X-ray anti-scatter grid lattice structure, detector device and medical image system
A grid structure, anti-scattering technology, applied in the field of medical imaging, can solve the problems of high manufacturing cost and complicated process, and achieve the effect of reducing manufacturing cost and difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
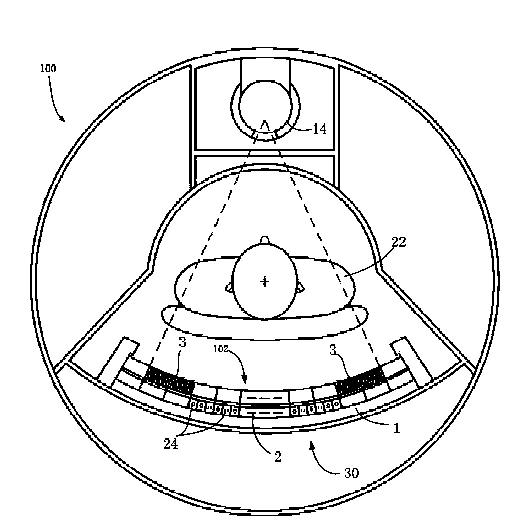
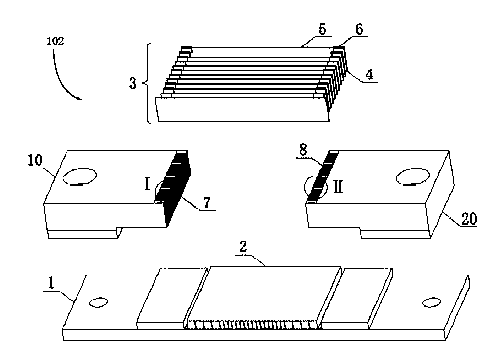
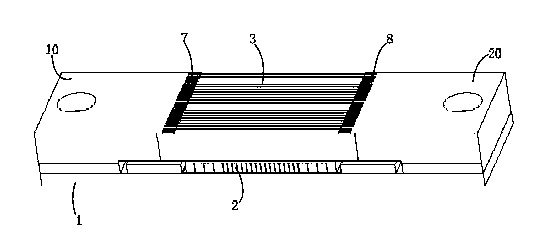
[0040] figure 1 is a schematic axial view of a Computed Tomography (CT) system 100 (here, as an example of a medical imaging system) having an X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 102 according to an embodiment of the present invention. like figure 1 As shown, the CT system 100 includes an X-ray emission source 14 and a detector arrangement 30 . The detector arrangement 30 includes an X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 102 and an X-ray detector 2 . The X-ray detector 2 includes an X-ray detector substrate 1 and a plurality of scintillation crystals 24 . During the scanning and imaging process, the X-ray emission source 14 emits X-rays. After the X-rays penetrate the human body 22 , they pass through the anti-scatter grid array module 3 and are received by the scintillation crystals 24 of the X-ray detector 2 . The X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 102 includes an anti-scatter grid array module 3 for absorbing scattered X-rays while absorbing as little effective X-rays as possib...
no. 2 example
[0056] Below, refer to Figure 8 and Figure 9 The X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 202 according to the second embodiment of the present invention is described.
[0057] Figure 8 It is a schematic exploded perspective view of the X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 202 and the X-ray detector 2 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 9 It is a schematic perspective view of the X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 202 and the X-ray detector 2 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 8 and 9 , the same components as those of the first embodiment described above have the same reference numerals. Meanwhile, the same components as those of the first embodiment described above will not be described repeatedly in this embodiment. like Figure 8 and 9 shown, with the X in the first embodiment
[0058] Different from the ray anti-scatter grid structure 102 , the X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 202 of the second embo...
no. 3 example
[0063] Below, refer to Figure 10 The X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 302 according to the third embodiment of the present invention is described.
[0064] Figure 10 It is a schematic diagram showing the positional relationship between the X-ray anti-scatter grid structure 302 and the X-ray detector 2 according to the third embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 10 , the same components as the first and / or second embodiments described above have the same reference numerals. Meanwhile, the same components as those of the first embodiment and / or the second embodiment described above will not be repeatedly described in this embodiment. like Figure 10 As shown, different from the X-ray anti-scattering grid structure 102 in the first embodiment, in the X-ray anti-scattering structure 302 in the third embodiment, a spacer 6 is respectively bonded to an anti-scattering grid sheet 5 . One of the two ends forms an anti-scatter grid module 4 .
[0065] Two or more ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com