A device and method for monitoring link failures of time-division multiplexed optical networks
A technology of network link and multiplexing light, applied in electromagnetic wave transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of low spatial resolution, small dynamic range, complex structure, etc., and achieve low spatial resolution and sensitivity. Improve and simplify the effect of the structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
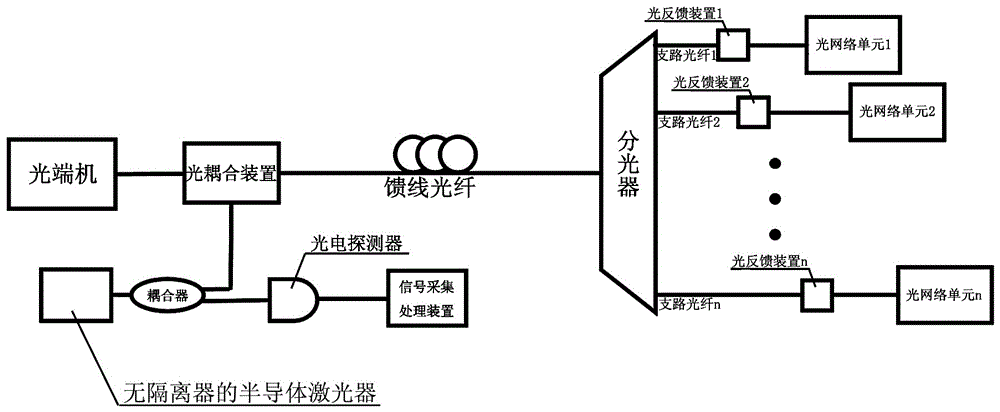
[0045] A device for monitoring link failures of a time-division multiplexing optical network, including a time-division multiplexing optical network and a monitoring device;
[0046] The time-division multiplexing optical network includes an optical terminal, a feeder optical fiber, an optical splitter of n channels, n branch optical fibers, and n optical network units; the optical terminal is connected to the common port of the optical splitter through the feeder optical fiber; the n optical splitters The splitting port is connected one by one to the incident end faces of n optical network units through n branch optical fibers;
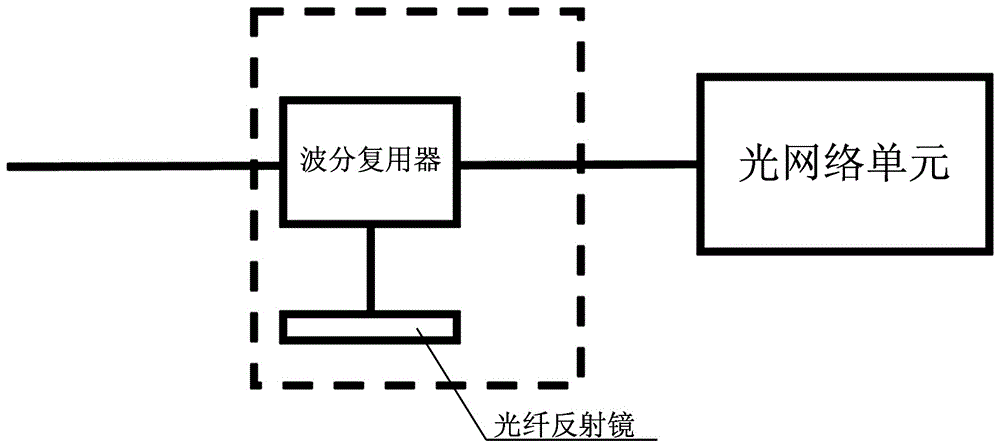
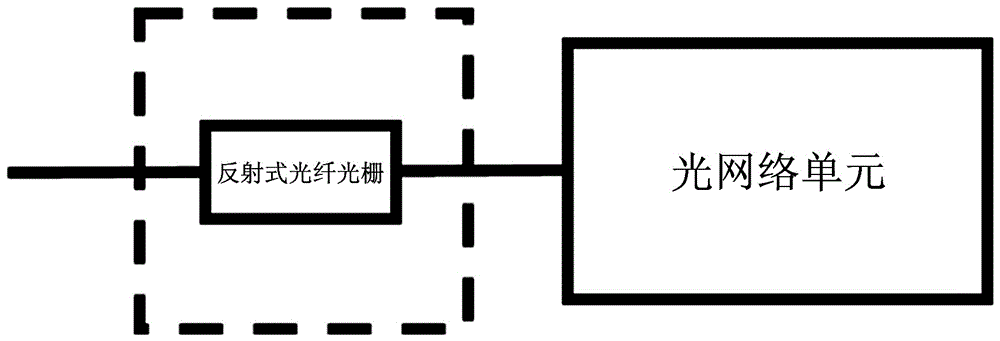
[0047] The monitoring device includes a semiconductor laser without an isolator, a coupler, an optical coupling device, a photodetector, a signal acquisition and processing device, and n optical feedback devices; the semiconductor laser without an isolator is connected to the coupler; the large ratio of the coupler The output end is connected to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] A device for monitoring link failures of a time-division multiplexing optical network, including a time-division multiplexing optical network and a monitoring device;
[0059] The time-division multiplexing optical network includes an optical terminal, a feeder optical fiber, an optical splitter of n channels, n branch optical fibers, and n optical network units; the optical terminal is connected to the common port of the optical splitter through the feeder optical fiber; the n optical splitters The splitting port is connected to the incident end faces of n optical network units through n branch optical fibers in one-to-one correspondence;
[0060]The monitoring device includes a semiconductor laser without an isolator, a coupler, an optical coupling device, a photodetector, a signal acquisition and processing device, and n optical feedback devices; the semiconductor laser without an isolator is connected to the coupler; the large ratio of the coupler The output end is ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] A device for monitoring link failures of a time-division multiplexing optical network, including a time-division multiplexing optical network and a monitoring device;
[0072] The time-division multiplexing optical network includes an optical terminal, a feeder optical fiber, an optical splitter of n channels, n branch optical fibers, and n optical network units; the optical terminal is connected to the common port of the optical splitter through the feeder optical fiber; the n optical splitters The splitting port is connected one by one to the incident end faces of n optical network units through n branch optical fibers;
[0073] The monitoring device includes a semiconductor laser without an isolator, a coupler, an optical coupling device, a photodetector, a signal acquisition and processing device, and n optical feedback devices; the semiconductor laser without an isolator is connected to the coupler; the large ratio of the coupler The output end is connected to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com