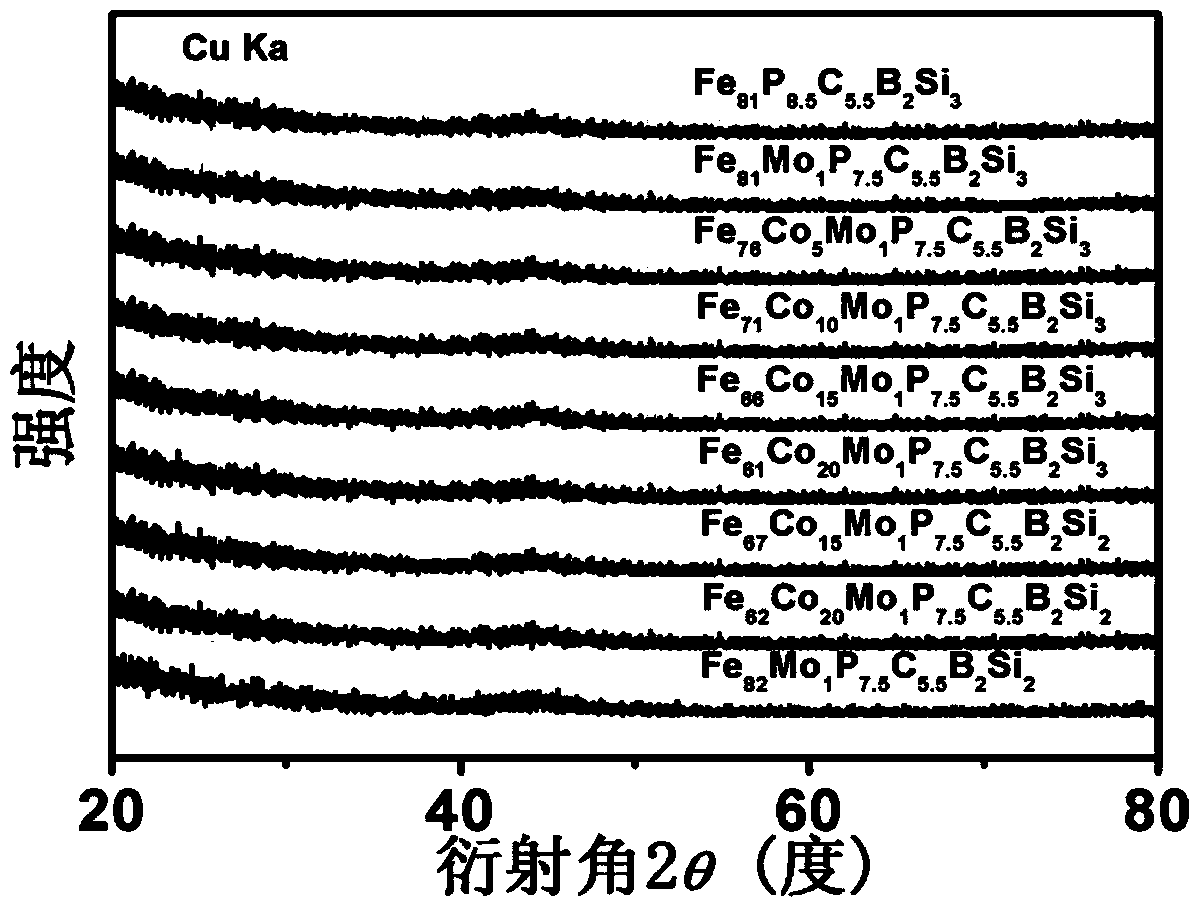
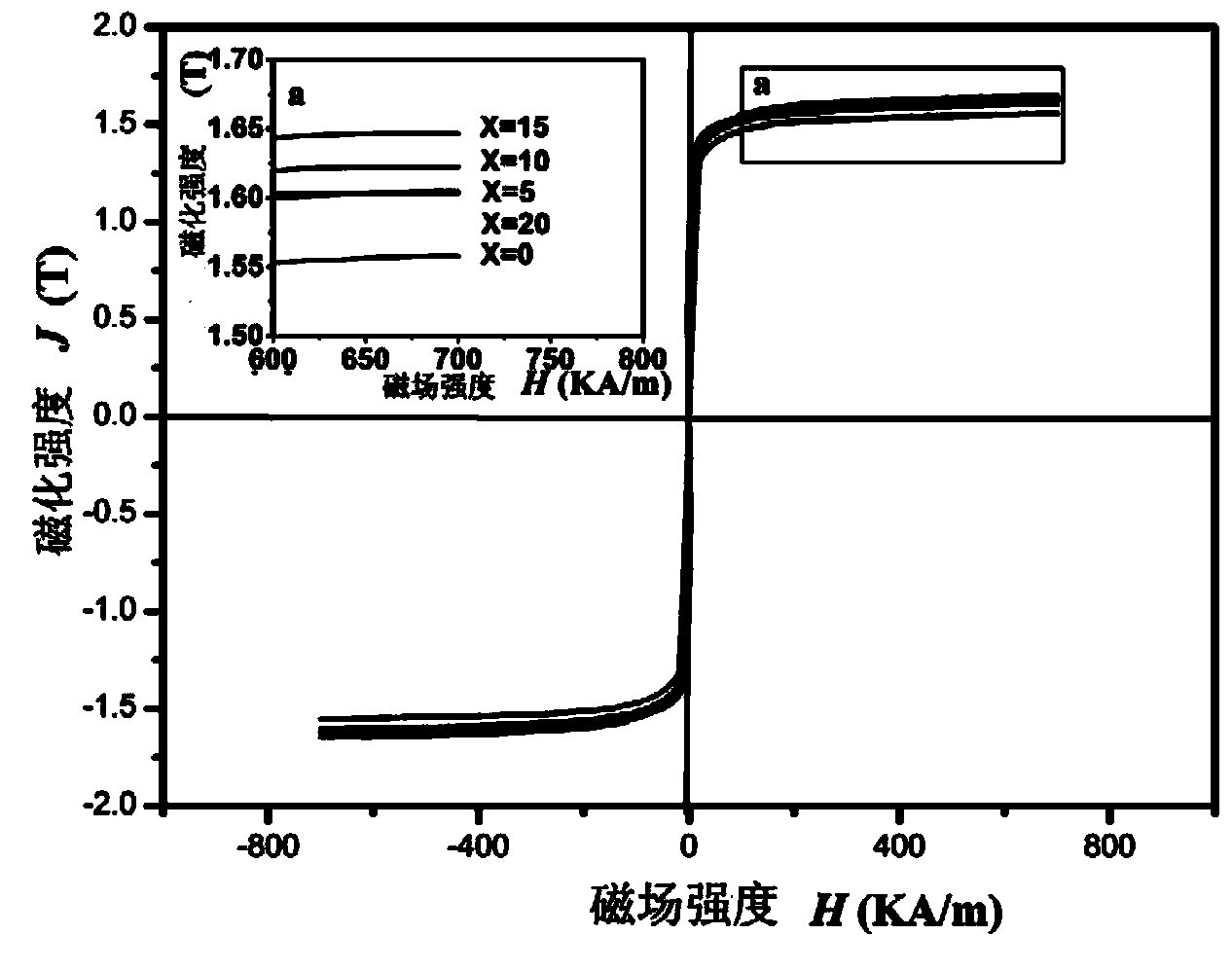
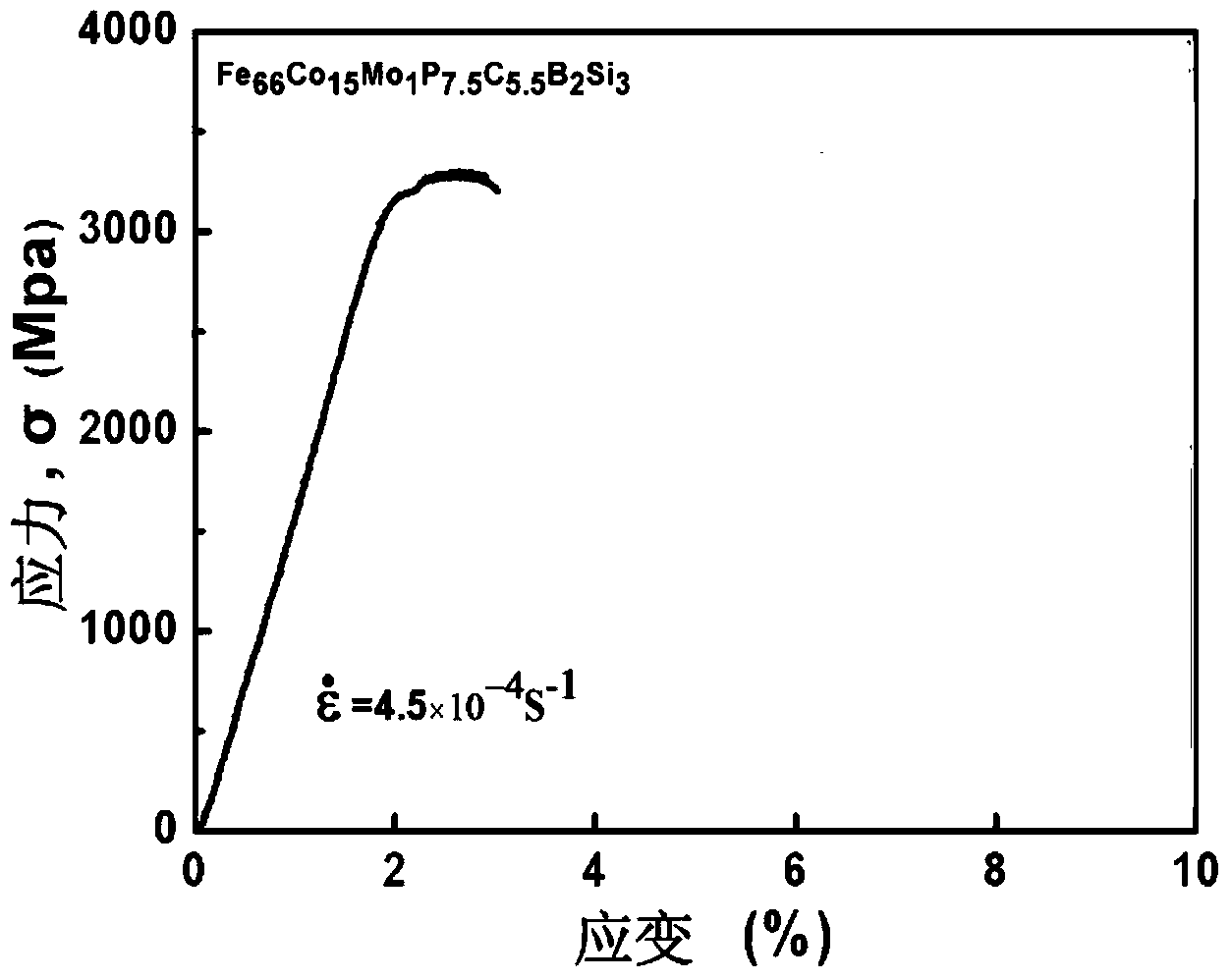
Blocky and stripped ferrum-based amorphous alloy with high magnetic element content, and preparation method
An iron-based amorphous alloy, element content technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reduced magnetic properties and saturation magnetization of the alloy system, and achieve high amorphous forming ability, high Strength, effect of strong industrial application potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: prepare Fe 81 Mo 1 P 7.5 C 5.5 B 2 Si 3 Amorphous Alloy Rods
[0032]According to the chemical expression of the composition of the iron-based amorphous alloy, the ingredients are prepared, and the raw materials of each alloy element are calculated and weighed according to the percentage of each atom in the alloy, and Fe, Co, Mo, Si, P, C are prepared by weighing. , elements of B, in a vacuum induction melting furnace (vacuum degree less than 2×10 -3 Pa) repeated smelting 3-5 times to make a master alloy ingot; the boron oxide coating agent was kept at a temperature of about 1200K under vacuum conditions (vacuum degree is less than 5Pa), and the moisture