Surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide and preparation method thereof
A cemented carbide and alloy technology, applied in the field of surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide and its preparation, can solve the problems of difficult balance, adjustment and limitation of wear resistance and strength, hardness and toughness, etc., and achieve excellent mechanical properties and improve Red hardness, fine grain effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-33
[0028] Embodiments 1-33 provide a surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide and a preparation method of the surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide.
[0029] The mass percentage of each component of the alloy binder phase used in Examples 1-33 is shown in Table 1 below, and the mass percentage of each component used to prepare the surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide is shown in Table 2 below.
[0030] Table 1 Composition of different alloy binder phases used in Examples 1-33
[0031]
[0032]
[0033] Table 2 Components used to prepare surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide in Examples 1-33
[0034]
[0035]
[0036] The preparation method of the gradient cemented carbide of embodiment 1-33 comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Preparation of alloy binder phase
[0038] Weigh the powders that make up the alloy binder phase according to the mass percentage, put the powders in the omnidirectional planetary ball mill, and use cemented carbide gr...
Embodiment 34
[0048] This embodiment provides a surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide and a preparation method of the surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide.
[0049] The composition of the alloy binder phase, raw material powder and paraffin wax in this example is consistent with that of Example 15.
[0050] In the preparation method of this embodiment, the preparation of the alloy binder phase, the preparation of the blank, the pressing of the blank, and the pre-sintering are consistent with those of Example 15. The difference between this example and Example 15 lies in the sintering step, which is as follows:
[0051] Put the green body in the sintering furnace, raise the temperature to 1200-1250°C at a speed of 5-8°C / min, then fill the sintering furnace with nitrogen and raise the temperature to 1420-1450°C at a speed of 1-3°C / min, Keep warm for 80min and maintain a pressure above 0.2MPa; then cool down to 1000-1200℃ at a rate of 2-6°C / min, keep warm for 120min, and maintain a ...
Embodiment 15
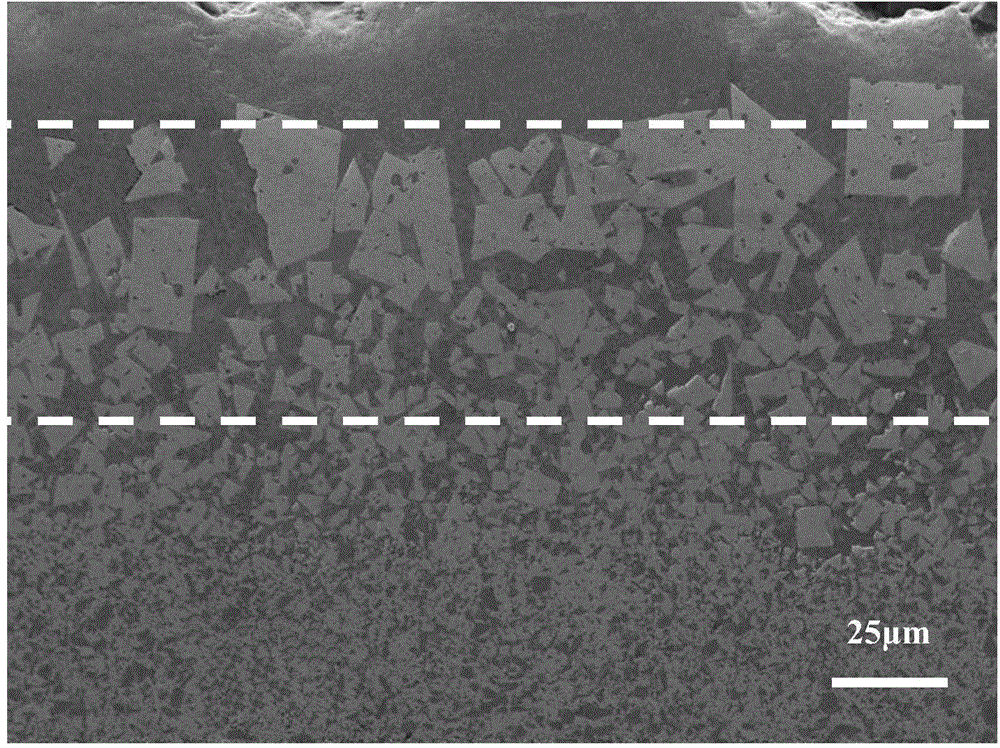
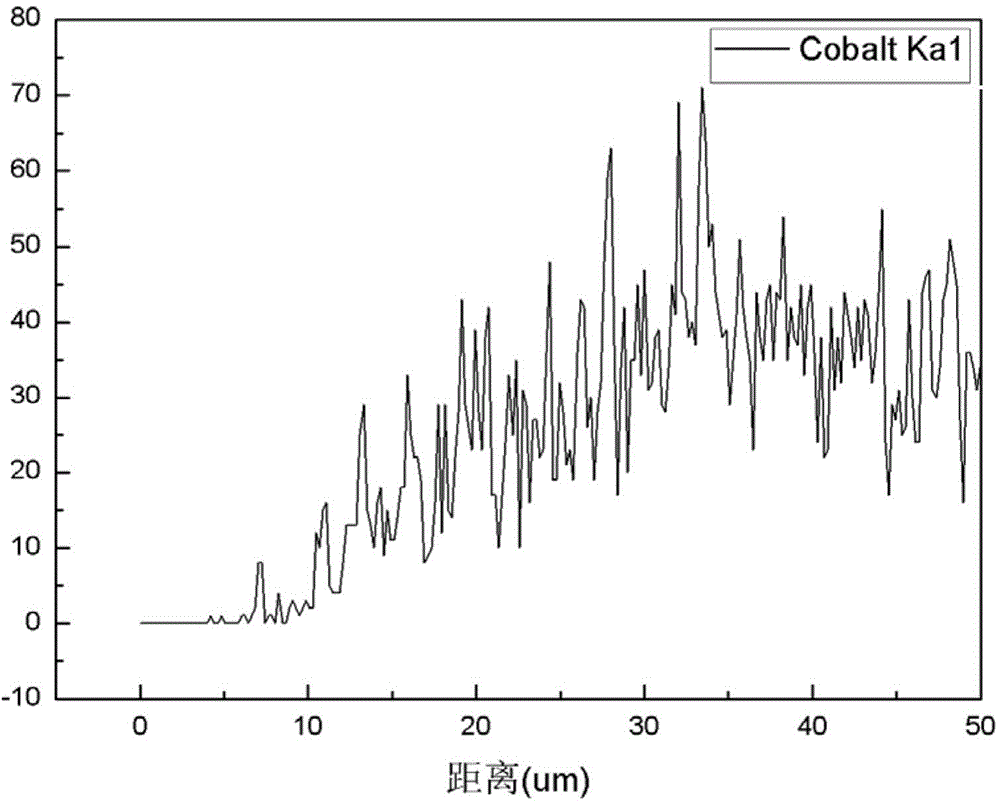
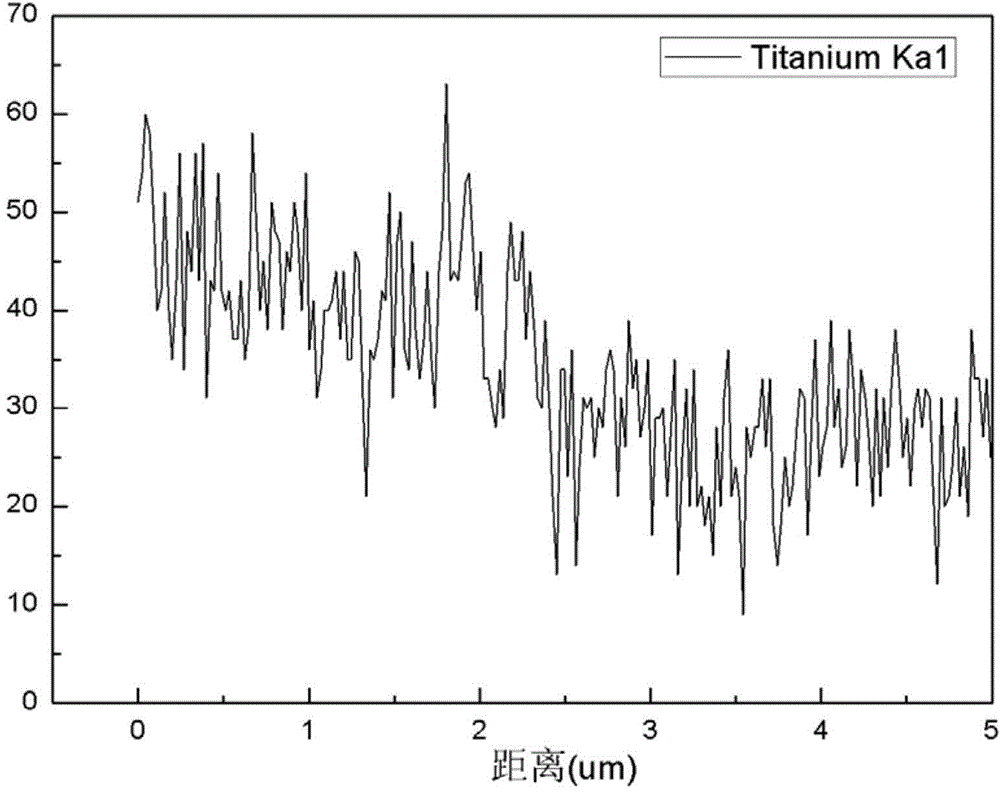
[0057] The cross-sectional microscopic morphology of the surface-hardened gradient cemented carbide HJ15 prepared in Example 15 is as follows figure 1 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that the cross section of the alloy is composed of surface layer, transition layer and internal layer; the surface layer is a region with a thickness of about 12 μm, followed by a transition layer with a thickness of about 50 μm, and the transition layer appears Abnormally grown WC grains, while the WC grains in the inner layer of the alloy are fine and evenly distributed. figure 2 is the line scan diagram of the Co content of the section of HJ15, image 3 is the line scan diagram of the Ti content of the section of HJ15 ( figure 2 with image 3 The "distance" in the middle abscissa refers to the vertical distance from the outer surface of the object to the scanning point). It can be seen from the figure that within 30 μm from the alloy surface, the Ti content of the alloy surface lay...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com