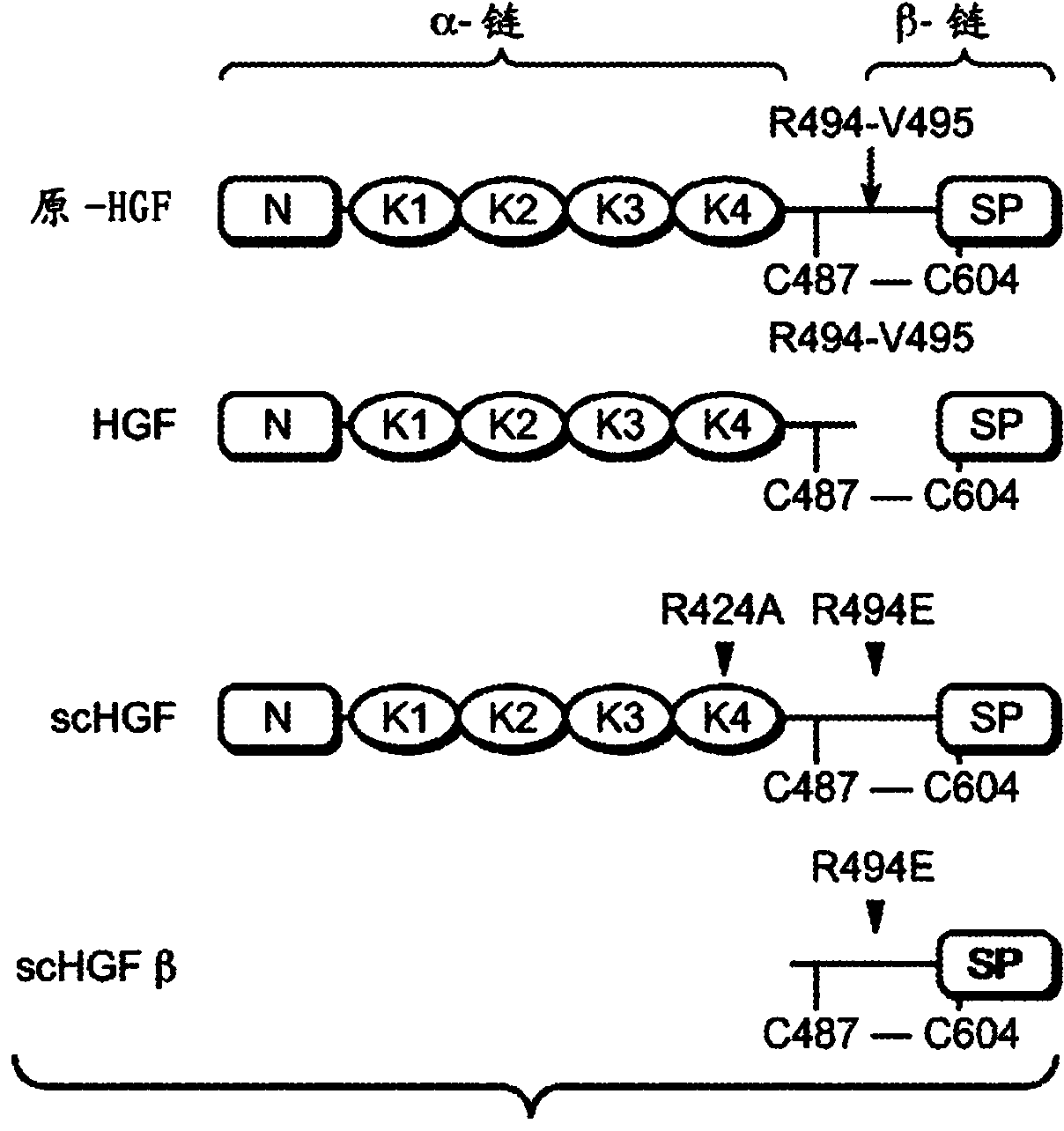
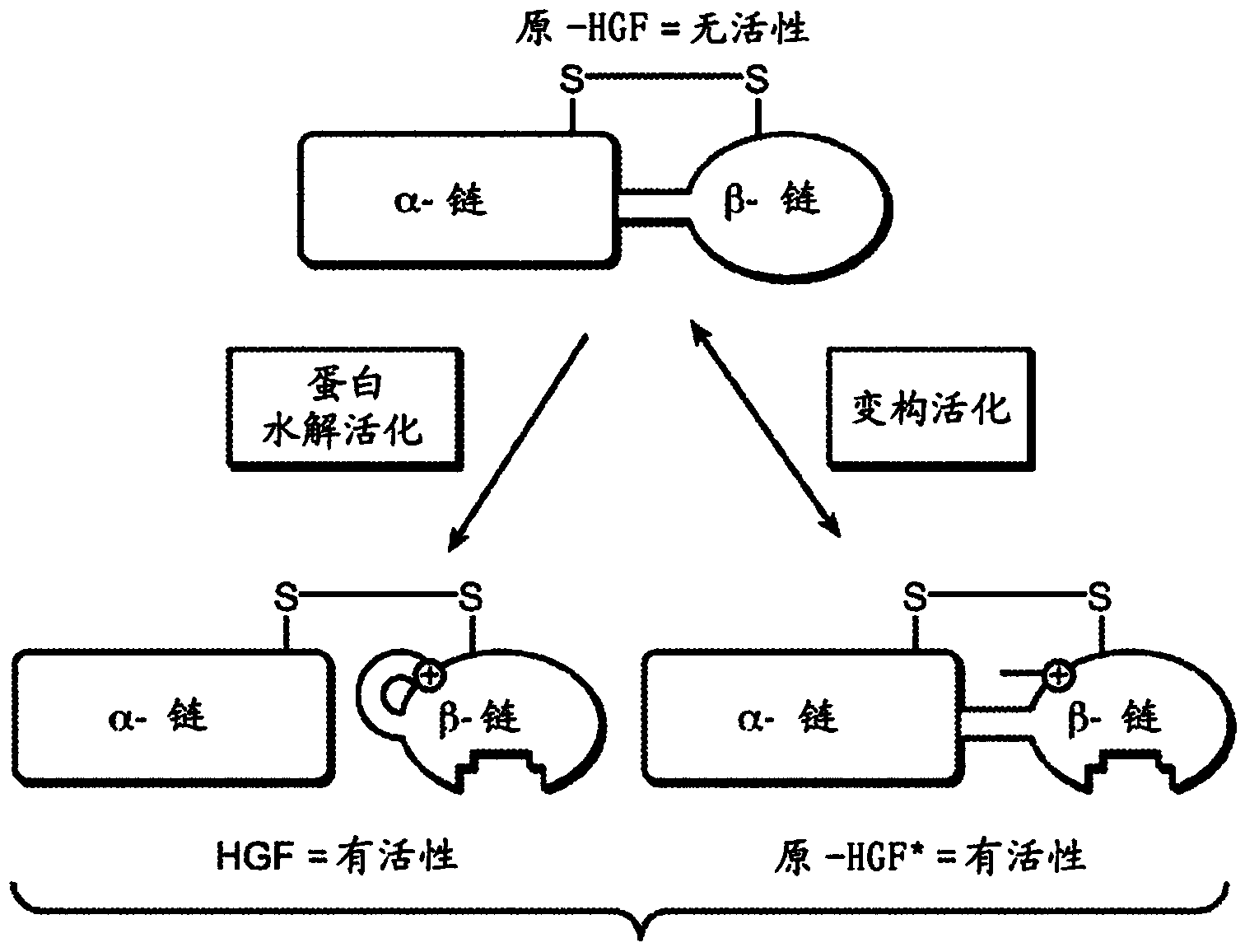
Zymogen activators
A technology of zymogen activating peptides and zymogens, which can be used in growth factors/inducing factors, animal/human proteins, digestive systems, etc., and can solve problems such as binding affinity limitation, weak therapeutic potential activator peptides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0278] Example 1: Phage display of a specific peptide library of zymogen-like scHGF with an activation pocket yields highly conserved sequence motifs
[0279] To identify peptides that specifically bind the activation pocket of the zymogen-like form of HGFβ (scHGFβ) with high affinity, based on the structural and sequence homology found in the N-terminal residues of the trypsin / chymotrypsin-like serine protease domain, Engineered phage peptide libraries. Interestingly, there is high structural homology between the activation pocket of the trypsin / chymotrypsin-like serine protease domain and that of HGFβ (Kirchhofer, D. et al. (2004) J Biol Chem 279:39915-24; Kirchhofer , D. et al. (2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5306-11), clearly highlighting the functional conservation of the N-terminal insertion mechanism. In addition to structural homology, the pfam (Finn, R.D. et al. (2010) Nucleic Acids Res38:D211-22) consensus sequence profile of the N-terminal residues frequently fou...
Embodiment 2
[0281] Example 2: A synthetic peptide based on a phage-derived consensus motif binds scHGFβ with high affinity and activates the binding of scHGFβ to Met