was removed; when the boron oxide coating agent was clarified without When there are bubbles, place the above-mentioned master alloy in a boron oxide coating agent under vacuum conditions, and purify at a temperature of 1200-1400K. During the purification process, let the alloy melt cool to solidify,...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: prepare Fe 76 co 5 Mo 1 P 7.5 C 5.5 B 2 Si 3 Amorphous Alloy Rods
[0038] Dosing according to the alloy composition, in the vacuum induction melting furnace (vacuum degree less than 2×10 -3 Pa) The raw materials prepared in Example 1 were smelted repeatedly 3-5 times to make a master alloy ingot; the boron oxide coating agent was kept at a temperature of about 1250K under vacuum conditions (vacuum degree is less than 5Pa), and moisture was removed; When the boron oxide coating agent is clear and free of bubbles, place the above master alloy in the boron oxide coating agent under vacuum conditions, and purify at a temperature of 1275-1400K. During the purification process, the alloy melt is cooled to solidification, and then Then heat up, melt and purify, and repeat the above melting and solidification process until no bubbles are generated at the interface of the alloy when melting again, and the interface is stable. The purified master alloy is m...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: prepare Fe 71 co 10 Mo 1 P 7.5 C 5.5 B 2 Si 3 Amorphous Alloy Rods
[0041] Dosing according to the alloy composition, in the vacuum induction melting furnace (vacuum degree less than 2×10 -3 Pa) The raw materials prepared in Example 1 were smelted repeatedly 3-5 times to make a master alloy ingot; the boron oxide coating agent was kept at a temperature of about 1300K under vacuum conditions (vacuum degree is less than 5Pa), and moisture was removed; When the boron oxide coating agent is clear and free of bubbles, place the above master alloy in the boron oxide coating agent under vacuum conditions, and purify at a temperature of 1275-1425K. During the purification process, the alloy melt is cooled to solidification, and then Then heat up, melt and purify, and repeat the above melting and solidification process until no bubbles are generated at the interface of the alloy when melting again, and the interface is stable. The purified master alloy is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| critical dimension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com