A Method for Calculating Building Loads in Hot Summer and Cold Winter Regions Using Principal Component Decoupling
A technology of cooling load and heat load, applied in the field of building energy consumption calculation in regional distributed energy planning, which can solve the problems of large difference between design conditions, small gap between valley and peak, and inability to obtain parameters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
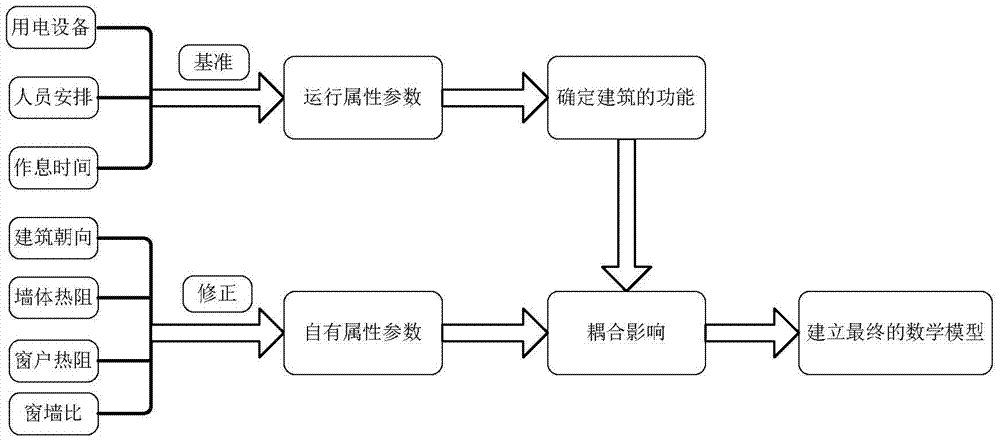
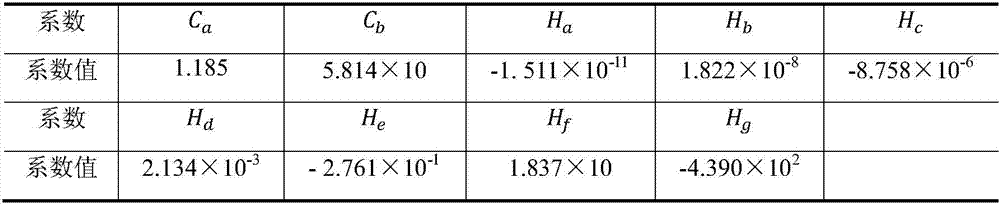
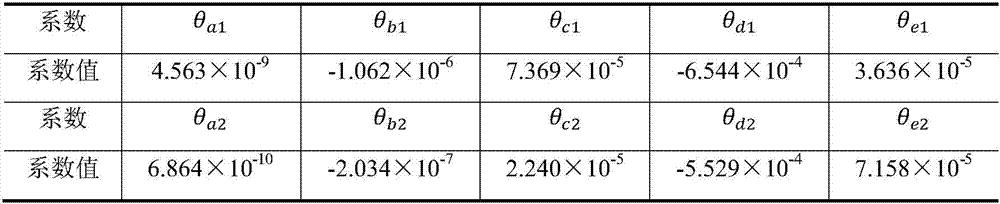
[0062] The invention provides a calculation method for determining the cooling and heating load of buildings in hot summer and cold winter regions by using the principal component decoupling method, and divides the factors affecting the cooling and heating load of buildings into two categories: the building's own attribute parameters and operating attribute parameters. The own property parameters include building orientation, wall and window material property parameters, window-to-wall area ratio, etc. When the building has been built, this type of data basically does not change, and they reflect the building's own attributes. The operating attribute parameters include the working hours of the building, personnel arrangements, indoor human comfort requirements, and indoor heat source disturbances such as various electrical equipment inside the building. In the actual use process, this type of data often changes with the change of user needs. They reflect the operating attribut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com