Method for thermally reversibly crosslinking styrenic thermoplastic elastomer material
A thermoplastic elastomer and styrene-based technology, applied in the field of chemical material preparation, can solve problems such as low strength and easy aging, and achieve the effects of low cost, improved mechanical properties, and simple methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
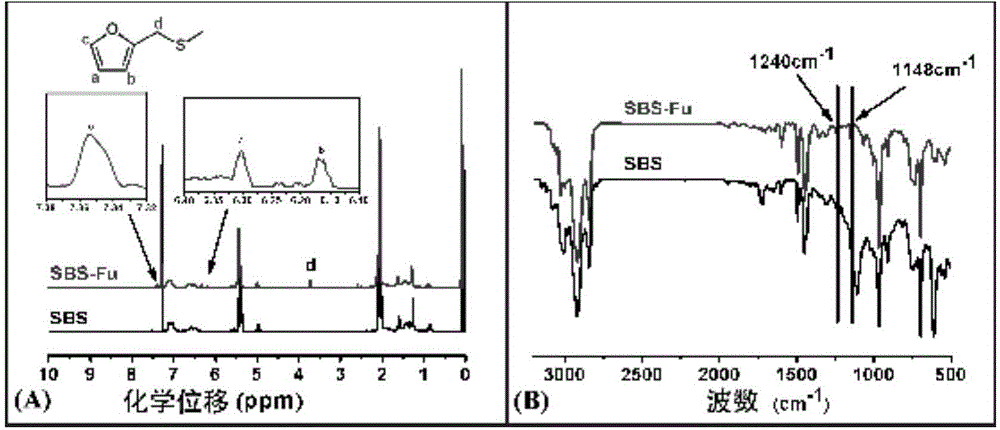
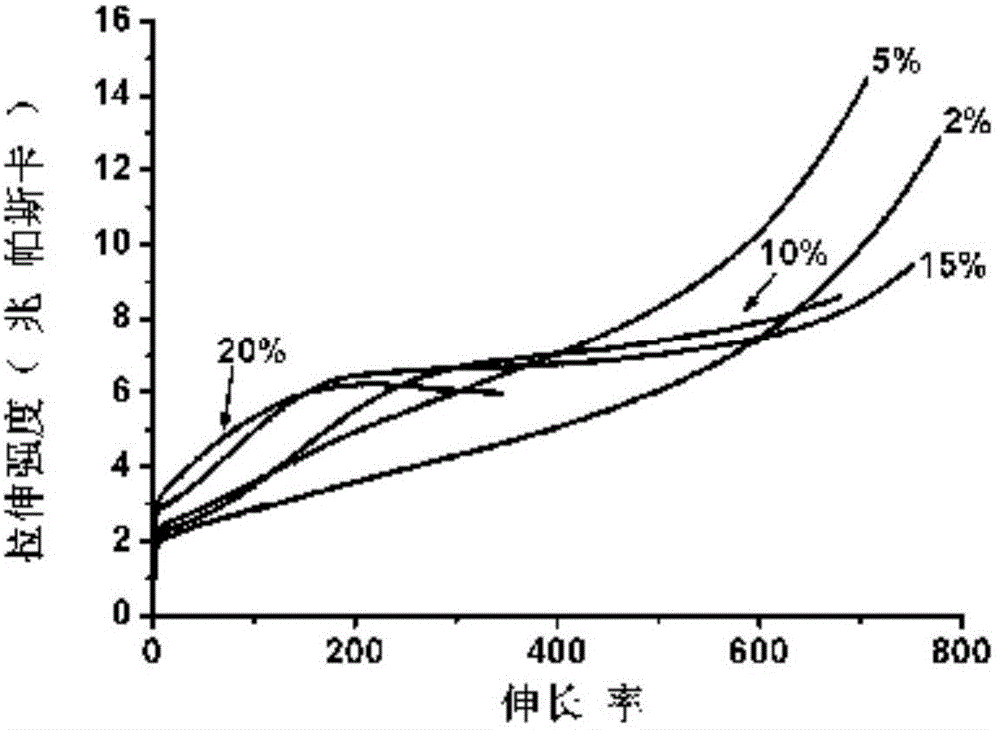
[0021] Dissolve SBS and furfuryl mercaptan in toluene in different proportions, add an appropriate amount of photoinitiator I907, and the grafting ratio of furfuryl mercaptan can be selected as 2%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, after stirring evenly , performing a click reaction under UV light. Then add N,N'-(4,4'-methylenediphenyl)bismaleimide with half the mole number of furan to the reacted solution (furan and maleimide structure The molar ratio is 1:1), after stirring evenly, heat cross-linking molding at 80°C. Table 1 shows the elongation at break and strength at break in tensile tests of various ratio materials. figure 1 It is the nuclear magnetic and infrared images of the SBS after furan grafting 20% in embodiment 1. figure 2 It is the stress-strain graph of the material of various proportions in embodiment 1.
