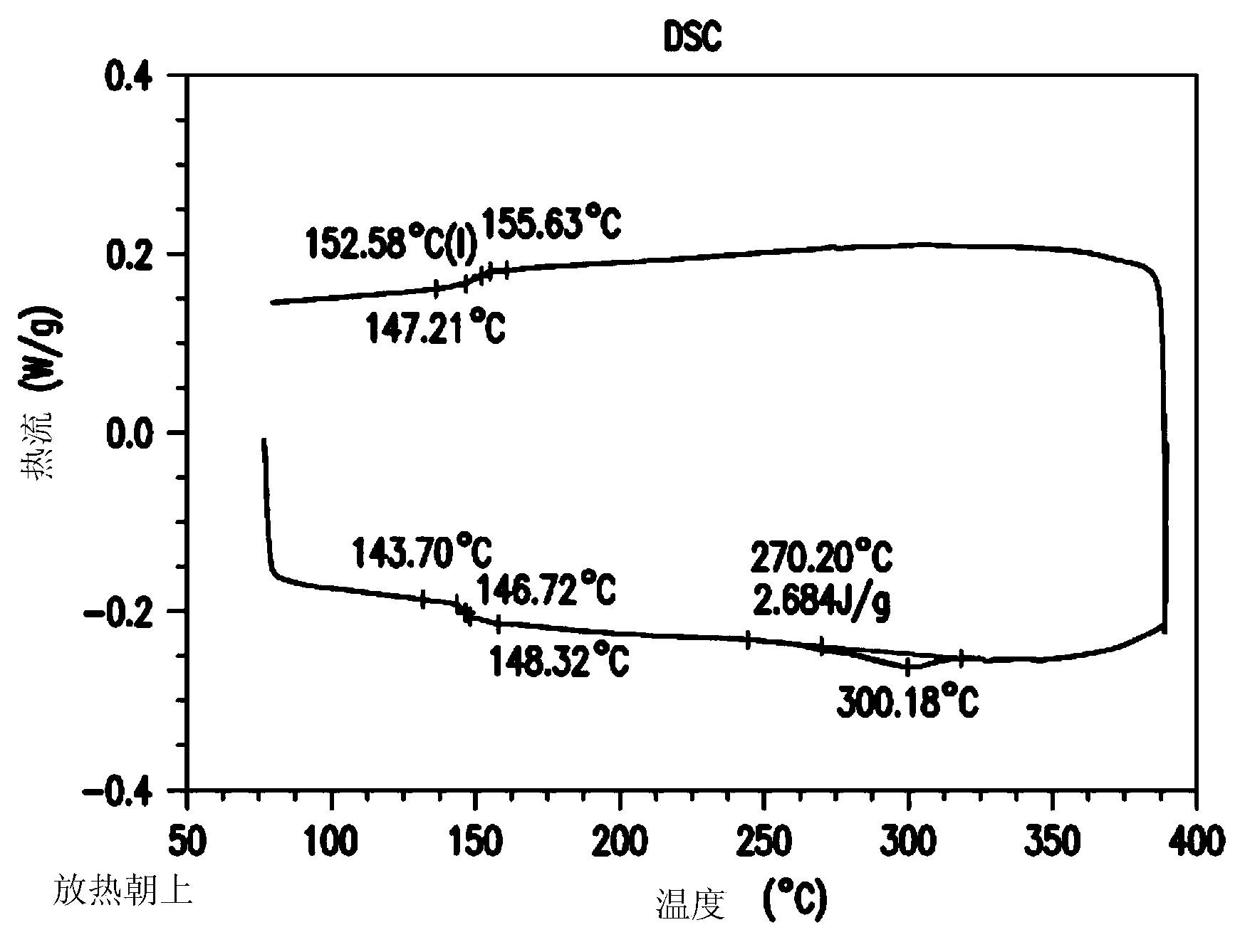
Image
Examples
example 1
[0065] Example 1 - Toughening with glass
[0066] Test laminates were made by weaving BGF104I617 finished glass fabric (glass reinforced to .55oz / yd 2 ) of the two layers are placed containing Cypek TM - Formed between unidirectional tape plies of DSE resin and Hexcel AS4 carbon fiber, an unsized carbon fiber typically used for 12K fibers (12,000 filaments) of 7 μm nominal diameter. No additional resin film is used. A control laminate was also formed which was identical to the test laminate described above but was not toughened with glass fabric. CAI performance was measured using ASTM D7136. Table 1 and Table 2 show the test results based on 4 test samples.
[0067] Table 1 – Controls
[0068]
[0069] Table 2 - Toughening with glass
[0070]
[0071] The glass fabric was found to improve CAI performance when compared to the control laminate. The glass interlaminar toughening material increased the CAI to 57 KSI (normalized to correct for ply thickness), a 2 ks...
example 2
[0074] Example 2 - Toughening with thermoplastic film
[0075] The same method was used to form a test laminate as described in Example 1 above, but using 0.25 mil Cypek TM - DSE membrane instead of glass fabric as middle leaf for toughening. CAI performance was measured using ASTM D7136. Table 3 shows the test results based on 4 test samples.
[0076] Table 3 – Using Cypek TM DSE toughened
[0077]
[0078] DISCOVERCypek TM The DSE film improves post-impact compression properties. 55.1 ksi (unnormalized) was achieved relative to 53.6 ksi (unnormalized) for the control.
[0079] Figure 5 is a photomicrograph showing the interlaminar region of a laminate formed according to this example.
example 3
[0080] Example 3 - Toughening with glass and thermoplastic film
[0081] Test laminates were laminated by Cypek TM DSE resin-impregnated UD tapes of AS4 carbon fiber with 2 glass fiber cloths (0.72oz / yd) inserted between adjacent UD tapes 2 ) ply and two 0.24 mil Cypek TM DSE membrane layer to manufacture. These test laminates were processed alongside the control laminates using standard cure process conditions of 710°F / 100 psi. CAI strength was measured using ASTM D7136. Table 4 and Table 5 show the test results based on 4 test samples.
[0082] Table 4 – Controls
[0083]
[0084] Table 5 – with glass / Cypek TM PEKK toughened
[0085]
[0086]
[0087] For Cypek-based TM For the DSE matrix carbon fiber reinforced control laminate, the CAI strength was 49.8 ksi after the 1500 in-lb / in impact energy test. For use with glass fabric and Cypek TM An average CAI strength of 55.0 ksi was obtained for the DSE film toughened laminate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com