Application of ginkgolic acid in the preparation of drugs for preventing and/or treating diseases caused by overactivation of osteoclasts
A technology of ginkgolic acid and medicine, applied in the field of new medicinal use of ginkgolic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
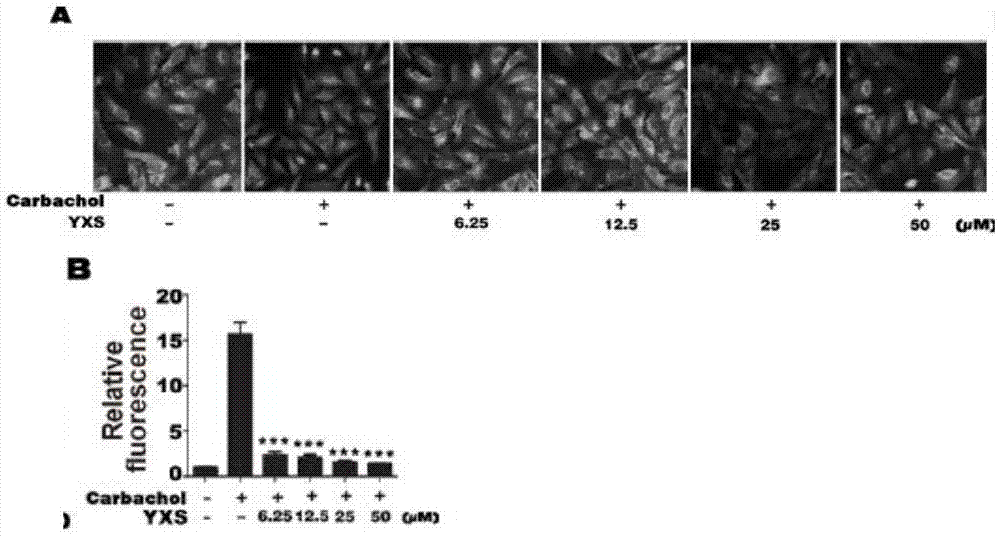
[0027] Example 1: Dose-effect relationship of ginkgolic acid (C17:1) inhibiting NFATc1 nuclear translocation
[0028] Principle: The high-content instrument can quantitatively detect the fluorescence changes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. NFATc1 in the EGFP-NFATc1-U2OS stably transfected cell line has been labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP), so the distribution of NFATc1 can be judged according to the fluorescence changes in the cytoplasm and nucleus and the cell picture, so as to determine its nuclear entry quantity. Carbachol was used as the stimulator of NFATc1 translocation into the nucleus, and the optimal stimulation time and dose were determined first in the preliminary experiment.
[0029] Methods: EGFP-NFATc1U2OS cells were inoculated in 96-well plates to culture cells, firstly treated with 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 μM ginkgolic acid (C17:1) (YXS) for 2 hours, then treated with 2 μM carbachol for 30 min, the cells were fixed and used After the nuclei were stained wi...
Embodiment 2
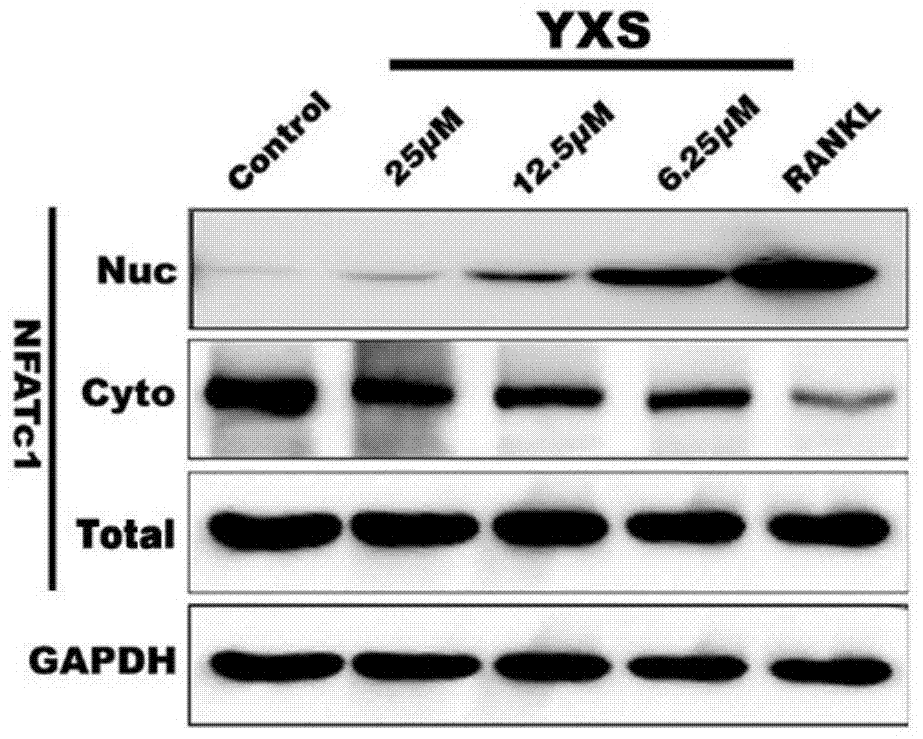
[0030] Example 2: Inhibitory effect of ginkgolic acid (C17:1) on RANKL-induced nuclear translocation of NFATc1 in osteoclast precursor cells
