Microsatellite markers for identifying parent-child relationships of Chinese Simmental cattle and application of microsatellite markers
A technology of Simmental cattle and microsatellite markers, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve the problems of high detection cost, time-consuming, low repeatability, etc., and achieve the effect of improving detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Screening and determination of microsatellite markers for paternity identification of Chinese Simmental cattle
[0047] 1. Selection and grouping of microsatellite marker loci
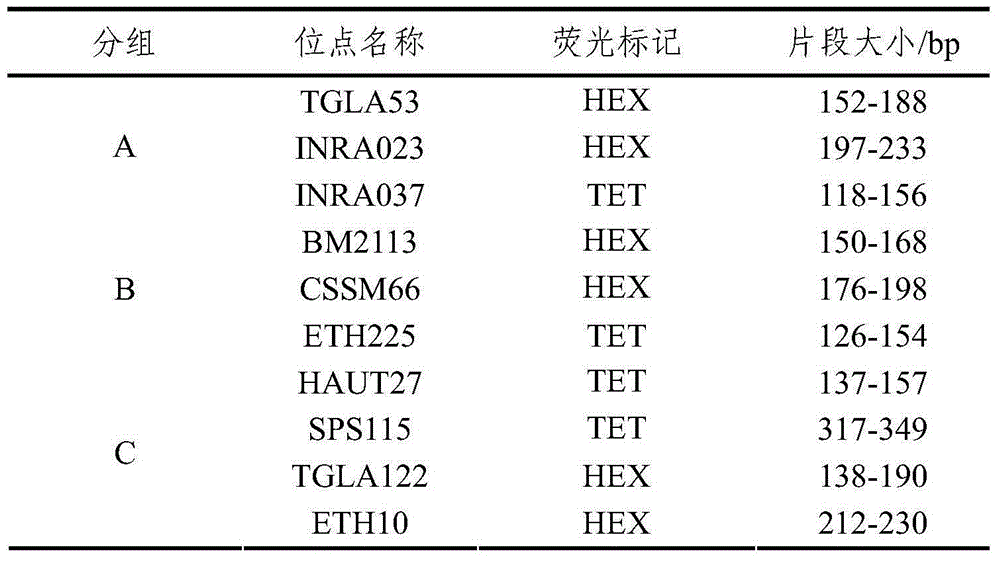
[0048] According to relevant reports of literature research, 14 microsatellite loci with 14 different chromosomes and high polymorphic information content in cattle were selected. The principle of selection is: rich alleles, high polymorphism, located on different chromosomes, no linkage relationship between each other, good repeatability, no "dumb alleles (NullAllele)" and so on. See Table 4 for details.
[0049] Table 414 Basic information of microsatellite loci
[0050]
[0051]
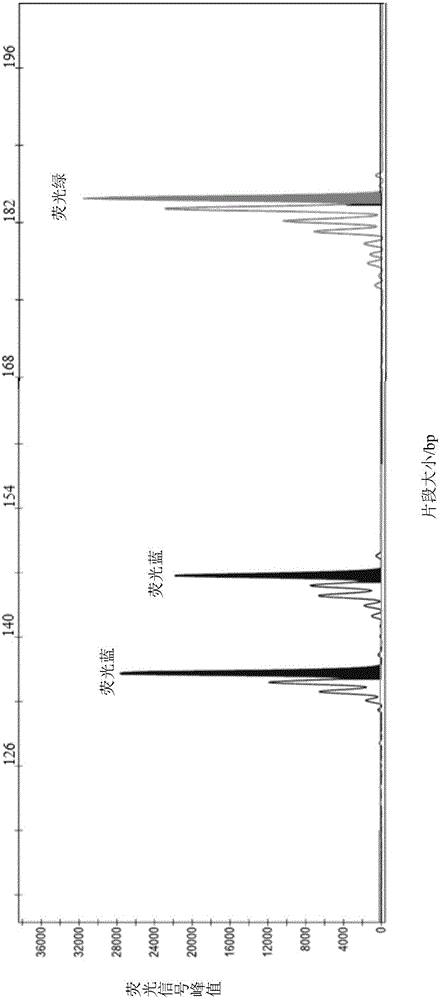
[0052] In order to reduce the detection cost of microsatellite genotyping, PCR products were mixed and grouped according to the fragment length of microsatellite markers and the fluorescent groups carried. In order to avoid non-specific band interference in the same group, the fluorescent colors i...
Embodiment 210
[0071] Application of Example 210 Microsatellite Markers in Identification of Parentage of Chinese Simmental Cattle
[0072] In this example, a father-son pair with a clear father-son relationship and an unrelated individual were selected from the Chinese Simmental cattle parent-child population for verification.
[0073] 1. Sample:
[0074] (1) Blood sample of offspring calf 19105102, No. 1;
[0075] (2) Frozen semen of the candidate male bull cow1171, No. 2;
[0076] (3) Frozen semen of candidate male bull 14_2620, No. 3.
[0077] 2. Identification requirements: DNA test, paternity test
[0078] 3. Inspection and results
[0079] The DNA of the sample to be tested was extracted, and after performing PCR amplification on 10 microsatellite genetic markers, it was detected on an ABI3730 automatic sequencer. The results are shown in Table 9.
[0080] Table 9 test results
[0081] site
number 1
number 2
number 3
[0082] TGLA53
162,...
Embodiment 310
[0085] Application of 310 microsatellite markers in the genetic improvement and breeding of Chinese Simmental cattle
[0086] 1. Sample:
[0087] Bull frozen semen, tube number 10008, sample number 1;
[0088] Bull frozen semen, tube number 20017, sample number 2.
[0089] 2. Identification requirements: DNA test, sample 1 and sample 2 consistency identification
[0090] 3. Inspection and results
[0091] The DNA of the sample to be tested was extracted, and after performing PCR amplification on 10 microsatellite genetic markers, it was tested on an ABI3730 automatic sequencer. The results are shown in Table 10.
[0092] Table 10 test results
[0093] site
number 1
number 2
TGLA53
162,166
162,166
BM2113
129,129
129,129
[0094] INRA023
206,207
206,207
TGLA122
150,154
150,154
CSSM66
188,199
188,199
ETH225
147,147
147,147
SPS115
333,337
333,337 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com