Epitaxial wafer structure and epitaxial wafer surface roughening method
A surface roughening and epitaxial wafer technology, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of no contribution to light emission, rising LED chip temperature, and high production costs, so as to improve light extraction efficiency and strong operability , The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and beneficial effects solved by the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
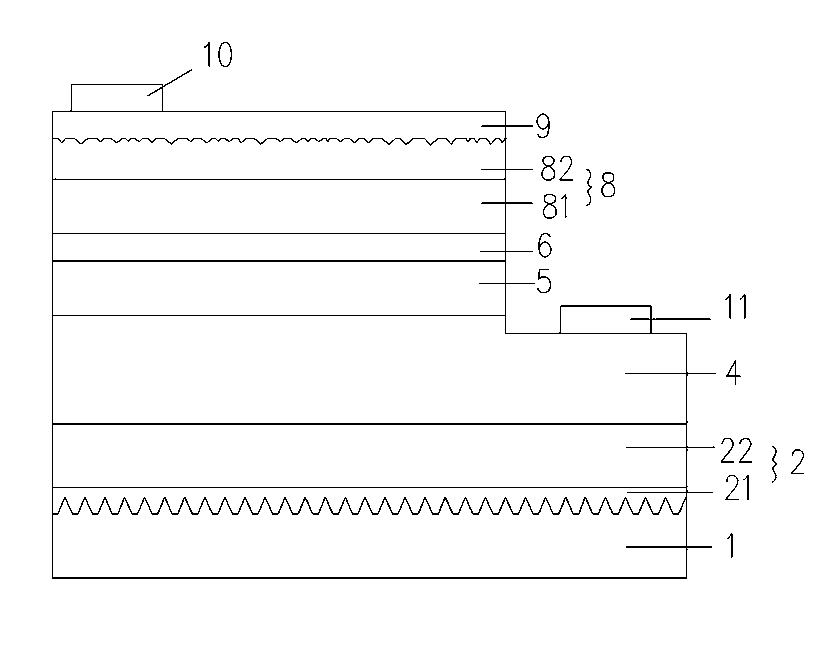
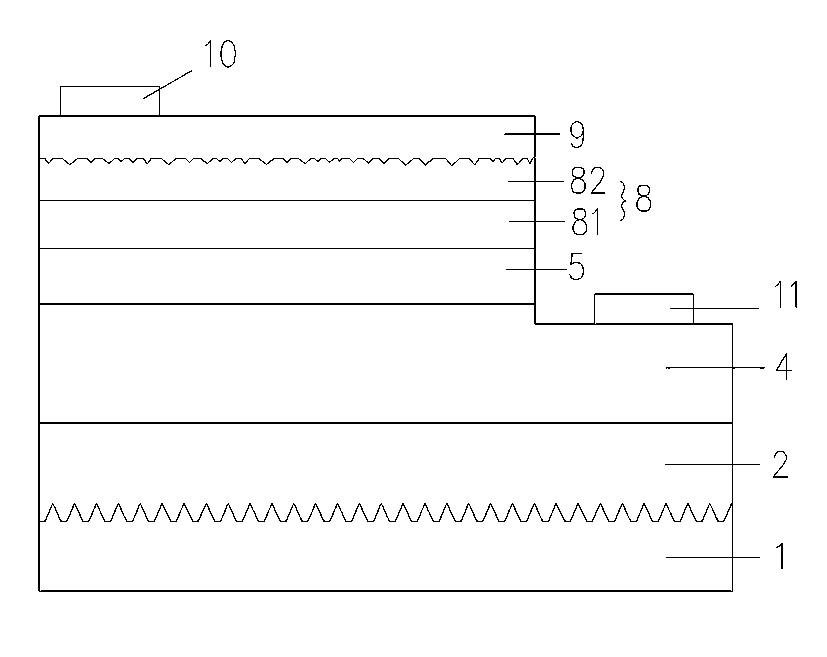
[0018] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides an epitaxial wafer structure, including a substrate 1, and a buffer layer 2, a first-type nitride layer 4, a light-emitting layer 5, and a second-type nitride layer 8 sequentially formed on the substrate 1, The second type nitride layer 8 includes a first nitride layer 81 and a second nitride layer 82 sequentially formed on the light emitting layer, the second nitride layer 82 is a heavily doped nitride layer, the Pits are distributed on the surface of the second nitride layer 82 .
[0019] In the present invention,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Doping concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com