Patterned opto-electrical substrate and method for manufacturing the same
一种光电基板、制作方法的技术,应用在电路、电气元件、半导体/固态器件制造等方向,能够解决发光效率的程度限制、降低差排密度程度等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
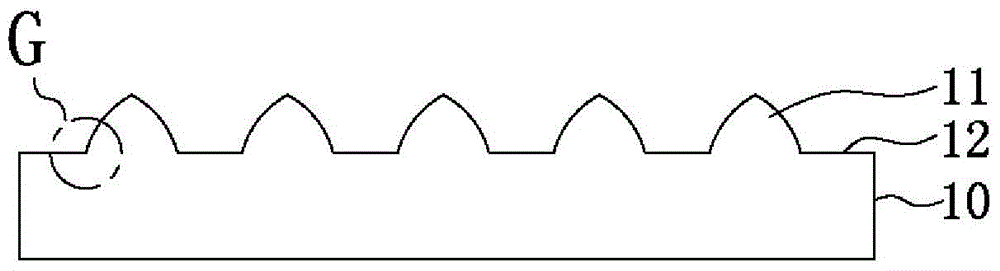
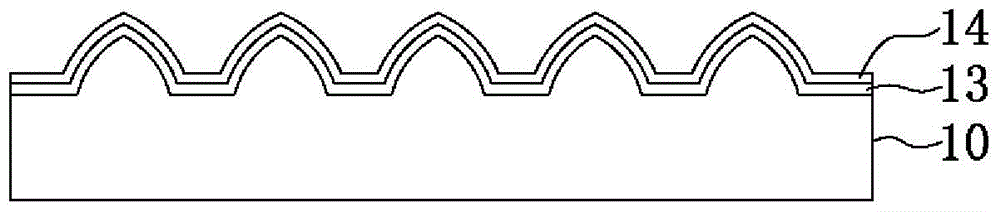
[0047] Please refer to Figures 1A to 1H , is a schematic diagram of the preparation process of the patterned optoelectronic substrate according to Example 1 of the present invention. First, please refer to Figure 1A and Figure 1B , provide a substrate 10, the substrate 10 is a sapphire substrate or a silicon substrate with a planar surface, and a first patterned structure 11 and a spacer region 12 are formed on the surface of the substrate 10 by the first etching process; wherein, in the first etching During the processing, a first photoresist layer (not shown) is provided on a part of the surface of the substrate 10, so that the first etching process selectively removes part of the substrate 10 to form micron-scale protrusions with a conical shape. The first patterned structure 11 of the structure and the spacer region 12 of the planar structure, and the height of the first patterned structure 11 (that is, the micron-scale protrusion structure) is 1.2 microns to 2 microns...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Please refer to figure 2 , is a schematic diagram of the patterned optoelectronic substrate of Example 2 of the present invention. Embodiment 2 is substantially the same as the patterned optoelectronic substrate and its manufacturing process described in Embodiment 1, except that the concave-convex pattern of the first patterned structure is different. Different from Embodiment 1, it is the first patterned structure with a conical micron-scale protrusion structure (please refer to Figure 1B ), in Embodiment 2, a first photoresist layer (not shown) is provided on a part of the surface of the substrate 20, so that the first etching process is to selectively remove part of the substrate 20 to form a cone-shaped The first patterned structure 21 of the micron-scale groove structure and the spacer region 22 of the planar structure; then, according to the manufacturing process of embodiment 1, the first patterned structure 21 contains a plurality of second patterned structu...
Embodiment 3 to Embodiment 5
[0055] Please refer to Figures 3A to 3C , are schematic diagrams of patterned optoelectronic substrates according to Embodiment 3 to Embodiment 5 of the present invention. Embodiment 3 to Embodiment 5 are substantially the same as the patterned optoelectronic substrate described in Embodiment 1 and the manufacturing process thereof, except that the shape of the first patterned structure is different.
[0056] Different from Embodiment 1, it is the first patterned structure with a conical micron-scale protrusion structure (please refer to Figure 1B ), please refer to Figure 3A , in Embodiment 3, a first photoresist layer (not shown) is provided on a part of the surface of the substrate 301, so that the first etching process is to selectively remove part of the substrate 301 to form a triangular cone-shaped The first patterned structure 311 of the micron-scale protruding structure and the spacer region 321 of the planar structure; then, according to the manufacturing proces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com