A method for co-transformation of oligonucleotide and elimination plasmid for essential gene point mutation of Escherichia coli
A technology of oligonucleotide and Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of gene inactivation, necessary gene modification methods are difficult to implement, and strains cannot survive.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
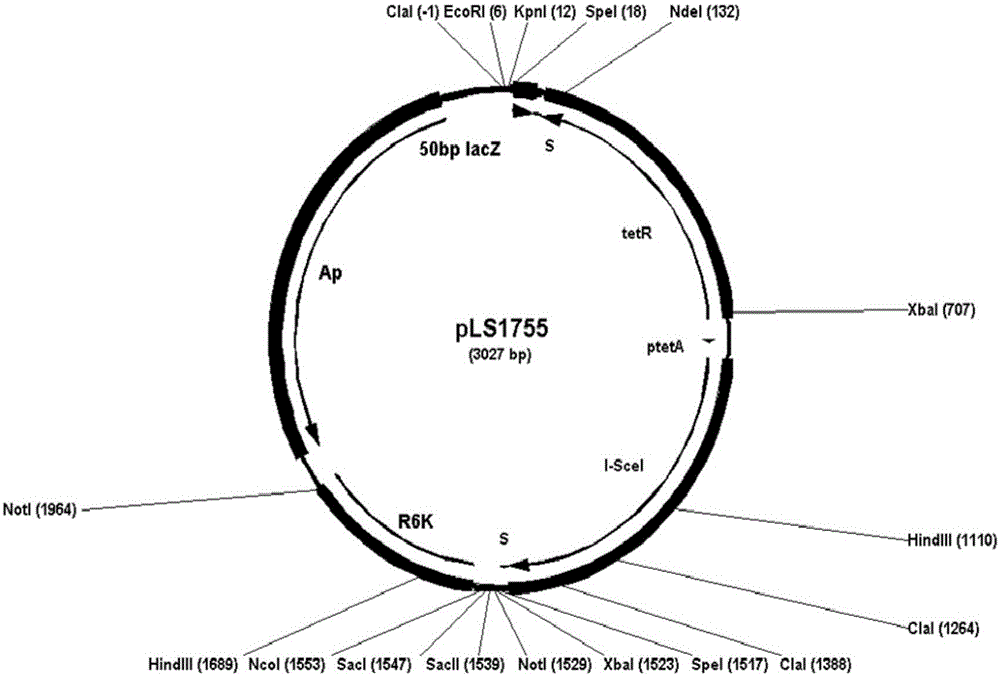
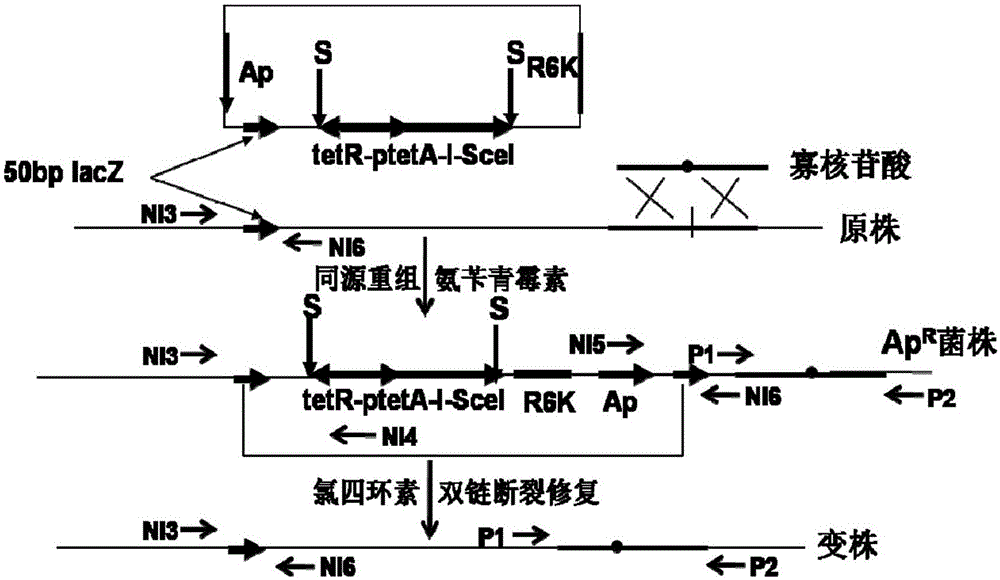
[0051] Example 1. Construction of integrative plasmid pLS1755, integrated into E. coli gene and eliminated
[0052] 1.1 Construction of pLS1755
[0053] Design primer LSKD7: 5'-GGG ATCGATGAATTCGGTACCACTAGT TATGGACAGCAAGCGAACCGG-3', (SEQ ID NO.1), ClaI, EcoRI, KpnI and SpeI restriction sites are underlined; LSKD8: 5'-GGG GCTCATGCGAGACCCCATGGGAGCTCCACC GCGGTGGCGGCCGCTCTAGAACTAGT TCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAG-3', (SEQ ID NO.2), XhoI, BsaI, NcoI, SacI, SacII, NotI, BamHI and SpeI restriction sites are underlined. Using pKD4 as a template, LSKD7 and LSKD8 were amplified by PCR to obtain a 1.5kb kanamycin resistance gene neo fragment, which was digested with ClaI-BsaI and then ligated with the 1.4kb vector part obtained by pKD4 digested with ClaI-NcoI and separated , transform the competent cells of BW25141, and obtain the recombinant clone pLSKD2 through screening.
[0054] Design primer NI1: 5'-GGG ACTAGT ttaccctgttatccctaTTATTTCAGGAAAGTTTCGGAG-3', (SEQ ID NO. 3), NI2: 5'-GGG...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2. Point mutation of the essential gene rpsL gene
