Electrical impedance tomography imaging plant root system architecture in-situ observation method
An electrical impedance fault, plant root technology, applied in the direction of material resistance, can solve the problems of poor measurement accuracy, inability to distinguish root health status, long time consumption, etc., to achieve strong resistance to external interference, portable and easy-to-operate equipment, and imaging speed. quick effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment, the scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
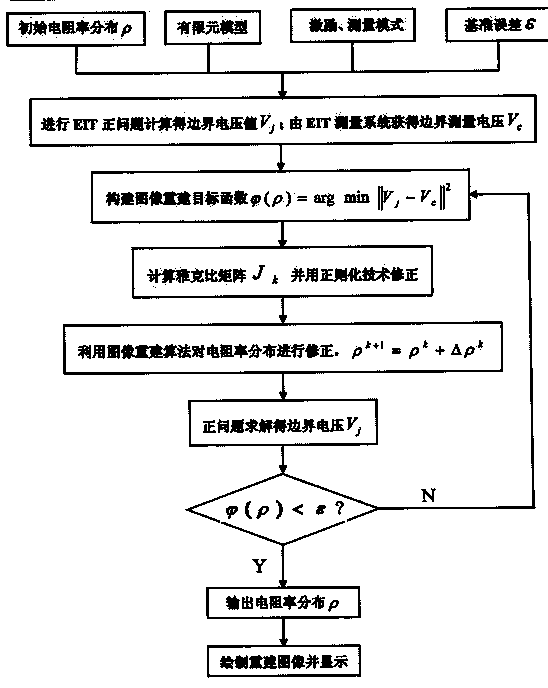
[0037] An electrical impedance tomography method for in-situ observation of plant root architecture, using such as Figure 4 The hardware shown, in which the computer provides the Matlab experimental platform, the LCR impedance tester provides excitation for the experimental system and measures the electrical impedance, multiple high-speed switches control the application of excitation and the selection of voltage (current) measurement electrode pairs, and there are 16 electrodes on the experimental container contact with test subjects. The computer, LCR impedance tester, and multi-channel high-speed switch are connected through the USB / GPIB interface for communication; and the LCR impedance tester and the multi-channel high-speed switch are connected through signal input and output lines; the multi-channel high-speed switch is co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com