A method for extracting and removing iron from chloride mixed solution
A mixed solution, extraction and iron removal technology, which is applied in the field of chemical industry and extraction chemistry, can solve the problems of strong water solubility and corrosion, and achieve the effect of overcoming the three-phase problem and simple extraction and removal of iron
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
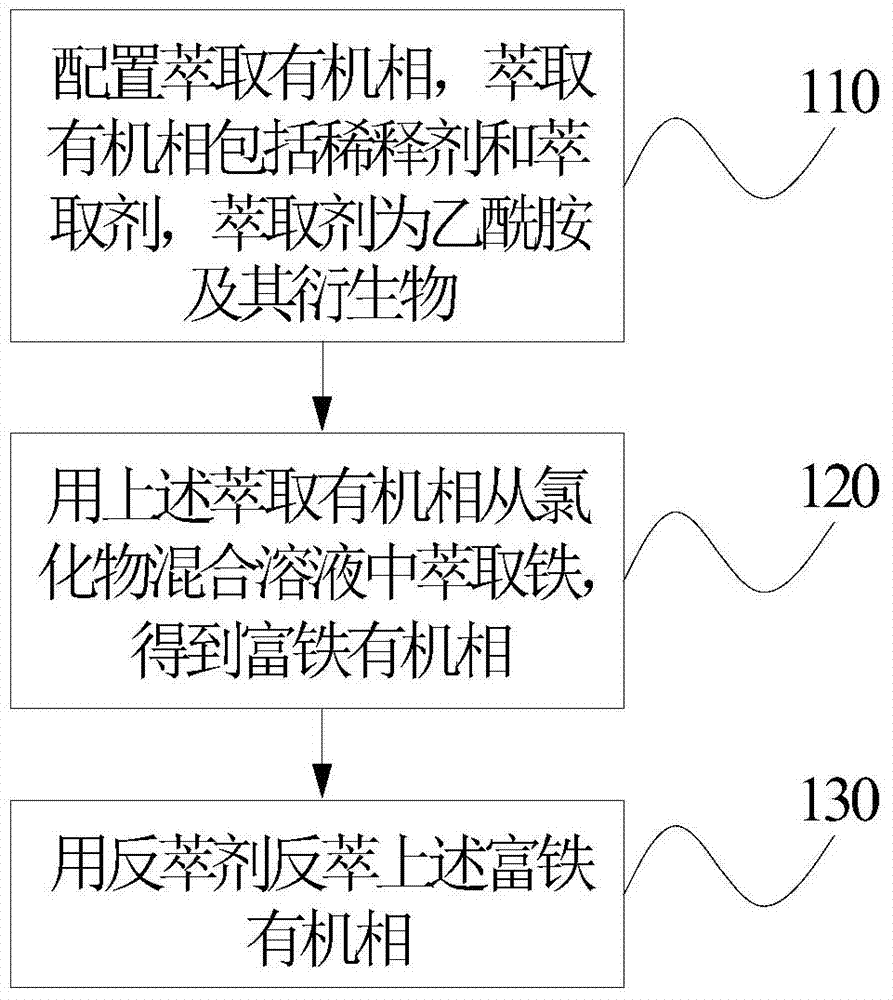
[0028] figure 1 It is a step flow chart of the method for extracting iron from a chloride mixed solution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
[0029] Reference figure 1 The steps of the method for extracting iron from the chloride mixed solution according to the embodiment of the present invention are as follows:
[0030] In step 110, an extraction organic phase is configured. The extraction organic phase includes a diluent and an extractant, and the extractant is acetamide and its derivatives.
[0031] In this embodiment, the extractant is N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)acetamide, and the diluent is sulfonated kerosene; and N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)acetamide and sulfonated kerosene The volume ratio is 3:7.
[0032] In step 120, the chloride mixed solution in this embodiment contains 0.5 mol·L -1 Fe 3+ 的HCl solution. The extraction organic phase is used to extract iron from the chloride mixed solution to obtain an iron-rich organic phase.
[0033] Specifically, the volume ratio (al...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In the description of Embodiment 2, the similarities to Embodiment 1 will not be repeated here, and only the differences from Embodiment 1 will be described. The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that in step 110, the extraction organic phase with different extractant concentrations is used for extraction, that is, N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)acetamide and sulfonated kerosene are adjusted. Different volume fractions. In step 120, the chloride mixed solution contains 0.5mol·L -1 Fe 3+ 的HCl solution, where H + The concentration is 3mol·L -1 . Refer to Example 1 for other steps. Table 2 shows the extraction effect of different extractant concentrations on iron.
[0039] Table 2
[0040] Extractant concentration / %2030405070 Iron extraction rate / %83.8599.8799.3199.4899.79
[0041] Table 2 shows that in the process of extracting iron from the chloride mixed solution according to the method of the present invention, the volume fraction of the extractant N,N-bis(2-ethyl...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is that: in step 120, H in the chloride mixed solution + The concentration is 3mol·L -1 . Adjust the different comparisons and analyze the extraction efficiency of iron removal. The extraction efficiency is shown in Table 3.
[0044] table 3
[0045] compared to 1:1 2:1 3:1 5:1 10:1 Iron extraction rate / %77.4994.8798.4099.3399.70
[0046] From the data in Table 3, it can be seen that the extraction organic phase composed of 30% (V%) N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)acetamide and 70% (V%) sulfonated kerosene has a content of 0.5 mol·L -1 Fe 3+ And 3mol·L -1 Extracting iron from the HCl mixed solution of chloride can achieve a better extraction effect when the ratio is 1:1. In actual production, only multi-stage countercurrent extraction can meet the requirements for extraction effect; However, when the comparison is larger, the extraction effect will be more excellent, but the increase in the amount of extractant will increase th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com