Breeding method utilizing wild rice resource to create japonica-type novel paddy rice species
A technology for wild rice and new germplasm, applied to other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, using microinjection methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of sterility of hybrid offspring, narrow genetic basis, and lack of flowering. To achieve the effect of shortening the breeding period, broad application prospects, and rapid stability of offspring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
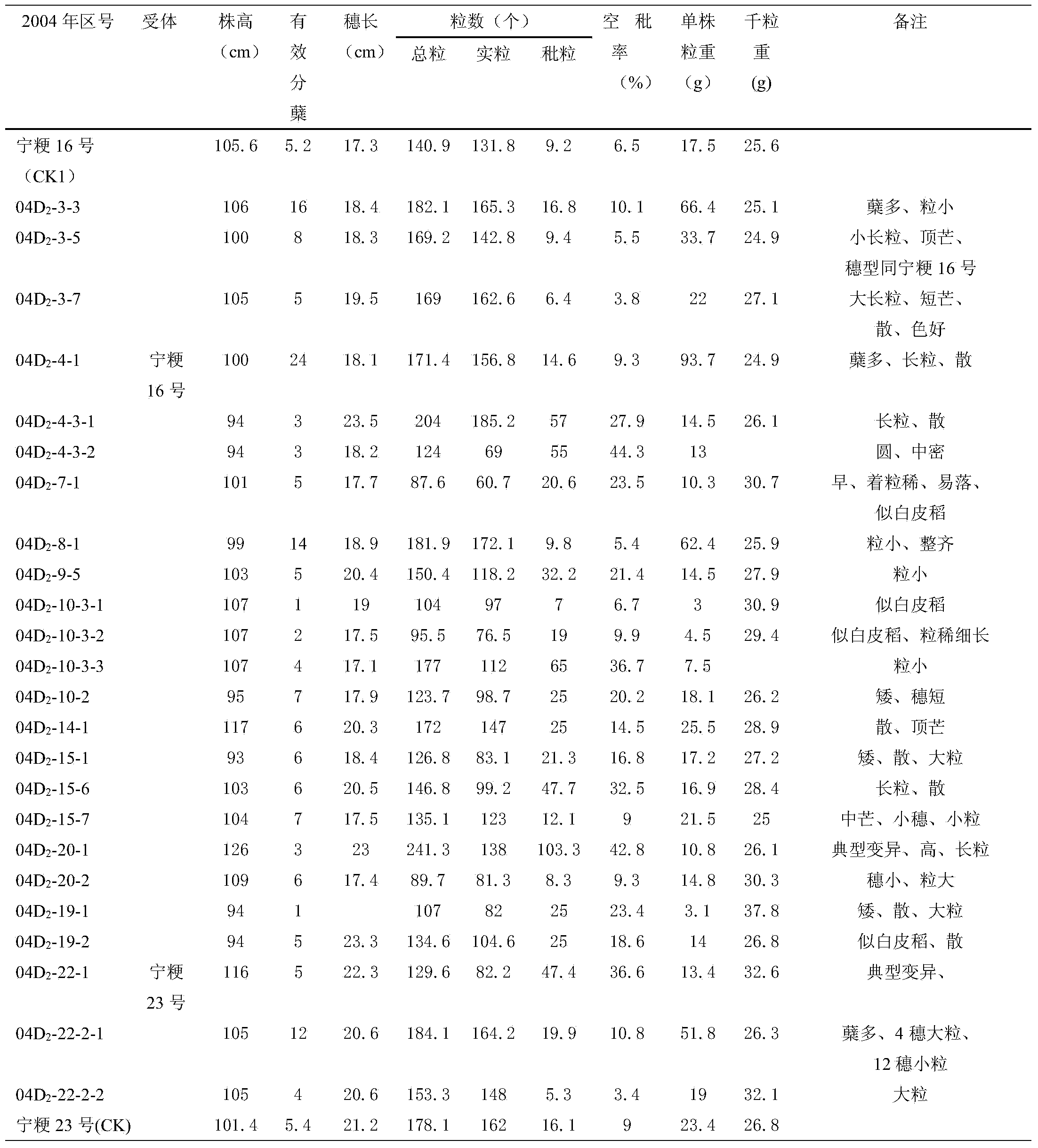
