Manufacturing method of inversion structure of III semiconductor light-emitting device
A technology for light-emitting devices and manufacturing methods, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high etching holes, complicated processes, and high production costs, achieve simplified manufacturing processes, omit metal protective layers, and solve the problem of transparent conductive layers and Effect of line convex mesa pattern alignment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
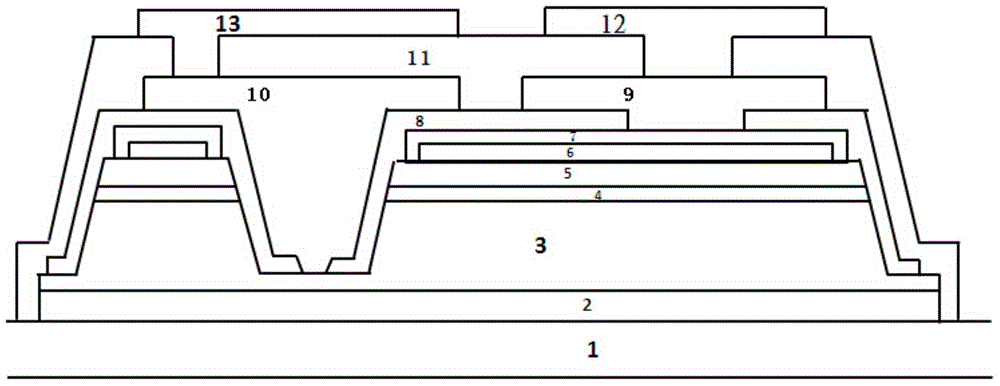
[0046] This embodiment provides a method for fabricating a flip-chip structure of a Group III semiconductor light-emitting device. For details, see Figure 2a-Figure 2g , including the following steps:
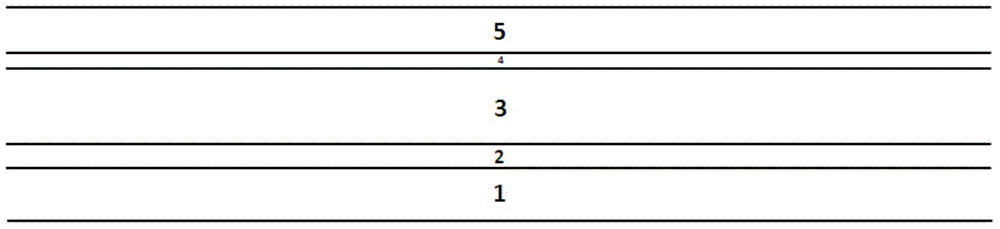
[0047] The first step: the structure diagram is as follows Figure 2a As shown, the method is to sequentially grow the substrate 1, the buffer layer 2, the n-type nitride semiconductor layer 3, the active layer 4, and the p-type nitride semiconductor layer 5 to form an epitaxial structure, and the epitaxial structure The upper surface of the upper surface is the upper surface of the p-type nitride semiconductor layer 5, and this structure is an epitaxial structure, which is obtained through the manufacturing process in the prior art. The method for making a flip chip on the epitaxial structure includes the following steps:
[0048] The second step: the structure diagram is as follows Figure 2b As shown, the method is to deposit a transparent conductive layer 14 on the upper...
Embodiment 2
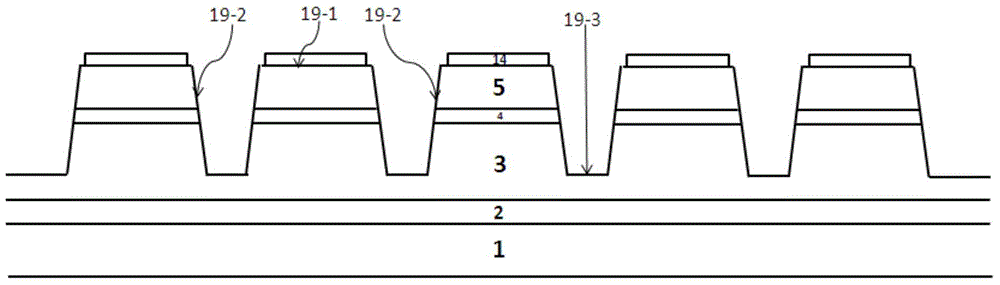
[0085] The new structure of the present invention adopts the technology of linear convex mesa 19 to replace the technology of multiple vias.
[0086] Such as Figure 3a Shown is a top view of a plurality of vias in the prior art, Figure 3b for Figure 3a Sectional view along the A-B direction.
[0087] Such as Figure 4a Shown is a top view of a linear convex table top, Figure 4b for Figure 4a Sectional view along the A-B direction.
[0088] The etched area of the line convex mesa 19 is single or multiple lines;
[0089] The substrate 1, the buffer layer 2, the n-type nitride semiconductor layer 3, the active layer 4 and the p-type nitride semiconductor layer 5 form a nitride semiconductor structure with a line convex mesa 19;
[0090] The linear convex mesa includes a first upper surface 19-1, a side surface 19-2 and a second upper surface 19-3, and the two ends of the first upper surface are respectively provided with the side surface and the second upper surface...
Embodiment 3
[0093] The lower end of the P-type wire electrode 15 is arranged on the surface of the first insulating layer structure 8-1 and on the transparent conductive layer 14 (such as Figure 5 shown).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com