Distributed multiple-mobile-node cooperative positioning system
A mobile node and cooperative positioning technology, applied in the information field, can solve problems such as no utilization, no cooperation of robots, memory consumption of distributed algorithms and uncontrollable amount of calculation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0094] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
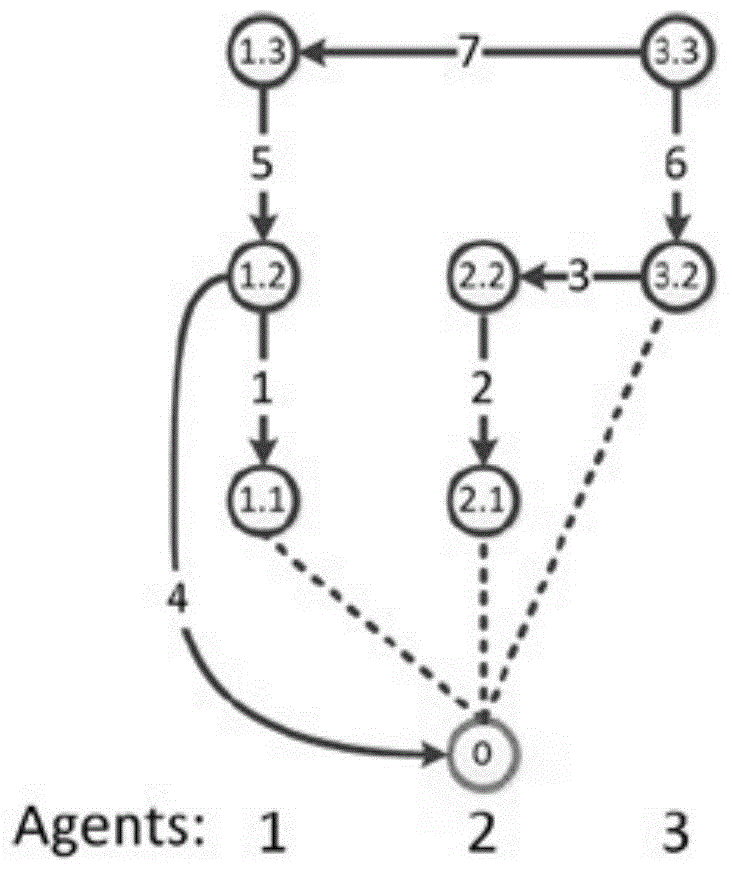
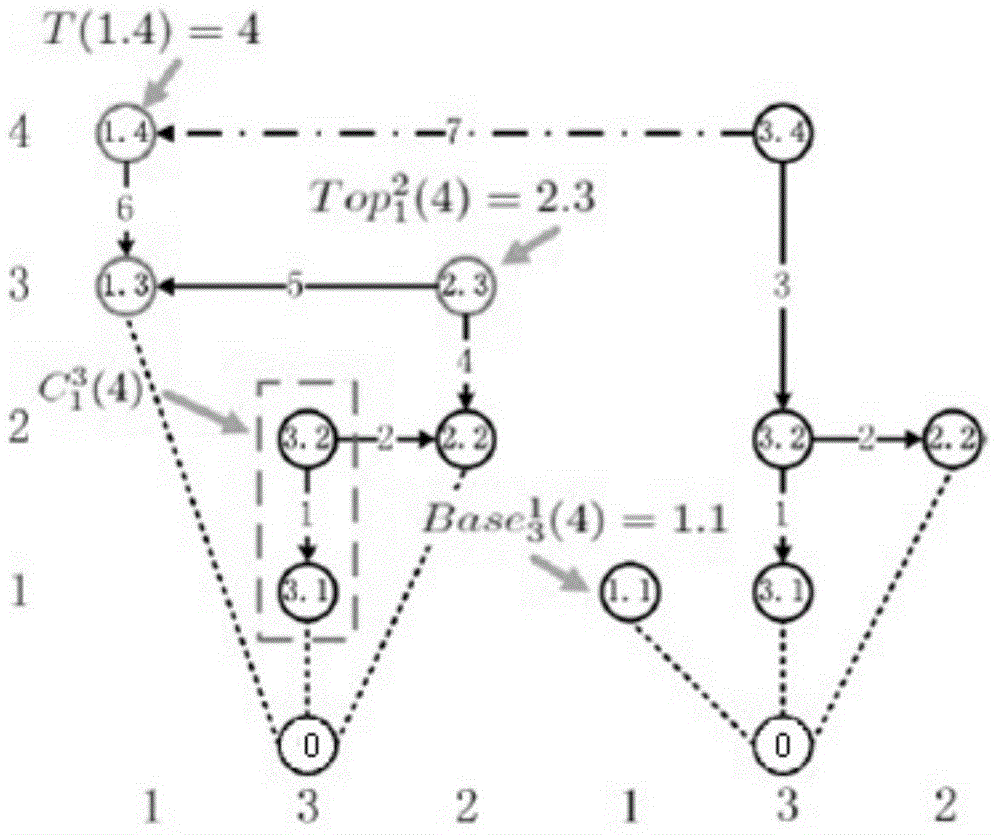
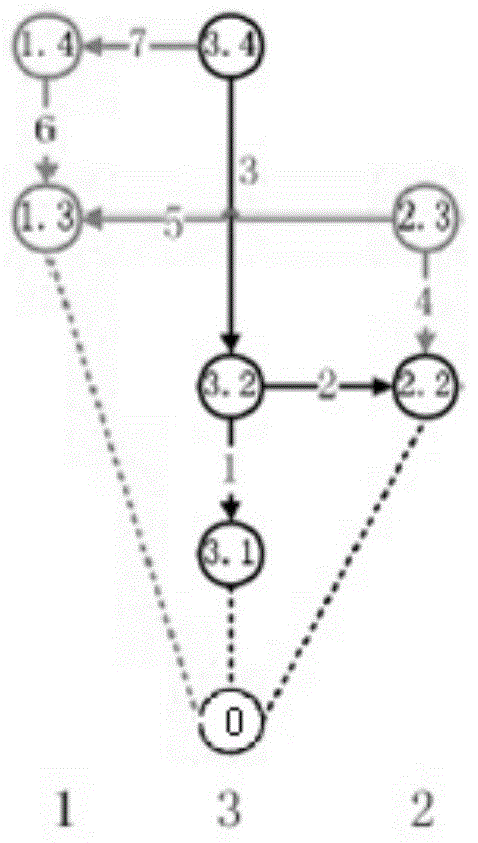
[0095] The distributed multi-mobile node cooperative positioning system of the present invention includes several mobile nodes, and each mobile node includes the following modules:
[0096] The mobile node's own movement estimation module (DR): monitors the change of the relevant position information of the mobile node itself within two time points through the inertial element, such as displacement change, distance change, angle change, etc. The position information refers to the two time points The coordinate change of the point in the Cartesian coordinate system.
[0097] Inter-mobile node ranging module (IM): used to measure the relative position information of the mobile node and another mobile node at the same time, such as relative position coordinate information, relative position distance information, relative position angle i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com