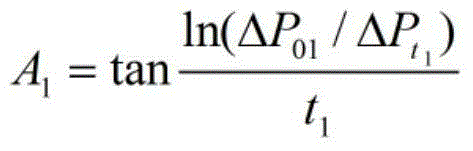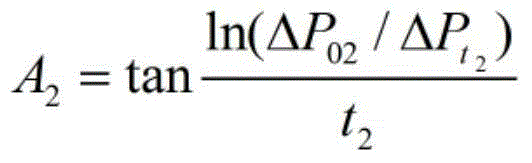Device and method for evaluating damage degree of working solution to tight reservoir
A technology for dense reservoirs and working fluids, applied in measuring devices, analysis of suspensions and porous materials, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as permeability testing, unsatisfied Darcy flow characteristics, and unsatisfactory gas pulse methods, etc., to achieve The effect of less experimental parameters and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
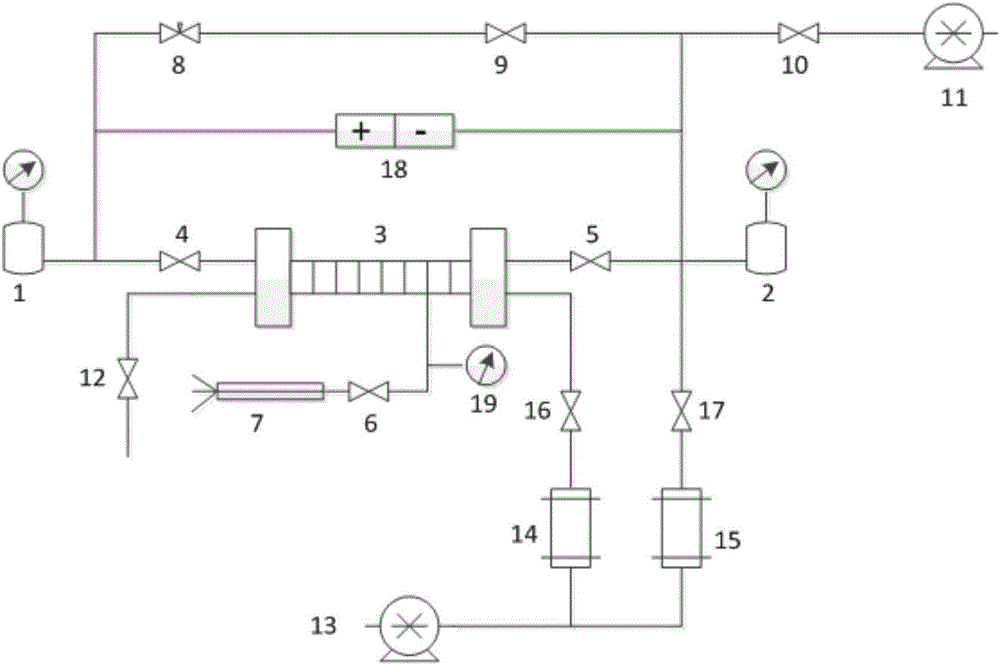
[0052] As shown in Figure 1, this embodiment discloses a device for evaluating the damage degree of the working fluid to the tight reservoir, which is used to evaluate the permeability (1.0-10 -5 )×10 -3 μm 2The degree of damage to the unconventional tight reservoir by the working fluid mainly includes the upstream standard chamber 1, the downstream standard chamber 2, the core holder 3, the confining pressure pump 7, the needle valve 8, the vacuum pump 11, the advection pump 13, the working fluid Intermediate container 14, formation water intermediate container 15, differential pressure gauge 18, confining pressure gauge 19. Wherein, the inlet of the core holder 3 is provided with a core holder inlet control valve 4, and the outlet is provided with a core holder outlet control valve 5; the outlet of the working fluid intermediate container 14 is provided with a working fluid intermediate container control valve 16, and the formation The outlet of the water intermediate cont...
Embodiment 2
[0090] my country's ×× Basin is rich in coalbed methane resources. In order to solve the problem of coal seam collapse in the development process, it is proposed to use a degradable polymer drilling fluid system. In order to test the damage degree of the drilling fluid to the coal seam of the XX mining area in the basin, the device and method of the present invention are used to conduct an evaluation experiment on the damage of the drilling fluid to the coal rock. At the same time, in order to understand the reliability of the experimental results, a comparative test is carried out using the conventional steady-state method . The device that present embodiment adopts is identical with embodiment 1, and the concrete steps of experimental method are as follows:
[0091] Step 1, drill the coal core, vacuumize for no less than 48 hours, and saturate the formation water of the target formation, the size of the coal core is as shown in the table
[0092] 1 shown;
[0093] Table 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0115] Block ×× is a low-porosity, low-permeability tight gas reservoir. After the gas well is drilled, it can only be established through fracturing. A clean fracturing fluid system is proposed to reduce the damage of fracturing fluid to the reservoir. In order to test the damage degree of the clean fracturing fluid system to the tight gas reservoir in the block, the device and method of the present invention are used to conduct a damage evaluation experiment. The device that present embodiment adopts is identical with embodiment 1, and the concrete steps of experimental method are as follows:
[0116] Step 1, drill the core, evacuate for not less than 48 hours, and saturate the formation water of the target formation, and the core size is shown in Table 5;
[0117] Table 5 × × block core size
[0118] Sample number
Length / cm
diameter / cm
LX-04
6.62
2.55
[0119] Step 2, put the core into the core holder 3, and apply the confining pres...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com