[0282] Based on the finding that the consensus ZAP contains features consistent with binding and insertion into the activation pocket, several related peptides were synthesized and used in a previously established scHGFβ activation assay to assess their affinity and ability to activate Met binding (Landgraf, K.E. et al. (2010) J Biol Chem 285:40362-72). Since scHGFβ interacts only weakly with the Met Sema-PSI domain compared to the active HGFβ form, biolayer interferometry was used in the activation assay to measure the direct enhancement of the peptide by scHGFβ on streptavidin coated with biotinylated Met. Avidin sensor surface binding affinity capacity (Landgraf, K.E. et al. (2010) J Biol Chem 285:40362-72). Thus, titration of the activator peptide should produce a significant increase in the surface response signal due...
Embodiment 3
[0293] Example 3: Synthetic peptides activate pro-HGF and stimulate cell survival
[0294] To test whether these new more potent peptide activators could also activate the full-length form of pro-HGF and stimulate Met signaling, the peptides were screened for activity in a cell survival assay. Uncleaved forms of pro-HGF (scHGF), which are inactive as Met ligands, have been shown to not stimulate cell survival under serum-starved medium conditions; however, activator peptides in combination with scHGF can signal via Met and greatly enhance cell survival, Similar to that of proteolytically activated HGF ligands (Landgraf, K.E. et al. (2010) J Biol Chem 285:40362-72). Peptide titration in the presence of scHGF was performed using Bx-PC3 cells and a robust activation of signaling via Met observed for scHGF was seen, reaching levels equivalent to HGF-induced signaling.
[0295] The IVGG.14 and IVdG.14 peptides exhibited dose-dependent activation of scHGF, EC 50 for ~20μM peptide ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com