Method for regenerating plants by hippeastrum hybridum hort. petal tissue induction
A technique for regenerating plants and petals, applied in the field of plant regeneration induced by Hippeastrum petal tissue, can solve the problem of low reproductive efficiency of Hippeastrum, achieve the effect of improving regeneration efficiency and improving reproductive efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
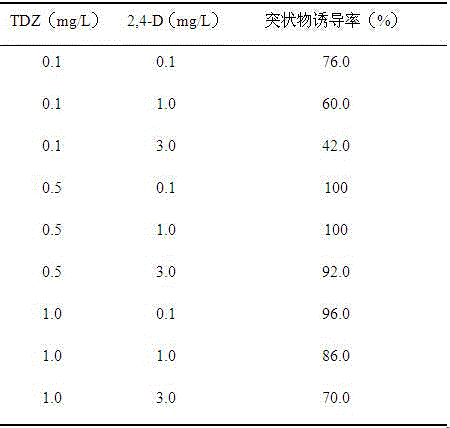
[0032] Example 1 Effects of TDZ and 2,4-D on the Induction of Petal Projections of Hippeastrum
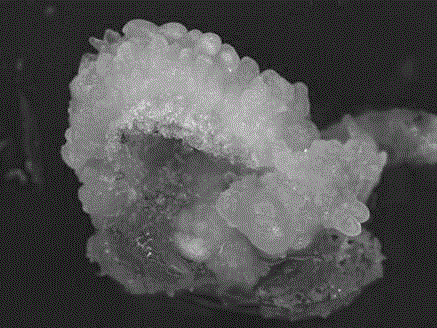
[0033] To study the effect of different concentrations of TDZ and 2,4-D on the induction rate of Hippeastrum petal protrusions: Take the young inflorescences of Hippeastrum, soak in 70% ethanol for 15 minutes, wash with sterile water for 3 times, cut off the outer bracts, and take out the flower buds , cut the petals perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the bud, cut them into ring-shaped petal filaments with a width ≤ 1.0mm, and use the petal filaments as explants; place the treated explants horizontally on the induction medium, and place them on the induction medium. 24~26°C, cultured in the dark for 8~12 weeks, the outer surface of the petals produces protrusions; the induction medium is MS medium as the basic medium, and a certain concentration of thiadizuron ( TDZ), 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), and 20-40g / L sucrose, pH 5.8-6.0, the experimental results are sho...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Effects of 6-BA on Adventitious Buds and Plantlet Regeneration
[0038]To study the effects of different concentrations of 6-BA on the induction of adventitious buds and plant regeneration: take the explants that produced protrusions and transfer them to the regeneration medium, at 24~26°C, 12~14h of light per day, and the light intensity was 1000 Cultivate under the environment of ~1400lux, protrusions form adventitious buds and then form complete plants; the regeneration medium is based on MS medium, and a certain concentration of 6-benzylaminoadenine is added according to Table 2, and 20~40g / L sucrose, pH 5.8~6.0, the experimental results are shown in Table 2. The results showed that the concentration of 6-BA affected the adventitious bud induction rate of Hippeastrum petals and plant regeneration rate. When the concentration of 6-BA was 0-0.5 mg / L, the induction rate of adventitious buds reached 100%, and the plant regeneration rate was ≥92%; when the c...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for inducing plant regeneration with Hippeastrum petal tissue, comprising the steps of:
[0044] S1. Explant treatment: take the young inflorescences of Hippeastrum just extracted, wash them with tap water, soak them in 70% ethanol for 15 minutes in an ultra-clean workbench, wash them with sterile water for 3 times, and cut off the outer bracts with a scalpel , and then take out the flower bud with tweezers, cut the petal perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the flower bud, cut into ring-shaped petal filaments with a width of 0.5-1.0 mm, and use the petal filaments as explants;
[0045] S2. Protrusion induction: quickly transfer the cut ring-shaped petal filament explants, place them horizontally on the induction medium, and culture them under dark conditions at 24-26°C. After about 1 week, the petal fine filaments The silk begins to expand, and at 8 to 12 weeks, a large number of protrusions are produced on the outer surface of the petal and the wound sit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com