Method for determining content of cadmium in soil by ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry)
An ICP-AES, 1.ICP-AES technology, applied in the field of ICP-AES determination of cadmium content in soil, can solve problems such as inability to obtain cadmium content measurement results, shift of cadmium element spectral absorption peak, difficulty in detecting cadmium content, etc. , to make up for the inability to accurately measure the cadmium content in soil, the method is simple and feasible, and the effect of high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] Below in conjunction with embodiment the present invention is described in further detail.
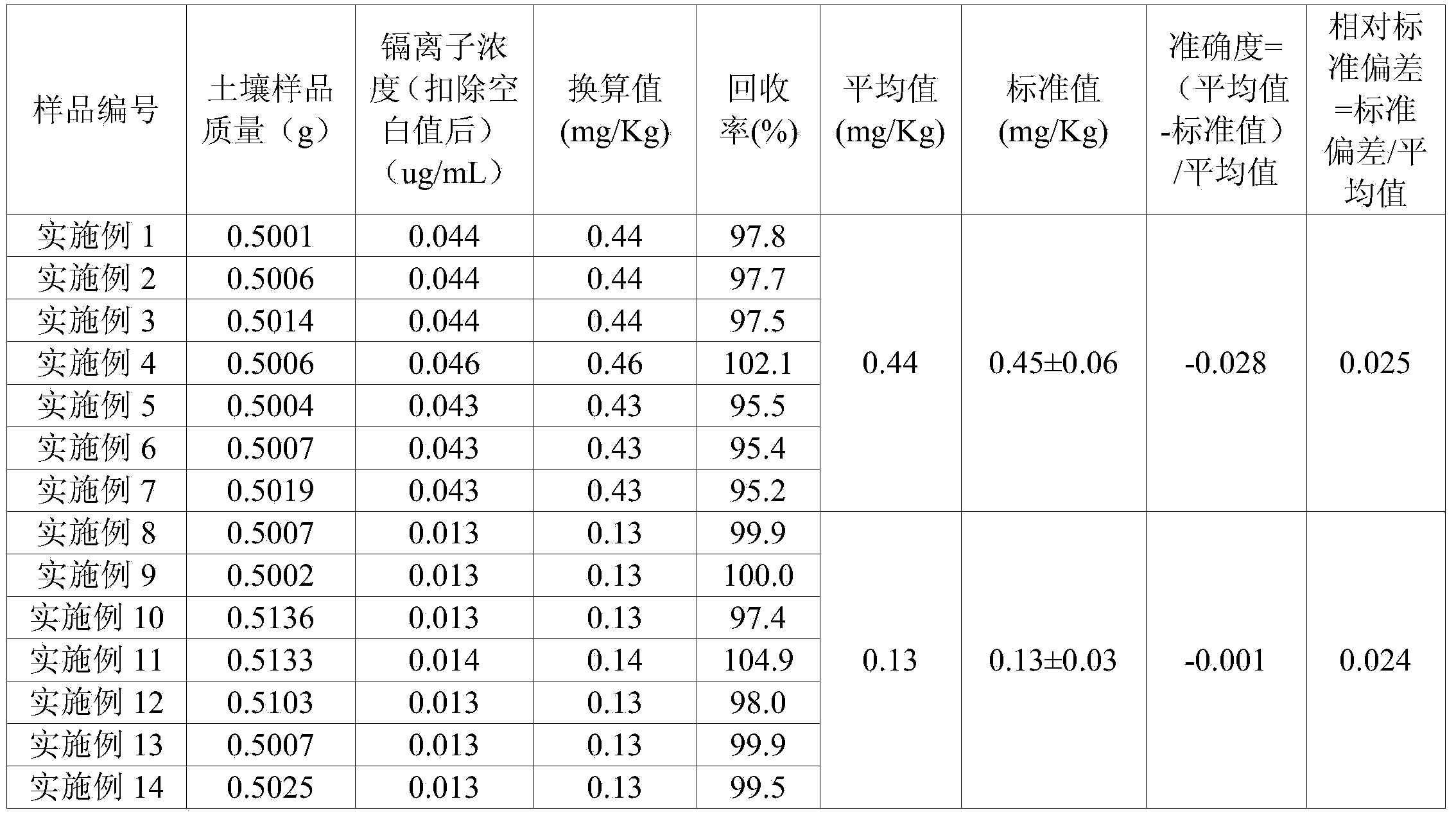
[0014] For verifying the accuracy of the inventive method measurement result, select the standard soil sample that the numbering of known concentration is 0.45 ± 0.06mg / kg is GBW07405 (GSS-5) as the first group of samples, the number of samples is 7, marked as implementation Examples 1 to 7, determine the cadmium content; select the standard soil sample numbered GBW07406 (GSS-6) with a known concentration of 0.13±0.03mg / kg as the second group of samples, the number of samples is also 7, and marked as implementation Examples 8-14, measure the cadmium content. The detection equipment used in the embodiment is 2100DV type ICP-AES (Perkin Elmer), and the water used is all ultrapure water prepared by the Millipore-Q ultrapure water system produced in the United States.
[0015] The assay method of cadmium content in the standard soil sample of embodiment 1~14 comprises the following...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com