[0022] Table 1
[0023]
Embodiment 2
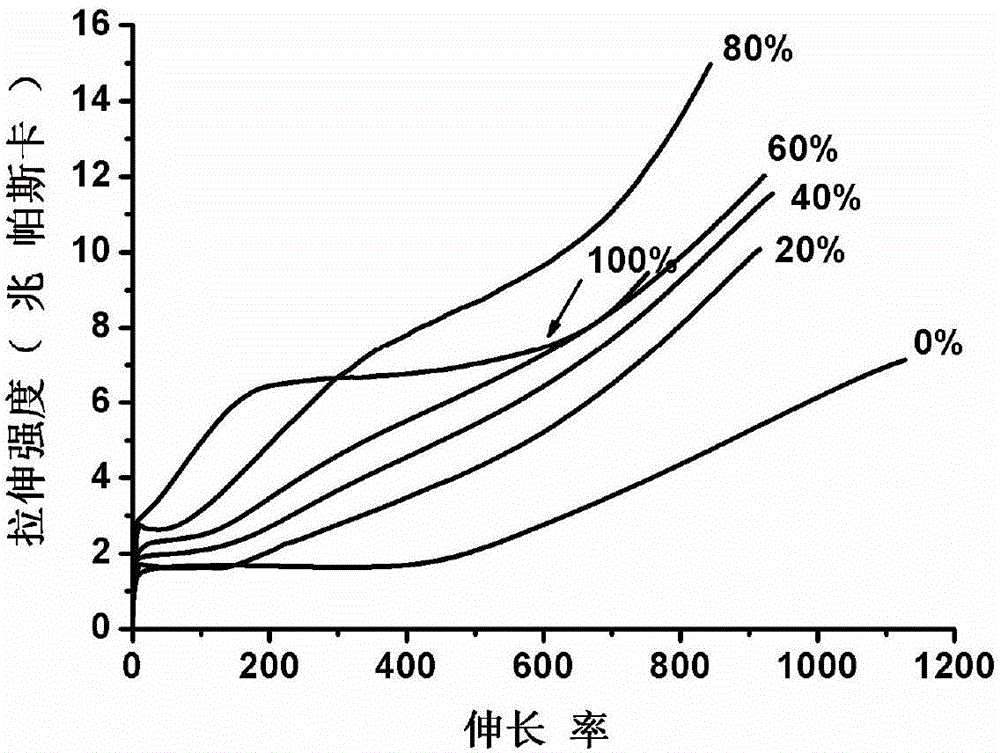
[0025] SBS and furfuryl mercaptan were dissolved in xylene, an appropriate amount of photoinitiator I907 was added, and the ratio was set to 15% of furfuryl mercaptan grafting. After stirring evenly, the click reaction was carried out under ultraviolet light. Then add different amounts of N,N'-(4,4'-methylenediphenyl)bismaleimide to the reacted solution, wherein the mole of maleimide accounts for the mole of furan The ratio is 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100%. After stirring evenly, it is heated at 80°C for cross-linking. Table 2 shows the elongation at break and strength at break in tensile tests of various ratio materials. image 3 It is the stress-strain graph of the material of various proportions in embodiment 2.
[0026] Table 2
[0027] Mole ratio of maleimide to furan Elongation at break (%) Breaking strength (MPa) 0 1127.56 7.14 20% 914.54 10.07 40% 922.54 12.02 60% 933.89 11.54 80% 843.21 14.96 100% 751.99 9.45 ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] In Example 2, the grafting amount of furan is 15%, and the sample whose molar ratio of maleimide to furan is 80% is cut into pieces after film formation, and the film is re-formed at 150°C under the condition of 10MPa, and the process is repeated three times , to test the tensile strength of each obtained film, and Table 3 shows the elongation at break and the strength at break in the tensile test of each re-produced material. Figure 4 is the stress-strain graph of the reshaped material in Example 3.
[0030] table 3
[0031] Elongation at break (%) Breaking strength (MPa) as it is 843.21 14.96 first remodeling 875.19 14.10 second remodeling 892.66 12.71
[0032] third remodeling 885.71 12.03
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com