Q-learning based vehicular ad hoc network routing method
A vehicle self-organization and network technology, applied in the field of Internet of Things communication, can solve complex and changeable problems, and achieve the effect of improving the success rate of transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
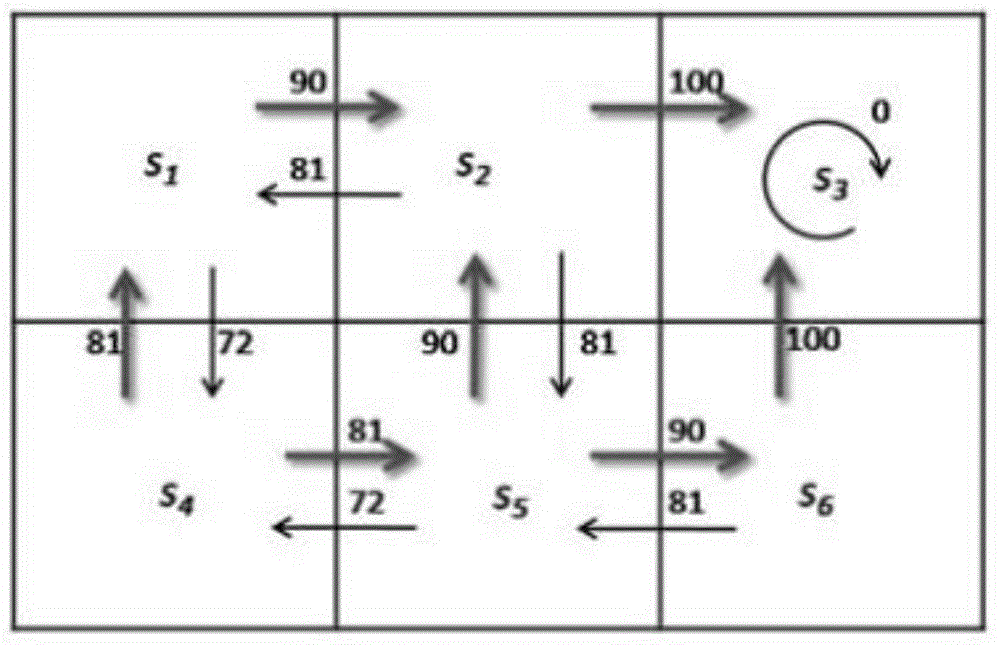
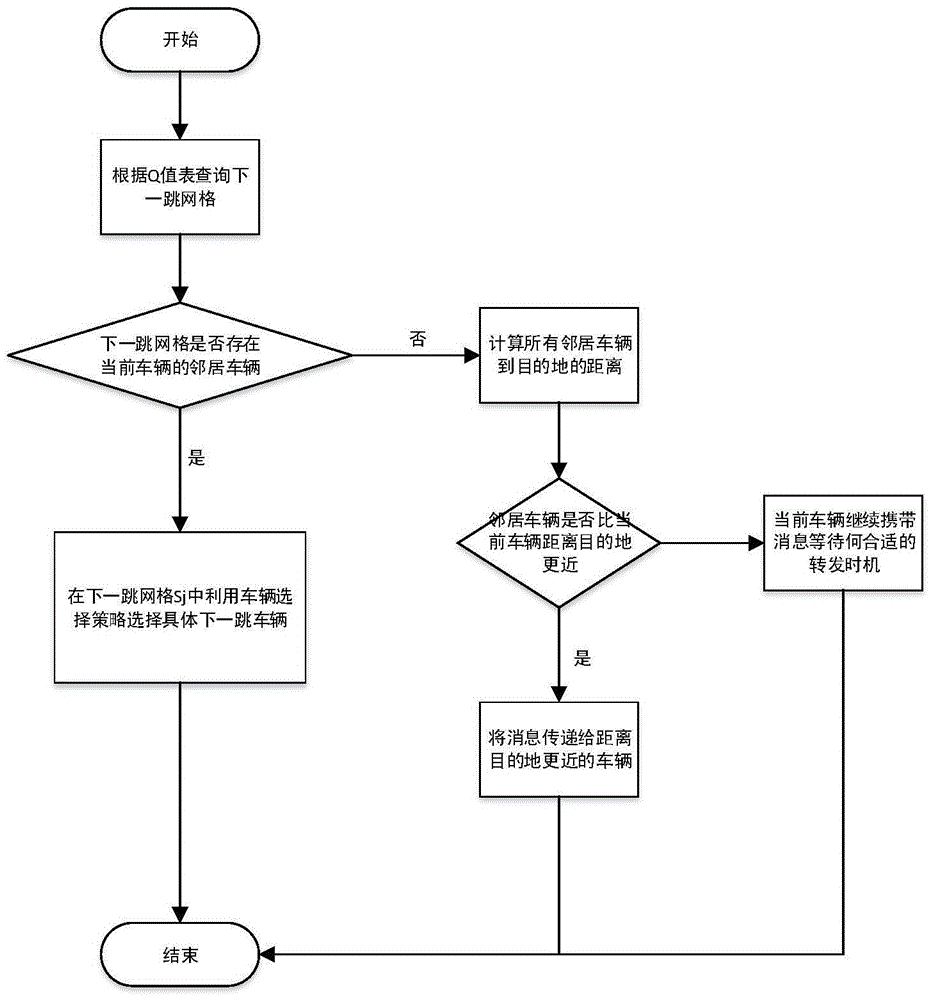
[0024] This part will describe the Q-learning and grid-based routing routing selection method in detail in conjunction with the above-mentioned drawings. The specific implementation of each part included in this method is as follows:
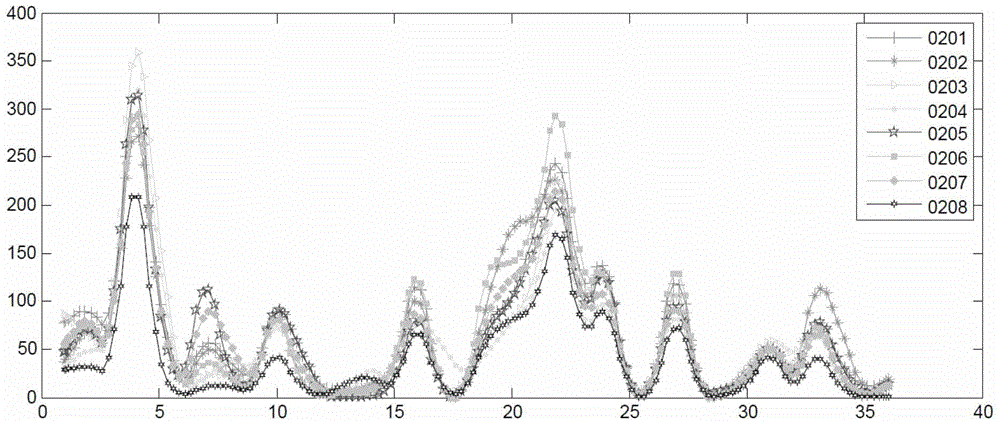
[0025] Step 1: Divide the urban area into equal grids, and record the track information of the passing vehicles in each grid in the past period of time. Since the vehicles in the network are all equipped with GPS global positioning system, the vehicles obtain neighbor node information by transmitting Hello data packets to each other. figure 1 It is the change of the number of vehicle GPS records in different grids in the area around Shanghai Railway Station from February 1, 2007 to February 8, 2007. Among them, the area is 1200m×1200m, and the side length is 200m. Since the frequency of vehicles uploading GPS points is fixed, the number of GPS records of vehicles in the grid can roughly indicate the frequency of passing vehicles in the grid. F...
Embodiment
[0048] In order to verify the beneficial effects of the present invention, simulation verification is performed on this embodiment.
[0049] In some applications of the urban traffic network, there is a high requirement for the success rate of data packet transmission, but not high requirements for the transmission delay of data packets, so in this kind of network, the success rate of data packet transmission is a measure of the vehicle Core metrics for the performance of routing protocols in ad hoc networks.
[0050] The Q-learning and grid-based routing algorithm proposed in the present invention is named as QGrid, and is subdivided into QGrid_G and QGrid_M according to the next-hop vehicle greedy selection strategy and Markov selection strategy. In order to verify the data transmission success rate and transmission delay performance of the QGrid algorithm in the vehicle ad hoc network, the present invention compares it with GPSR and HarpiaGrid. GPSR is a classic routing pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com