Method for simultaneously detecting cadmium and lead ions by employing sulfhydrylated peroxidized poly(m-phenylenediamine) modified bismuth membrane electrode
A technology of peroxidizing poly-m-phenylenediamine and poly-m-phenylenediamine is applied in the direction of electrochemical variables of materials, which can solve the problems of decreased conductivity of conductive polymers, time-consuming operation, de-doping, etc., and achieves improved electrostatic attraction. , Increase the detection ability, the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] a, the preparation contains 0.1M H 2 SO 4 , 0.1M m-phenylenediamine and different concentrations of mercaptosuccinic acid electrolyte solution, using cyclic voltammetry, the potential range is -0.2 ~ 1.2V, and the scan rate is 50mV / s, it is modified on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, one step The mercapto-polym-phenylenediamine modified electrode was obtained by the method.
[0029] b. The electrode prepared in step a was peroxidized in a 0.2M sodium hydroxide solution at a constant potential of 1.0V for 8 minutes to obtain a peroxidized mercapto-poly-m-phenylenediamine modified electrode.
[0030] c. In the oxygen-filled state, place the modified electrode in step b in the Bi-containing 3+ , Pb 2+ and Cd 2+ The bismuth film was deposited in situ in the NaAc-HAc buffer solution, and a bismuth film electrode modified with thiolated and peroxidized poly-m-phenylenediamine was obtained.
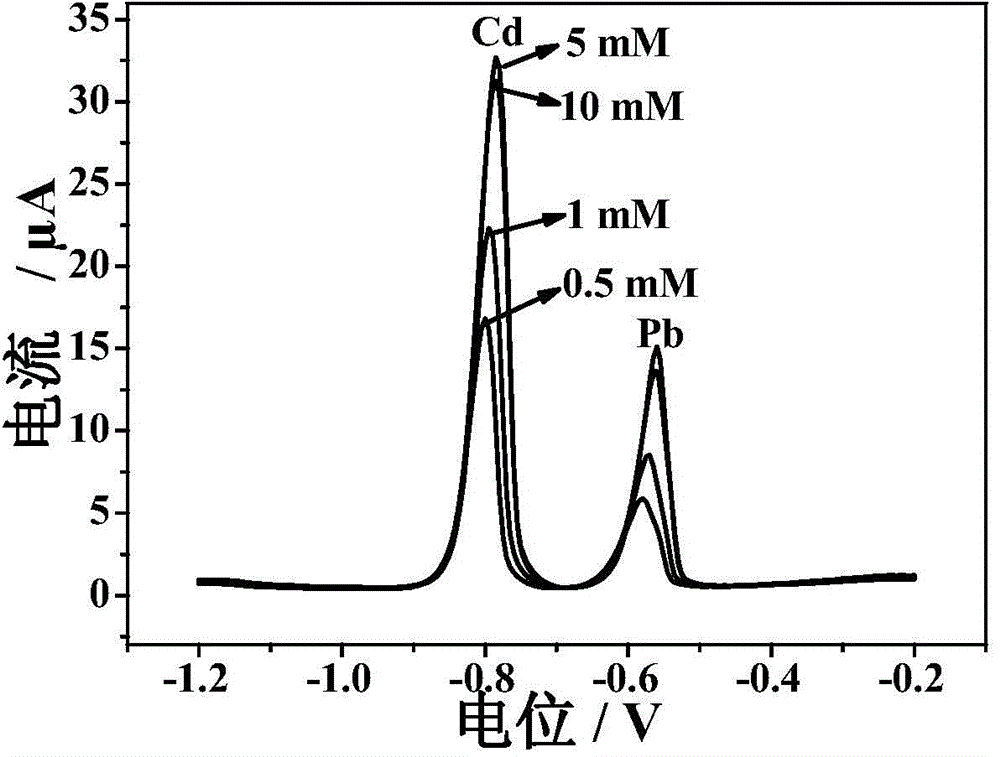
[0031] In order to investigate the impact of the concentration of me...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Firstly, a bismuth film electrode modified with thiolated and peroxidized poly-m-phenylenediamine was prepared, and the preparation process was the same as in Example 1.
