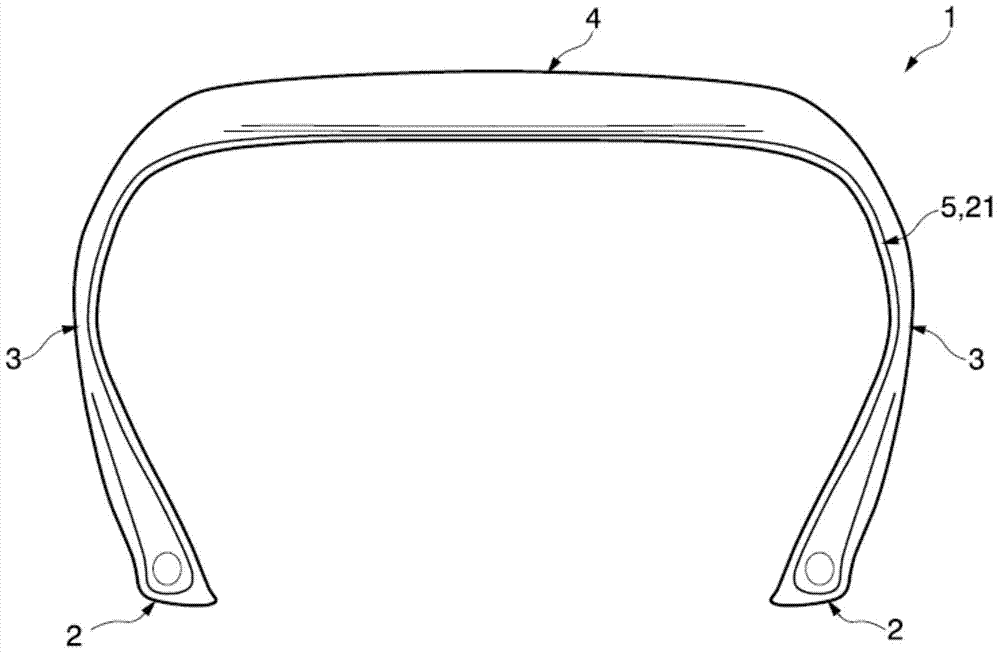
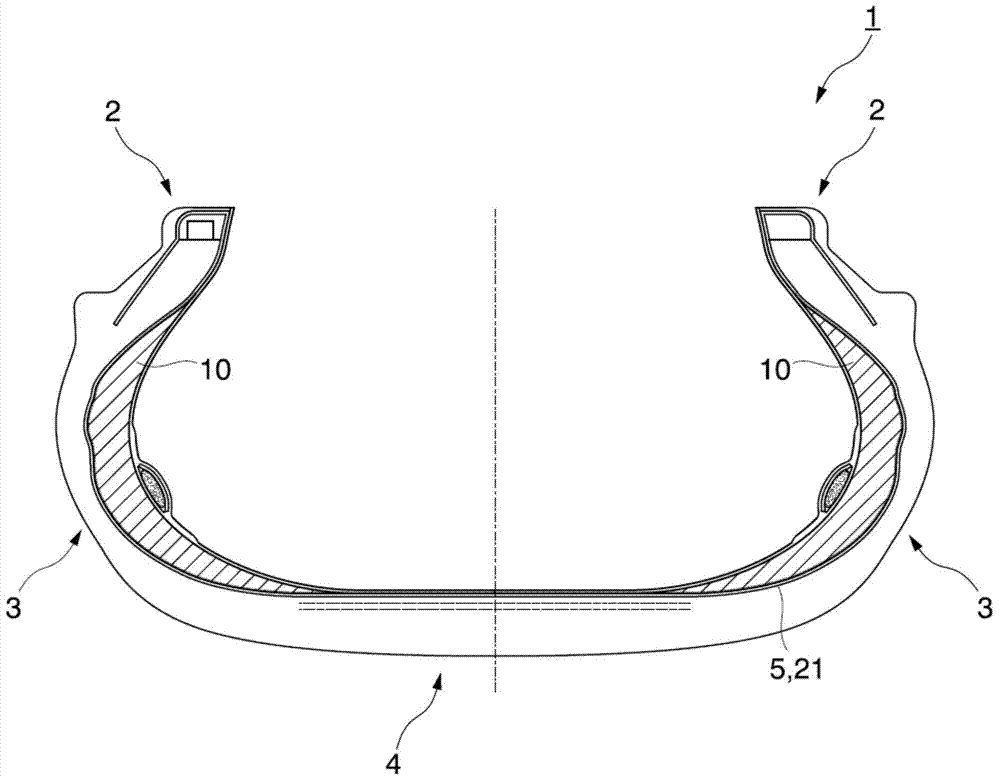
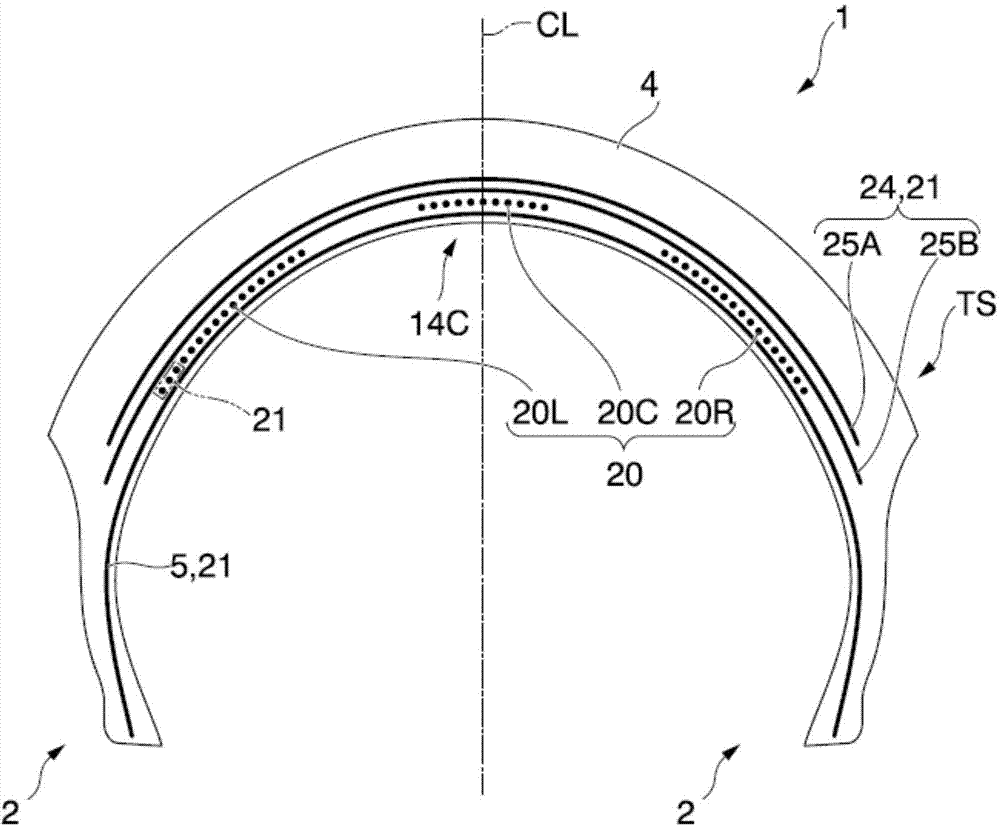
Cord, rubber-cord composite structure, and tire
A composite and cord technology, applied in motorcycle tires, tire parts, reinforcement layers of pneumatic tires, etc., can solve the problems of low initial elastic modulus, low tire operation stability, etc., to improve high-speed durability, Excellent tire performance and the effect of reducing environmental load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 6 and comparative example 1 to 4
[0271] [Manufacture of multifilament]
[0272] Dissolve the pulp in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (C2AmimAc), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethylphosphate (C2mimDEP) or N-methylmorpholine- The dissolved cellulose solution in N-oxide (NMMO) was filtered and degassed. Next, the dissolved cellulose solution was extruded through the extruder in the coagulation bath (in the solidification tank) after being heated to the spinning temperature, and thus used for compounding of Examples 1 to 6 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4 Silk (purified cellulose fiber) was obtained through a washing process and a drying process (refer to Table 1).
[0273] The properties of the multifilaments used in the respective Examples and the respective Comparative Examples were measured by the following test methods, and the results thereof are shown in Table 1.
[0274] (1) Denier of raw yarn
[0275] 100 m of multifilament was sampled, dried at 130° C. for 30 minutes, then cooled to room temperatu...
Embodiment 7 to 12 and comparative example 5 to 7
[0310] [Manufacture of Multifilament A]
