Method for detecting microbe quantity and drug content of semisolid preparation through near infrared spectroscopy
A technology of near-infrared spectroscopy and microbial quantity, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, individual particle analysis, particle and sedimentation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as quality accidents, long detection cycles, and out-of-control drug quality, and achieve the effect of non-destructive samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0035] 1. Sample and its reference value information
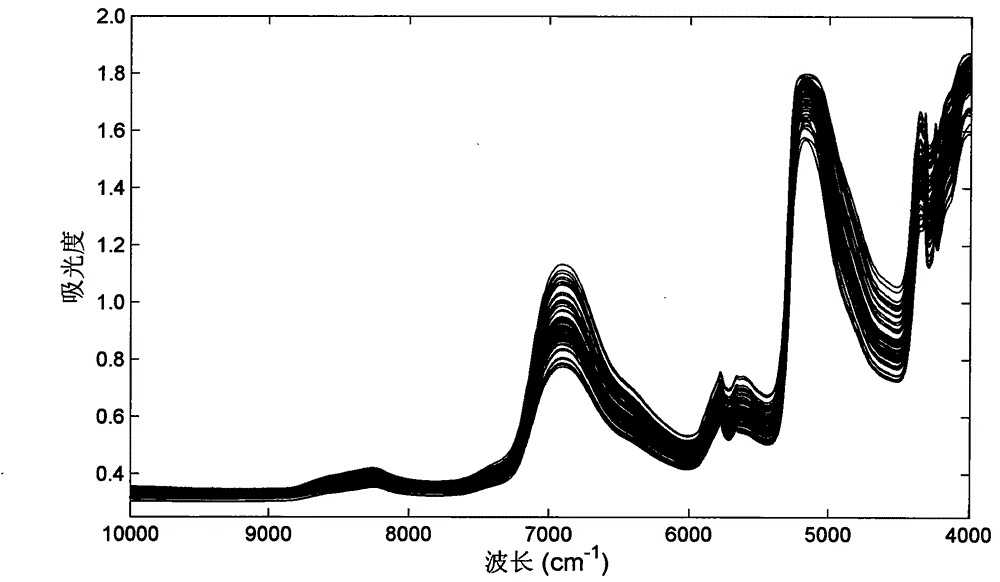
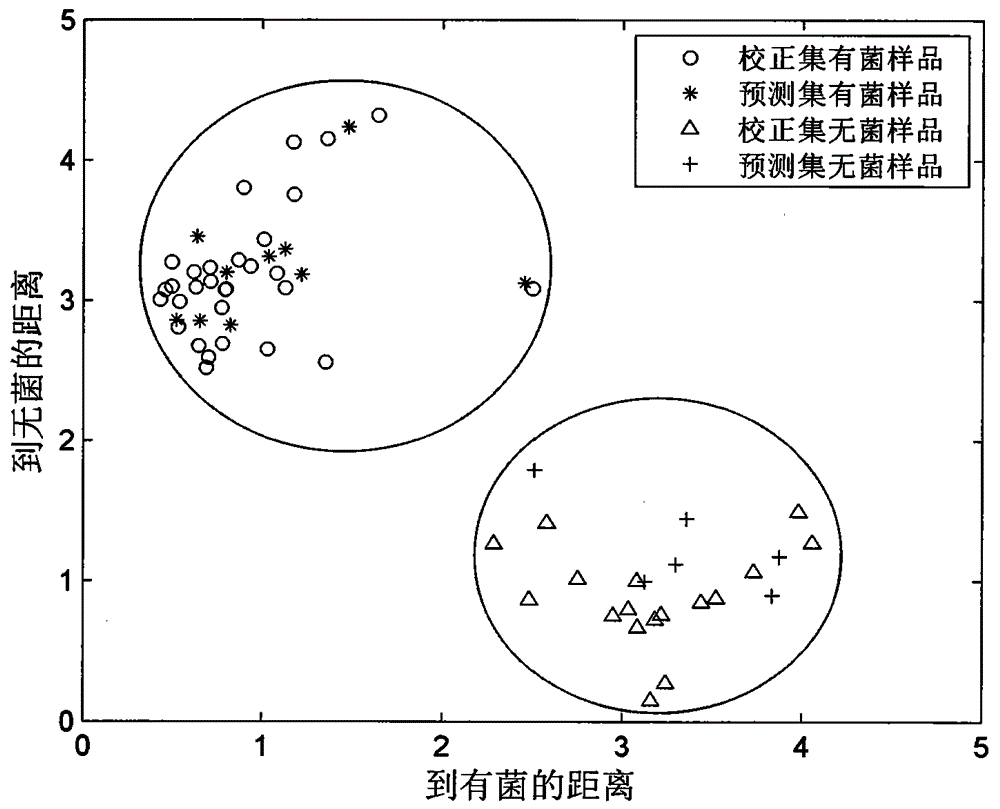
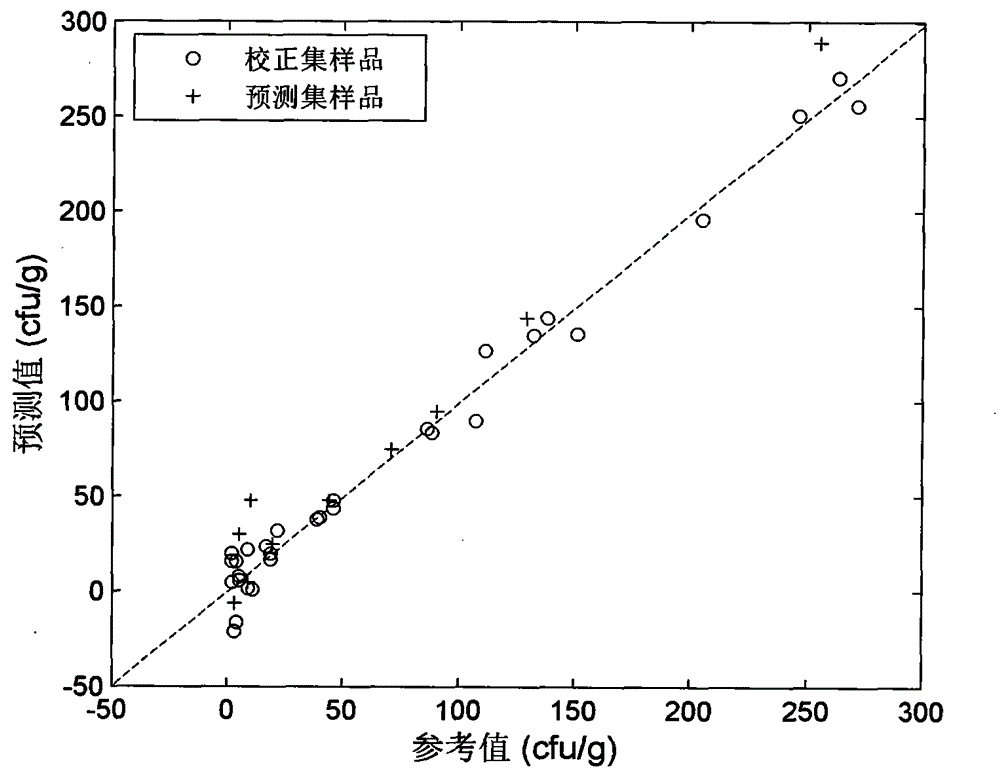
[0036] 63 tazarotene gel samples in aluminum packaging were entrusted to an authorized manufacturer to prepare by the standard addition method. The content of tazarotene in the samples ranged from 0.41 to 0.48 mg / g, which was equivalent to the labeled amount of commercially available samples (0.50 mg / g) of 82%-136%. In a standardized laboratory, 40 samples were taken, and about 5 g of tazarotene gel was extruded from an aluminum package on a sterile operating table, placed in a sterile transparent plastic ziplock bag, and added to Escherichia coli by standard addition method. Bacterial suspension, quickly sealed to prevent microbial contamination during the test, prepared 40 bacteria-contaminated samples, the number of Escherichia coli ranged from 2-271cfu / g; the remaining 23 samples were added with the same amount of sterile culture solution in the same way, Obtain a sterile sample.
[0037] 2. Measurement of near-infra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com