Non-corrosive liquid setting accelerator used in coal mine paste filling, and preparation method thereof
A paste filling and quick-setting agent technology, applied in the field of liquid accelerators, can solve the problems that the paste cannot fill the goaf by itself, the storage stability of the accelerator is not good, and the work of adding the accelerator is inconvenient, etc., to achieve Overcoming the effects of ultra-short setting time, mature filling technology, and improved filling efficiency of paste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] The preparation method of paste quick-setting agent comprises the following steps:
[0035] 1) Modification of liquid sodium aluminate: add 5-15% sodium carbonate to water to prepare a modifier, add sodium aluminate with an alumina content of 20-30wt% to the modifier, sodium aluminate and modified The mass ratio of the active agent is 12:1~5:1.
[0036] 2) The reaction between modified sodium aluminate and aluminum sulfate: add the modified liquid sodium aluminate prepared in step 1) dropwise to the aluminum sulfate solution with an alumina content of 12-16% to obtain a stable solution; The mass ratio of liquid sodium aluminate to aluminum sulfate solution is 1:2~1:4;
[0037] 3) Add 0.5~2% alcohol amine, stir evenly;
[0038] 4) Add 5~10% plasticizer and stir evenly to get the finished product.
[0039] In the step 1), the whole process of sodium aluminate modification needs to be carried out in not less than 1000S -1 It is carried out under high-shear stirring and...
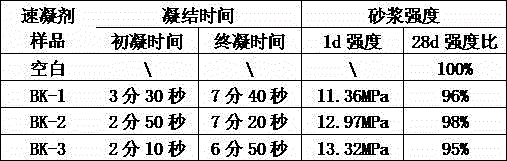
Embodiment 1
[0049] 1. Liquid sodium aluminate modification: under high shear stirring (1000S -1 ) state slowly add 50 parts of liquid sodium aluminate to 10 parts of 5% sodium carbonate. When the gel appears, add 25 parts of water, continue to add the remaining liquid sodium aluminate solution after the gel is dissolved, and continue to react for 1 hour to obtain modified liquid sodium aluminate L-1
[0050] 2. Reaction of modified sodium aluminate and aluminum sulfate: under high shear stirring (3000 S -1 ) state, slowly drop 100 parts of L-1 into 200 parts of aluminum sulfate solution with an alumina content of 16%, to prevent the formed aluminum hydroxide gel from agglomerating and agglomerating. The dropwise addition time was 30 minutes, and the temperature was controlled at about 20°C. After the dropwise addition was completed, the solution was slowly heated to 60°C and kept for 1 hour to obtain a yellow transparent liquid S-1.
[0051] Three, the deployment of accelerator:
[005...
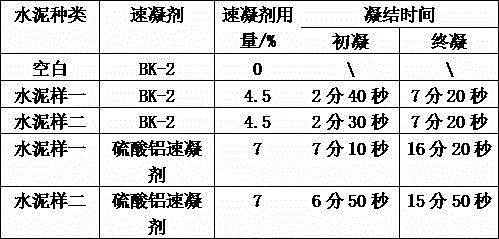
Embodiment 2
[0060] 1. Liquid sodium aluminate modification: under high shear stirring (1500S -1 ) state slowly add 80 parts of liquid sodium aluminate to 10 parts of 15% sodium carbonate. When the gel appears, add 25 parts of water, continue to add the remaining liquid sodium aluminate solution after the gel is dissolved, and continue to react for 2 hours to obtain modified liquid sodium aluminate L-2;
[0061] 2. Reaction of modified sodium aluminate and aluminum sulfate: under high shear stirring (4000 S -1 ) state, slowly drop 100 parts of L-2 into 400 parts of aluminum sulfate solution with an alumina content of 12%, to prevent the formed aluminum hydroxide gel from agglomerating and agglomerating. The dropwise addition time is 60 minutes, and the temperature is controlled at about 40°C. After the dropwise addition is completed, the solution is slowly heated to 80°C and kept for 2 hours to obtain a yellow transparent liquid S-2.
[0062] 3. Preparation of quick-setting agent: Add tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com