Method for measuring response matrix of liquid crystal corrector through least square method
A technology of least squares and response matrix, applied in the field of adaptive optics, can solve the problems of expression error, deterioration of liquid crystal adaptive optics imaging effect, and interference of response matrix measurement accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
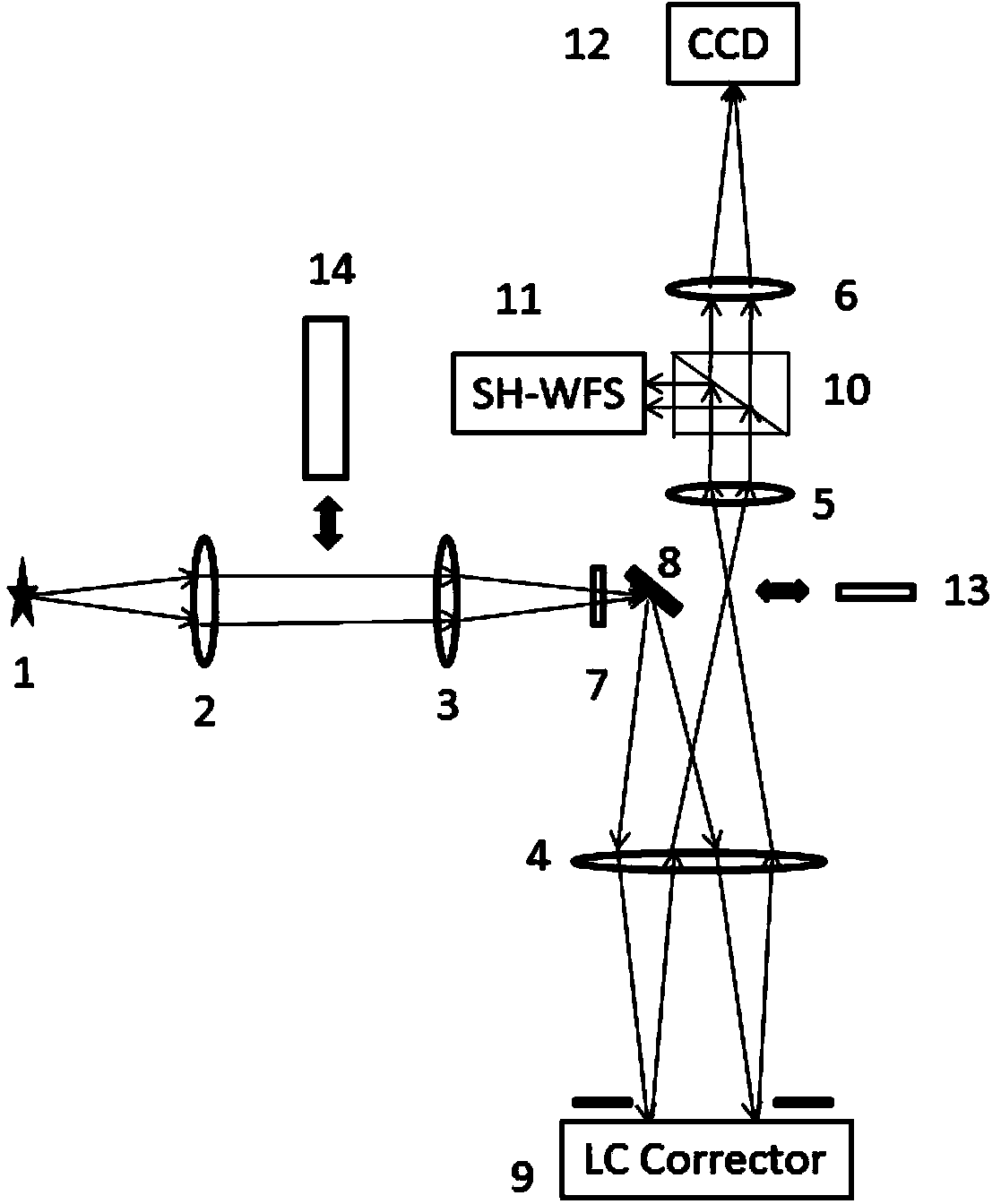
[0029] First, set up on the laboratory optical platform such as figure 1 The liquid crystal adaptive correction imaging optical path shown, wherein 1 is the point light source of the fiber bundle, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 are respectively the first lens, the second lens, the third lens, the fourth lens, and the fifth lens, and 7 Monochromatic film with a wavelength of 780nm, 8 is a mirror set at 45°, 9 is a liquid crystal wavefront corrector, 10 is a PBS polarizing beam splitter, 11 is a Hartmann wavefront detector, 12 is an imaging CCD, 13 is a 1 / 2 wave plate, and 14 is a turbulence simulator. The liquid crystal wavefront corrector 9, the Hartmann wavefront detector 11, the imaging CCD12 and the turbulence simulator 14 are all connected to the computer storing the adaptive correction imaging control software, and the computer is inserted with the Geforce9800GTX GPU picture processor of nVidia Corporation , which is a very general GPU image processor.
[0030] The technical paramet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com