Method for improving plasticity of magnesium alloy sheets
A magnesium alloy and thin plate technology, which is applied in the field of improving the plasticity of magnesium alloy thin plates, can solve problems such as the lack of effective methods for plasticizing magnesium alloy thin plates, and achieve the effects of easy deformation in the thickness direction, improved plasticity, and reduced yield strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1 A kind of method for improving the plasticity of magnesium alloy sheet
[0024] A method for improving the plasticity of a magnesium alloy sheet in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
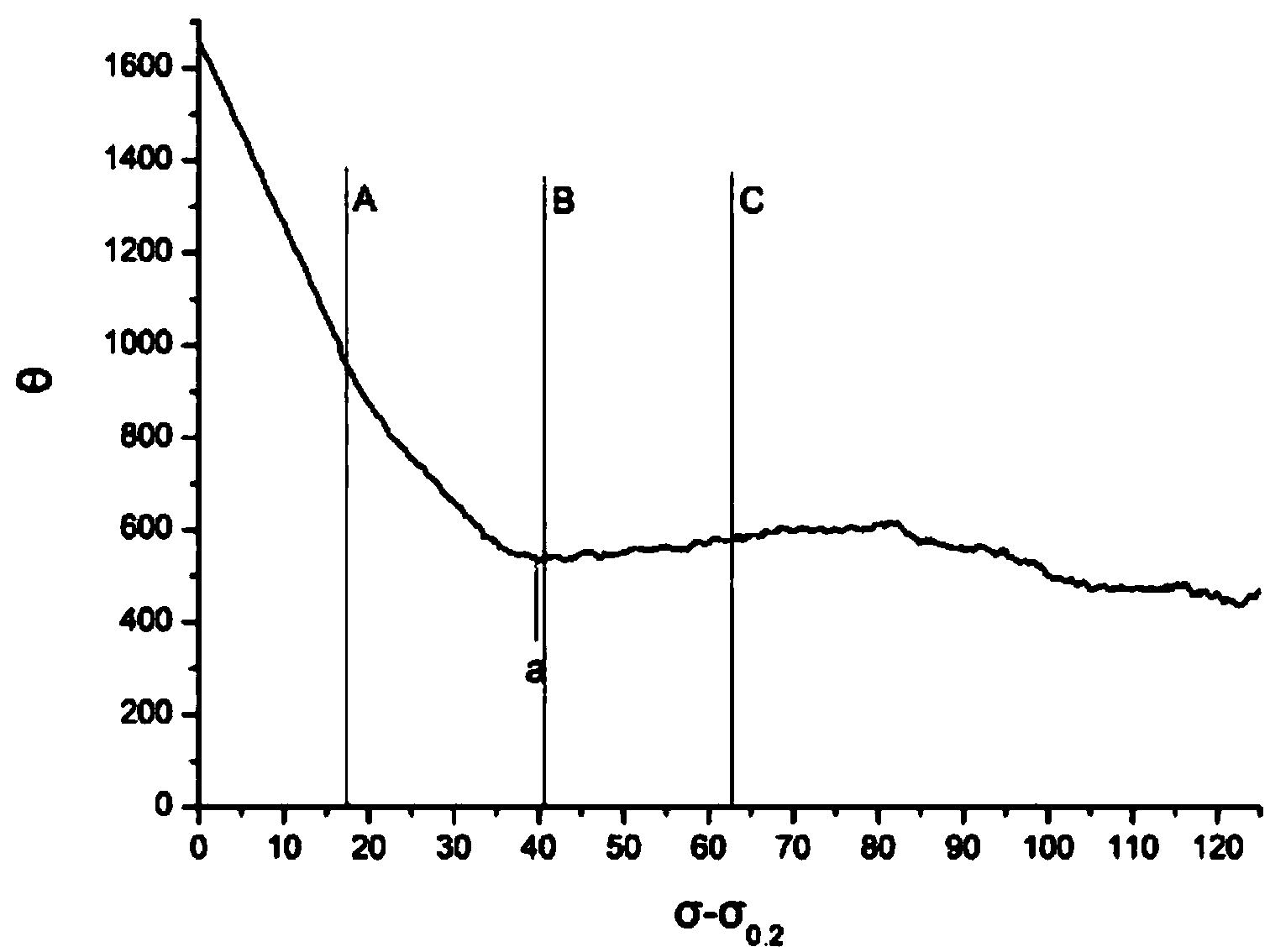
[0025] S1) Take samples from the AZ31 magnesium alloy sheet products to be improved and stretch them at room temperature at 0° along the extrusion or rolling direction of the sheet. You can choose to stretch at room temperature on an electronic universal testing machine, and the stretching rate is 10 -3 -10 -1 the s -1 , make a true stress-strain curve, make a work hardening curve according to the true stress-strain curve, and determine the work hardening rate (θ) and strength (σ-σ 0.2 ) in relation to each other;