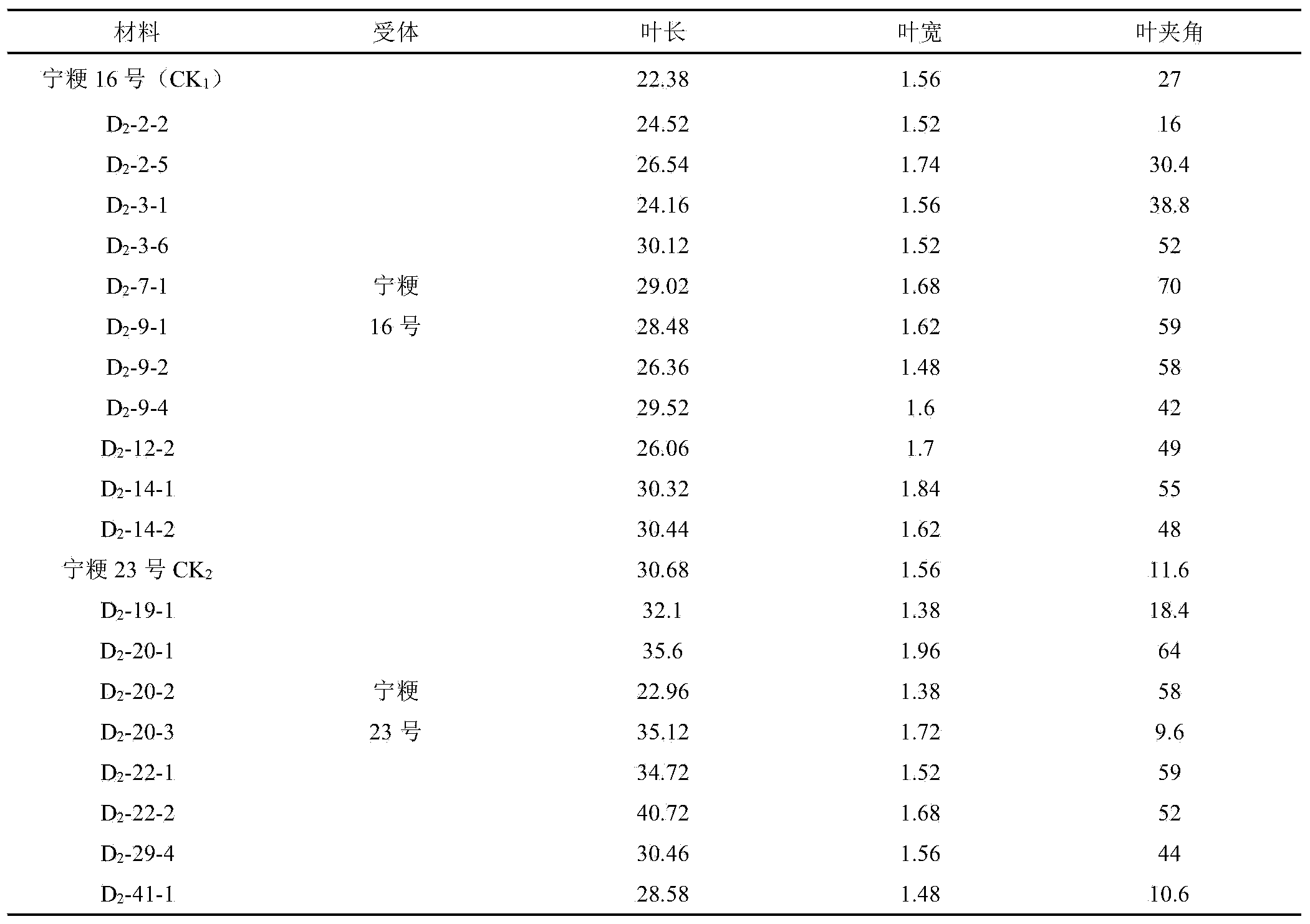
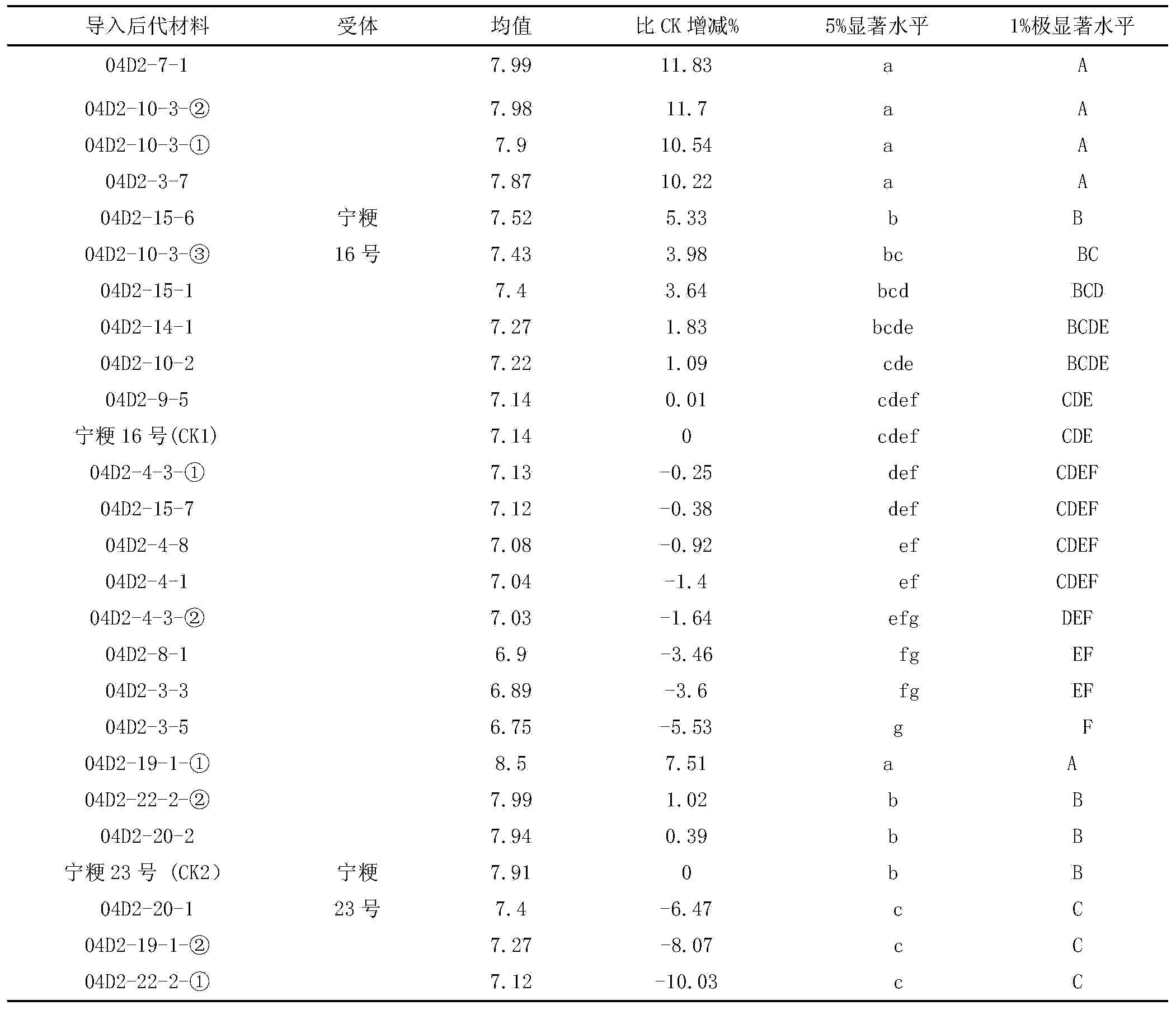
[0027] The experimental materials in this example are wild rice DNA, Ningjing No. 16 and Ningjing No. 23. Utilize wild rice resource to create the breeding method of new japonica rice germplasm in the present embodiment, comprise the following steps:
[0028] A kind of breeding method of utilizing wild rice resources to create new japonica rice germplasm of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0029] S1. Extraction of wild rice genomic DNA
[0030] (a) Cut 5g of leaves at the booting stage and put them into a 50ml mortar;
[0031] (b) Add liquid nitrogen to the mortar in step (a), 50ml each time, 3 to 4 times in total, quickly grind into fine powder, and pour the fine powder into a 50ml plastic centrifuge tube;
[0032] (c) Add 25ml of preheated extraction buffer and 25μl of β-mercaptoethanol to the centrifuge tube in step (b), mix well and bathe in water at 65°C for 30min; extraction buffer 100mmol / L Tris-HCl pH8.0, 500mmol / L NaCl, 50mmol / L EDTA pH8.0, ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com