[0311] The dissolved cellulose solution in which the pulp was dissolved in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethylphosphate (C2mimDEP) or N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) was filtered and removed. gas. Next, the dissolved cellulose solution was extruded through the extruder in the coagulation bath (in the solidification tank) after being heated to the spinning temperature, and thus used for compounding of Examples 7 to 12 and Comparative Examples 5 to 7. Silk A (purified cellulose fiber) was obtained through a washing process and a drying process (refer to Table 2).
[0312] [Manufacture of multifilament B]
[0313] Multifilament B (nylon) used in Examples 7 to 12 and Comparative Example 6 was obtained through a melt spinning process (refer to Table 2).
[0314] The properties of the multifilaments used in the respective Examples and the respective Comparative Examples were measured by the following test methods, and the results thereo...
Embodiment 13 to 17 and comparative example 8 to 13
[0350] [Manufacture of multifilament (raw yarn)]
[0351] Dissolve the pulp in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (C2AmimAc), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethylphosphate (C2mimDEP) or N-methylmorpholine- The dissolved cellulose solution in N-oxide (NMMO) was filtered and degassed. Next, the dissolved cellulose solution was extruded through an extruder in a coagulation bath (in a water bath) after being heated to the spinning temperature, and thus Examples 13 to 17 and Comparative Examples 8 to 13 shown in Table 3 The multifilament (refined cellulose fiber) is obtained through a washing process and a drying process.
[0352] The properties of the multifilaments used in the respective Examples and the respective Comparative Examples were measured by the following test methods, and the results thereof are shown in Table 3.
[0353] (1) Raw yarn fineness
[0354] 100 m of the obtained multifilament was sampled, dried at 130° C. for 30 minutes, and then cooled to room temperat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com