[0063] The gene number of the rpsL gene on the E. coli genome is b3342, and the design oligonucleotide R507: 5'-G*T*C*A*GACGAACACGGCATACTTTACGCAGCGCGGAGTTCGGTTTT C TAGGAGTGGTAGTATACACGAGTACATACGCCACGTTTTTTGCG-3', (SEQ ID NO.9), * indicates the phosphorothioate linkage, and the underline indicates the mutation site. 5 pmol R507 and 100 ng pLS1755 were electrotransformed as in Example 1, and 100 ampicillin-resistant colonies were amplified and cultured. Primers R509: 5'-CAGGATTGTCCAAAACTCTAC-3', (SEQ ID NO.10), R510: 5'-GGCATCGCCCTAAAATTCGG-3', (SEQ ID NO.11) were designed. Randomly pick 30 clones, use R509 and R510 as primers for colony PCR amplification to get 540bp. The 540bp product was sequenced with R510 as a primer, and two clones with expected point mutations were obtained. Attached is the sequencing map of the rpsL gene point mutation Figure 4 It shows that the 128th base of the open reading frame...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3. Point mutation of the essential gene rpoB gene
[0065] The gene number of rpoB on the E. coli genome is b3987, and the design oligonucleotide R508:
[0066] 5'-A*C*G*T*ACACCCGACTCACTACGGTCGCGTATGTCCAATCGAAACCC T TGAAGGTCCGAACATCGGTCTGATCAACTCTCTGTCCGTGTACGC-3', (SEQ ID NO.12), * is a phosphorothioate linkage, and the underline is a mutation site. 5 pmol R508 and 100 ng pLS1755 were electrotransformed as in Example 1, and 100 ampicillin-resistant colonies were amplified and cultured.
[0067] Primers R511: 5'-GTAGAGCGTGCGGTGAAAGAG-3', (SEQ ID NO.13), R512: 5'-GGATACGTCCATGTAGTCAAC-3', (SEQ ID NO.14) were designed. Randomly pick 20 clones, use R511 and R512 as primers for colony PCR amplification, and get 557bp. The 557b product was p-sequenced with R511 as a primer, and two clones were found to have expected point mutations. Attached is the sequencing map of rpoB gene point mutation Figure 5 It shows that the 1691st base of the open reading frame is m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com