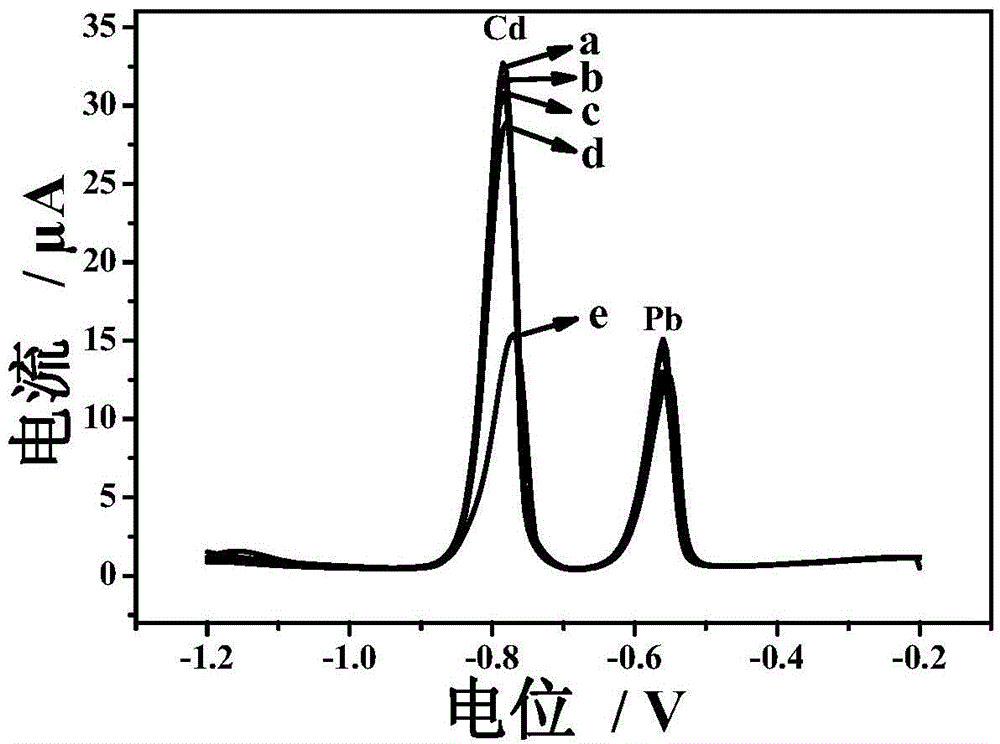
[0034] In order to investigate the influence of the in-situ deposition potential on the detection of cadmium and lead ions in step c, the deposition potentials of -0.9V, -1.0V, -1.1V, -1.2V and -1.3V were respectively used to detect cadmium and lead ions. test, see the results figure 2 , it can be seen that at -1.0V, it has higher sensitivity and relatively flat background current. Although the peak currents detected at -1.1V, -1.2V, and -1.3V are higher than -1.0V, the background current is also lower due to hydrogen evolution. increased, so the in situ deposition potential was chosen to be -1.0 V.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Firstly, a bismuth film electrode modified with thiolated and peroxidized poly-m-phenylenediamine was prepared, and the preparation process was the same as in Example 1.
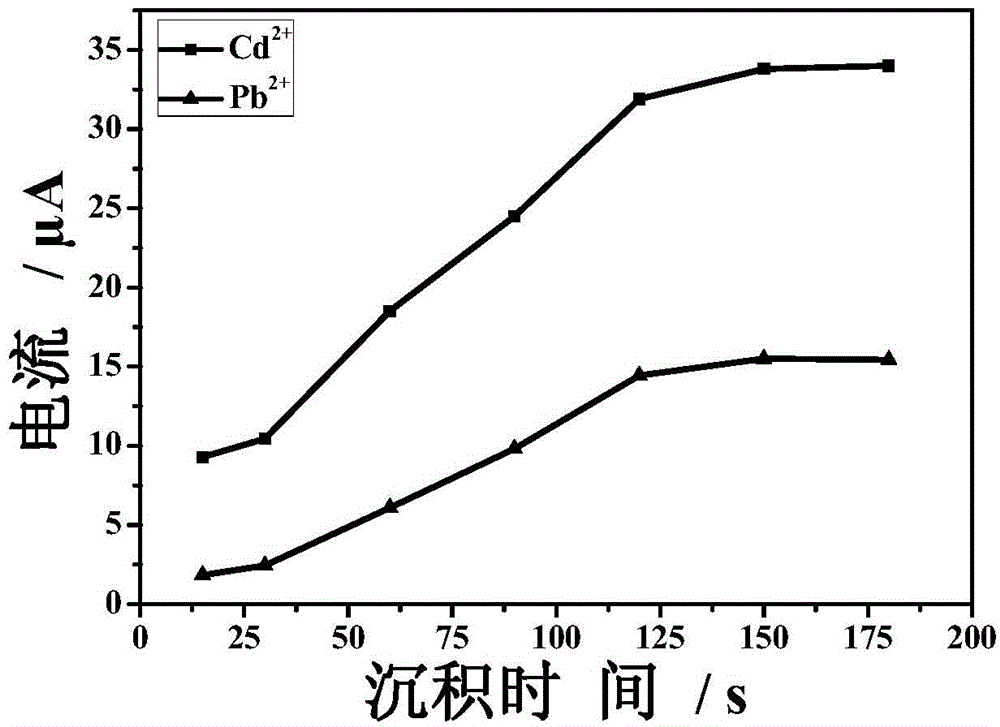
[0037] In order to investigate the influence of the in-situ deposition time in step c on the detection of cadmium and lead ions, therefore, the deposition times of 15s, 30s, 60s, 90s, 120s, 150s, and 180s were respectively used to detect cadmium and lead ions. The results are shown in image 3 , it can be seen that after 150s, the lead and cadmium ions deposited on the surface of the electrode are close to saturation, and a higher detection result is achieved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com