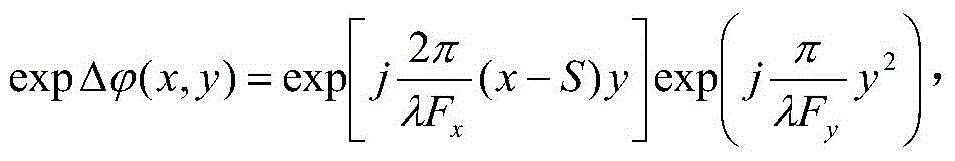Hyperbolic wavefront difference self-scanning direct-looking synthetic aperture imaging lidar
A technology of synthetic aperture laser and hyperbolic wavefront difference, which is applied in the re-radiation of electromagnetic waves, radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of limiting radar working distance and difficulty in long-distance detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
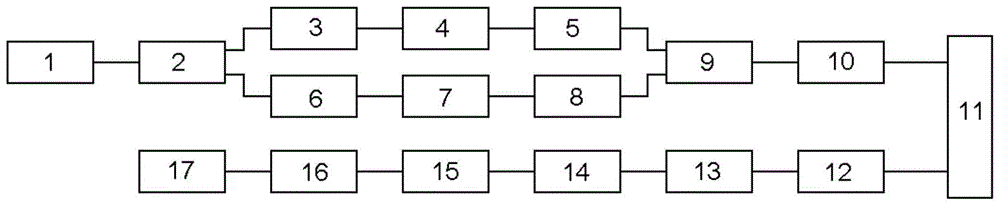
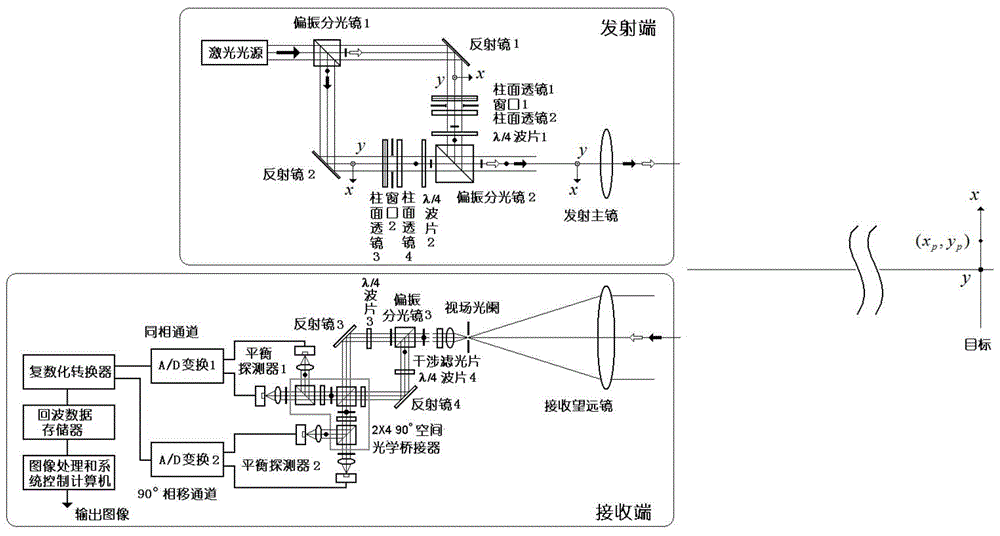
[0057] figure 2 It is a structural diagram of an embodiment of the hyperbolic wavefront difference self-scanning direct-looking synthetic aperture laser imaging radar of the present invention. The corresponding relationship between the structural components of the embodiment and the structural components of the basic principle is shown in Table 1.
[0058] Table 1 Correspondence of the structural components of the embodiment with respect to the components of the basic principle structure
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] The cross-track direction is defined as the x-direction, the along-track direction is defined as the y-direction, and an (α,β) coordinate system is defined, which is rotated by 45° relative to the (x,y) coordinate system.
[0062] The phase distr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com