Effect of olive polyphenol on improving deterioration of aging-related movement function
A technology of olive polyphenols and motor function, which is applied in the field of improving effect of olive polyphenols on aging-related motor function decline, can solve the problem of no improvement effect of olive polyphenols on motor function decline, and achieve the effect of reliable research basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
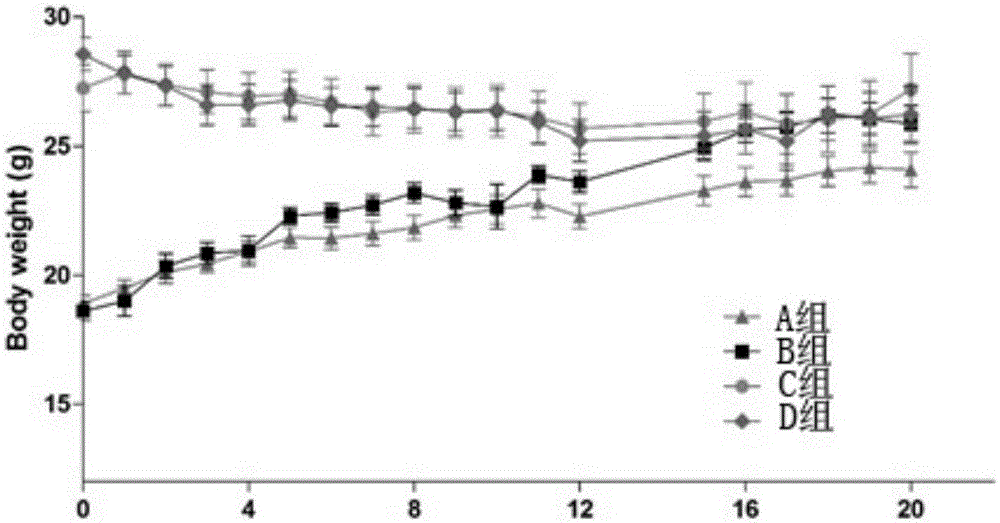
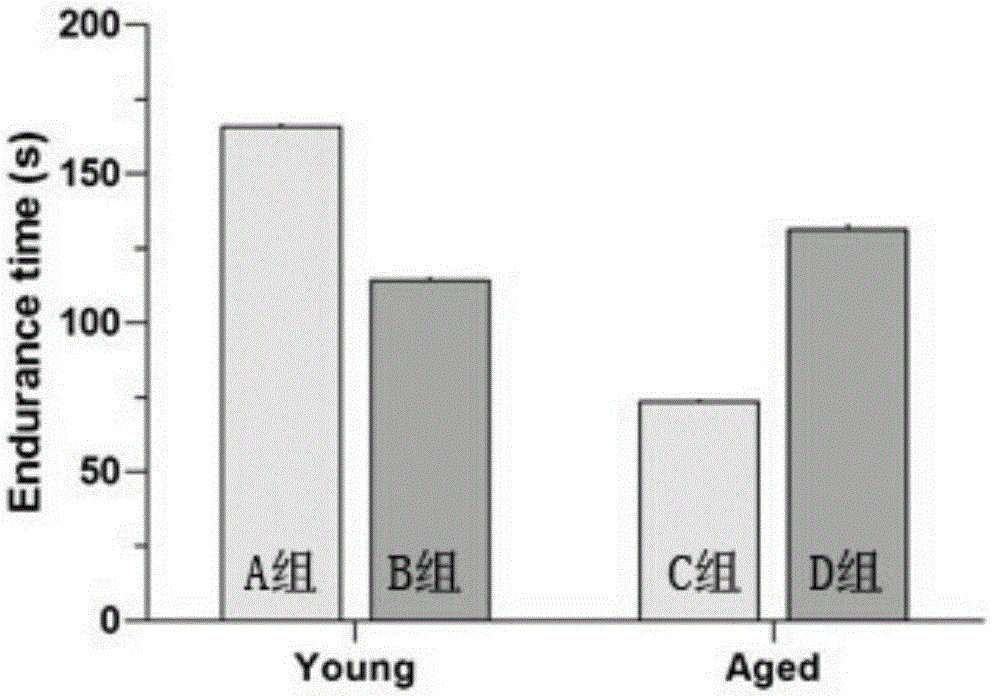
[0017] Male C57BL / 6J mice aged 2.5 months were randomly divided into two groups A and B, and male C57BL / 6J mice aged 15.5 months were randomly divided into two groups C and D. Among them, groups B and D were taken as the experimental group, and they were given olive polyphenol (HT-Ac aqueous solution) for intervention by intragastric administration; groups A and C were taken as the control group, and they were given corresponding volumes of water. The body weight and food intake of the experimental mice were monitored weekly, and the experiment lasted for 20 weeks. After 20 weeks of HT-Ac intervention, the mice were subjected to Rotarod performance test. The specific plan is shown in the table below:
[0018] group
number of mice
Starting month age
intervene
intervention dose
Group A - Young Group
15
2....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com