Supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion capable of reducing minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil
A carbon dioxide, miscible pressure technology, applied in drilling composition, bulk chemical production, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of weak van der Waals force, weak solubility, low dielectric constant, etc., to reduce the miscible pressure , The effect of reducing interfacial tension and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] In this embodiment, the supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion capable of reducing the minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil is composed of a carbon dioxide-friendly surfactant, a cosolvent and supercritical carbon dioxide.
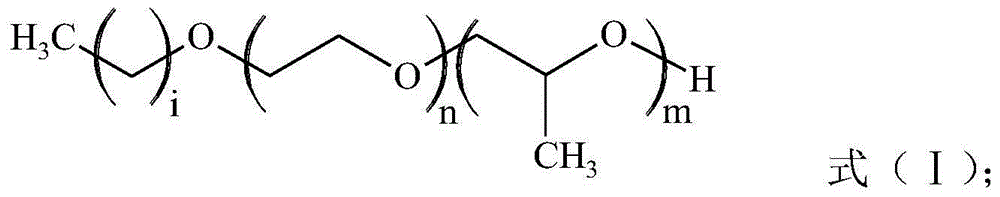
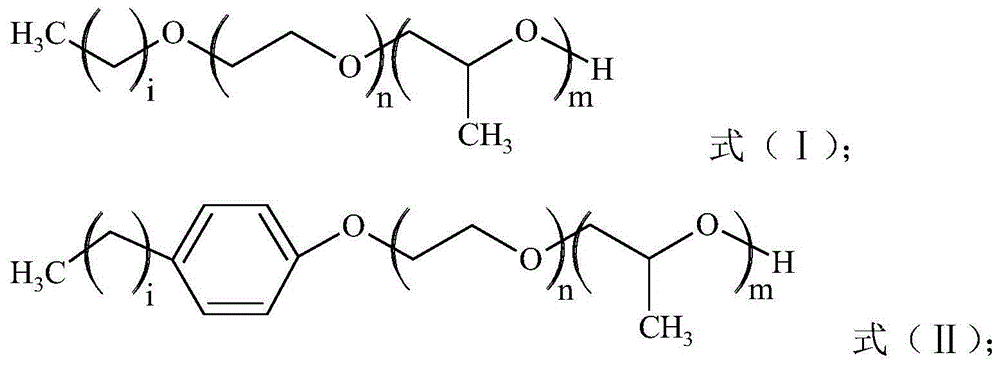
[0035]The pro-carbon dioxide surfactant is fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether as shown in formula (I):
[0036]
[0037] In formula (I): m=6, n=2, i=13.
[0038] The weight of the fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether is 0.5wt% of the weight of the supercritical carbon dioxide, and the cosolvent is ethanol, and the weight of the ethanol is 0.4wt% of the weight of the supercritical carbon dioxide.
[0039] Under the condition that the temperature is 60°C, the minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil A is 20.7MPa; after adding the supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion of this embodiment, the minimum miscible pressure of supercritical carbon dioxide and crude oil A is 15...
Embodiment 2
[0041] In this embodiment, the supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion capable of reducing the minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil is composed of a carbon dioxide-friendly surfactant, a cosolvent and supercritical carbon dioxide.
[0042] The pro-carbon dioxide surfactant is fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether as shown in formula (I):
[0043]
[0044] In formula (I): m=6, n=0, i=15.
[0045] The weight of the fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether is 0.6 wt% of the weight of the supercritical carbon dioxide, and the cosolvent is amyl alcohol, and the weight of the amyl alcohol is 0.3 wt% of the weight of the supercritical carbon dioxide.
[0046] At a temperature of 70°C, the measured minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil B is 18.3 MPa; after adding the supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion of this example, the measured minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil B is 13.8 MPa, t...
Embodiment 3
[0048] In this embodiment, the supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion capable of reducing the minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil is composed of a carbon dioxide-friendly surfactant, a cosolvent and supercritical carbon dioxide.
[0049] The pro-carbon dioxide surfactant is fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether as shown in formula (I):
[0050]
[0051] In formula (I): m=8, n=2, i=13.
[0052] The weight of the fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether is 0.6 wt% of the weight of the supercritical carbon dioxide, the cosolvent is butanol, and the weight of the butanol is 0.4 wt% of the weight of the supercritical carbon dioxide.
[0053] At a temperature of 60°C, the measured minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil C is 23.7 MPa; after adding the supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion of this example, the measured minimum miscible pressure of carbon dioxide and crude oil C is 17.2 MPa, the minimum mis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com