[0031] Principle: The RANKL pathway is considered to be a key pathway in the process of osteoclast differentiation and formation. Intracellular calcium fluctuations directly induced by RANKL lead to phosphorylation of intracellular calcineurin kinase, which selectively activates NFATc1 and promotes its translocation into the nucleus, thereby initiating NFATc1-dependent gene expression during osteoclast differentiation. In the absence of NFATc1, osteoclasts cannot differentiate into osteoclasts even if the RANKL pathway is normally activated.
[0032] Methods: Osteoclast precursor cells RAW264.7 cells were seeded in medium cell culture dishes and treated with 50ng / ml RANKL and 0, 6.25, 12.5, 25M ginkgolic acid (C17:1) (YXS) for two days. The nuclear protein isolation kit was used to extract nuclear protein, cytoplasmic protein, and tota...
Embodiment 3
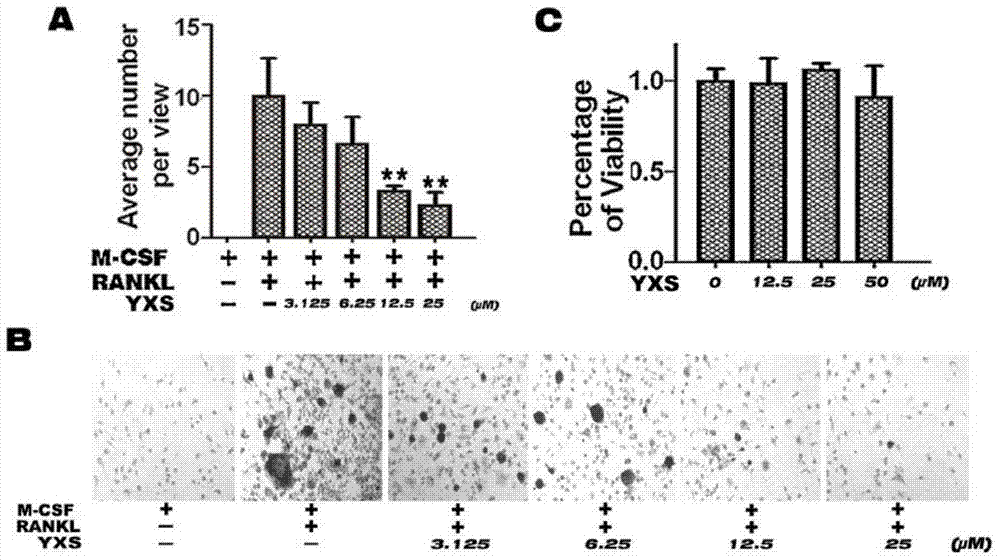
[0034] Example 3: Inhibitory effect of ginkgolic acid (C17:1) on osteoclast differentiation
[0035] Principle: Under the continuous stimulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and RANKL, bone marrow mononuclear cells contact each other and fuse to form multinucleated cells, and differentiate to form mature osteoclasts with a seal ring structure, and secrete osteoclasts. The characteristic enzyme of bone cells is tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), and the number of osteoclasts can be detected by staining for TRAP.
[0036] Methods: Bone marrow mononuclear cells were isolated from the femur of C57 / BL6 mice, and the cell density was adjusted to 100,000 / mL after counting, and 30 ng / mL of recombinant mouse macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) was added and inoculated in 96 Well culture plate, add 100 μL to each well. On the second day, the cells were induced with RANKL at a concentration of 50ng / mL, and 0, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, and 25 μM ginkgolic ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com