[0026] S2) Find the maximum inflection point of the curve from the work hardening curve obtained in step S1 and define it as the critical value a, such as figure 1 As shown in , values A, B, and C represent different work hardening stages near th...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2 A kind of method for improving the plasticity of magnesium alloy sheet
[0030] A method for improving the plasticity of a magnesium alloy sheet in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
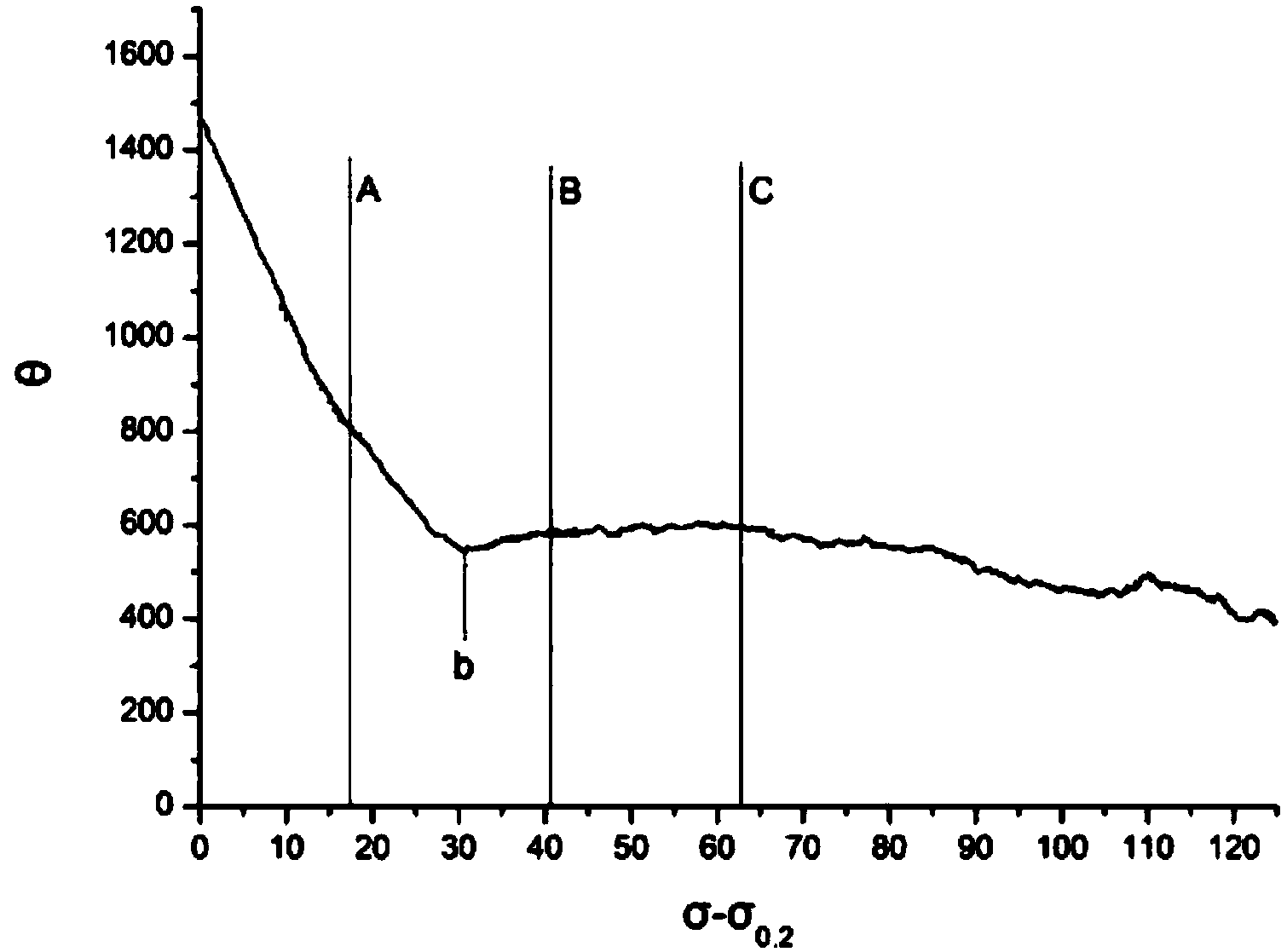
[0031] S1) Take samples from the AZ31 magnesium alloy sheet products to be improved and stretch them at room temperature at 45° along the extrusion or rolling direction of the sheet, and the stretching rate is 10 -3 -10 -1 the s -1 , make a true stress-strain curve, make a work hardening curve according to the true stress-strain curve, and determine the work hardening rate (θ) and strength (σ-σ 0.2 ) in relation to each other;
[0032] S2) Find the maximum inflection point of the curve from the work hardening curve obtained in step S1 and define it as the critical value b, such as figure 2 As shown in , values A, B, and C represent different work hardening stages near the range of critical value b. In this embodiment, A, B, and C are respectively 2%, 4%, an...