Non-invasive pressure measuring method for esophageal varices
A technology for esophageal flexures and veins, which is applied in the field of medical testing and can solve the problems of unconvincing pressure measurement results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
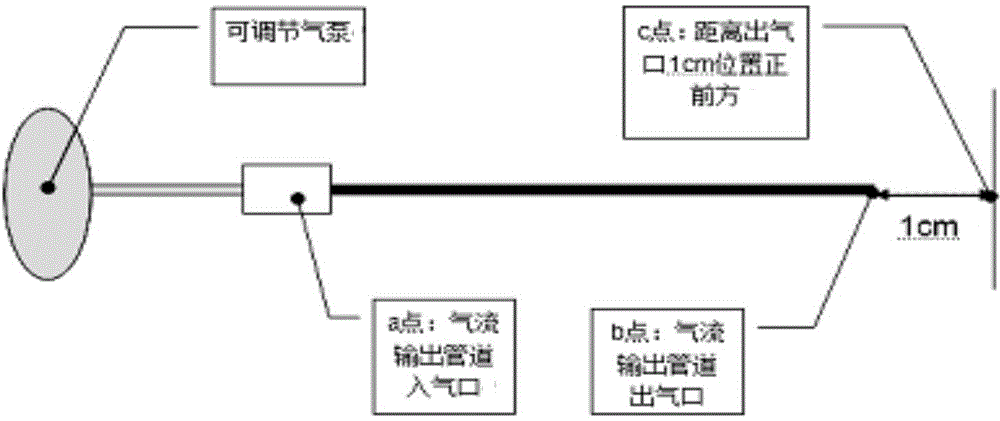
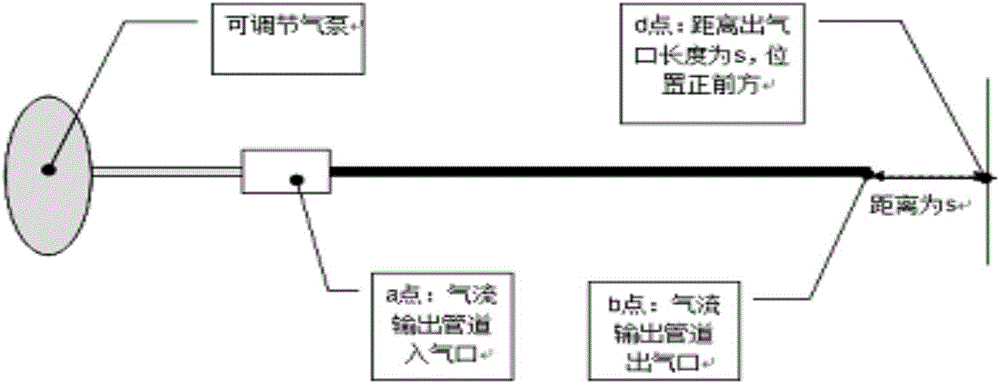
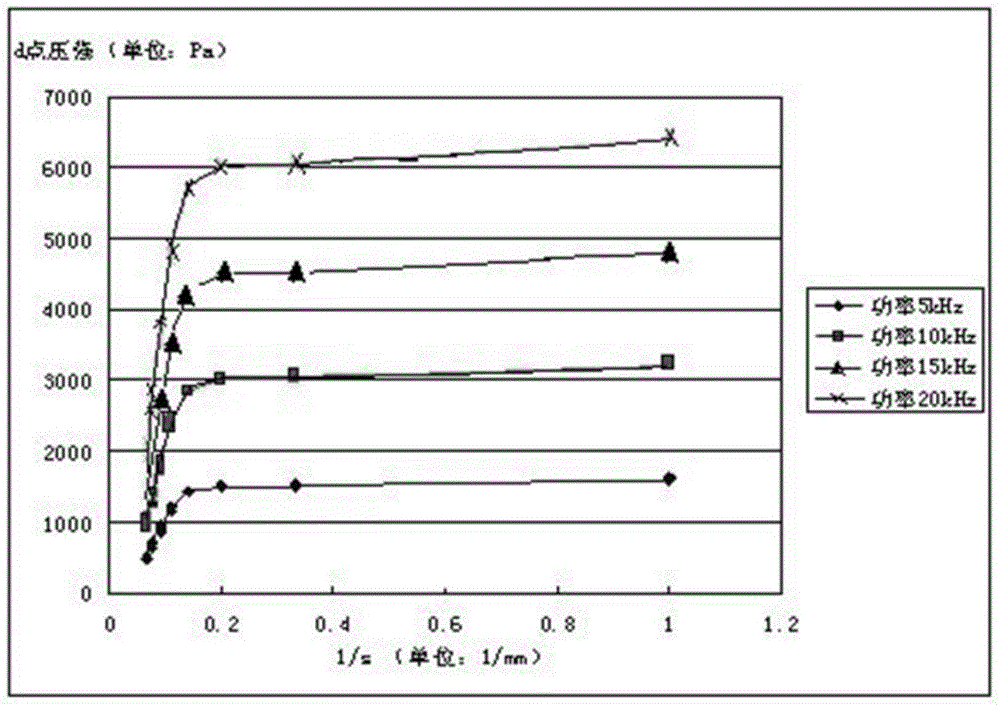
[0078] Embodiment 1 Basic research, obtain the relationship between the pressure P2 impacting the blood vessel wall and the pressure P1 at the air inlet port of the gas pipeline; obtain the relationship between the pressure P2 impacting the blood vessel wall and s, and the s is the gas outlet of the gas pipeline distance from the vessel wall.
[0079] 1. The experiment of the pressure change after the air flow passes through the pipeline
[0080] 1.1 Basis: Place the ventilation pipe and the manometer in a container without the influence of air flow, and set up the pressure sensor at the gas inlet end of the gas pipeline and the position s away from the gas pipeline outlet, respectively, s and the inner diameter of the gas pipeline d The value is consistent with the actual pressure measurement, adjust the working current frequency of the air pump to change the airflow pressure, and record the airflow pressure P1 at the air inlet of the air pipeline at different times and the p...
Embodiment 2
[0127] Example 2 In vitro bionic blood vessel experiment and in vitro blood vessel experiment
[0128] 1 In vitro bionic blood vessel experiment
[0129] 1.1 Materials and methods
[0130] 1.1.2 Experimental method
[0131] (1) Place the simulated blood vessel in a horizontal position, and then connect the bionic blood vessel made of plastic to the broken end of the pipeline reserved for the simulated blood vessel, and confirm that the connection part is tight without leakage. ((Note: The composition of the simulated blood vessel instrument - make a glass tube with a scale and fix it on a fixed frame. The lower part of the glass tube is connected to a horizontally placed plastic tube, and the other end of the plastic tube is connected to a tee tube, cut off the middle part of the plastic tube, and the broken end part is used to connect the simulated blood vessel)
[0132](2) Open the three-way valve at one end of the simulated blood vessel, inject normal saline from the upp...
Embodiment 3
[0174] Embodiment 3 animal blood vessel experiment
[0175] 1 Research Background
[0176] At present, there are two types of extravenous manometry for esophageal varices, one is wall-attached manometry of esophageal varices, and the other is balloon manometry designed according to the principle of cuff manometry. Although there are many reports on in vitro experiments, animal experiments and clinical trials of these two types of non-invasive intravenous manometry methods, it is confirmed that these two manometry methods have clinical significance and feasibility. However, factors such as esophageal peristaltic contraction, coughing, nausea, and belching will inevitably affect the measurement results, and it is difficult to effectively reduce interference and improve accuracy. deviation. The present invention is based on the new method of airflow and laser detection technology, which is a non-contact pressure measurement without contact with the blood vessel wall, and is les...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com