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3 A kind of method for improving the plasticity of magnesium alloy sheet
[0036] A method for improving the plasticity of a magnesium alloy sheet in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
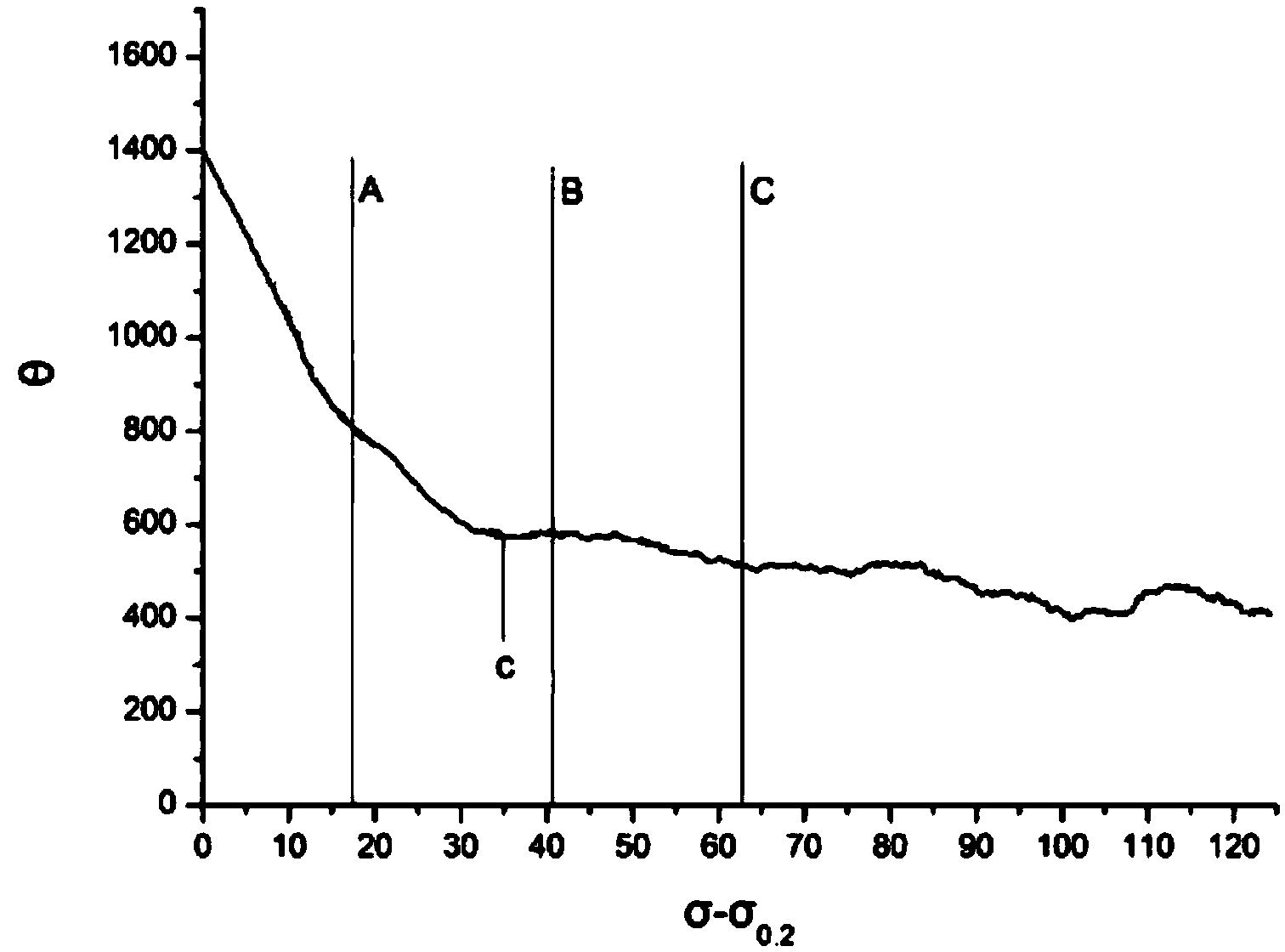
[0037] S1) Take samples from the AZ31 magnesium alloy sheet products to be improved and stretch them at room temperature at 90° along the extrusion or rolling direction of the sheet, and the stretching rate is 10 -3 -10 -1 the s -1 , make a true stress-strain curve, make a work hardening curve according to the true stress-strain curve, and determine the work hardening rate (θ) and strength (σ-σ 0.2 ) in relation to each other;
[0038] S2) Find the maximum inflection point of the curve from the work hardening curve obtained in step S1 and define it as the critical value c, such as image 3 As shown in , values A, B, and C represent different work hardening stages near the range of critical value c, and A, B, and C described in this embodiment are respectivel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com