A kind of substituted urea herbicide residue degrading bacterial strain and its production
A herbicide and urea-substituting technology is applied in the field of substituted urea herbicide residual degrading strains and the inoculum produced therefrom, which can solve problems such as being difficult to remove, and achieves protection of health, low production and use costs, and good removal effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1, isolation and identification of bacterial strain
[0042] The invention provides a bacterial strain capable of efficiently degrading urea herbicides and the bacterial agent produced therefrom. The bacterial strain used is Gram-negative bacteria LR2014-1, which is isolated from the soil of a pesticide factory in Rudong, Jiangsu. The specific isolation and screening methods for strains are as follows:
[0043] Take 5.0g of soil sample and add it to 100ml of liquid inorganic salt medium (hereinafter referred to as MM) containing 0.2mM Liguron, culture it on a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm for 7 days, and transfer it to fresh In the same medium, four consecutive enrichment cultures were carried out. Dilute the fifth-generation enrichment solution on MM solid medium containing 0.2mM Ligulong, culture at 30°C for 5 days, pick a single colony on the plate and put it in 3ml liquid LB test tube medium, then save and transfer Into 20mL MM medium containing 0.2mM Rigur...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2, laboratory degradation experiment
[0046] 2.1 Preparation of seed solution
[0047] Insert the strain LR2014-1 into 100mL LB medium containing 0.2mM Liguron, cultivate it on a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm, collect the bacteria by centrifugation at 6000rpm after 48h, wash the bacteria twice with MM, and finally resuspend with 10mL MM , as a seed solution for later use.
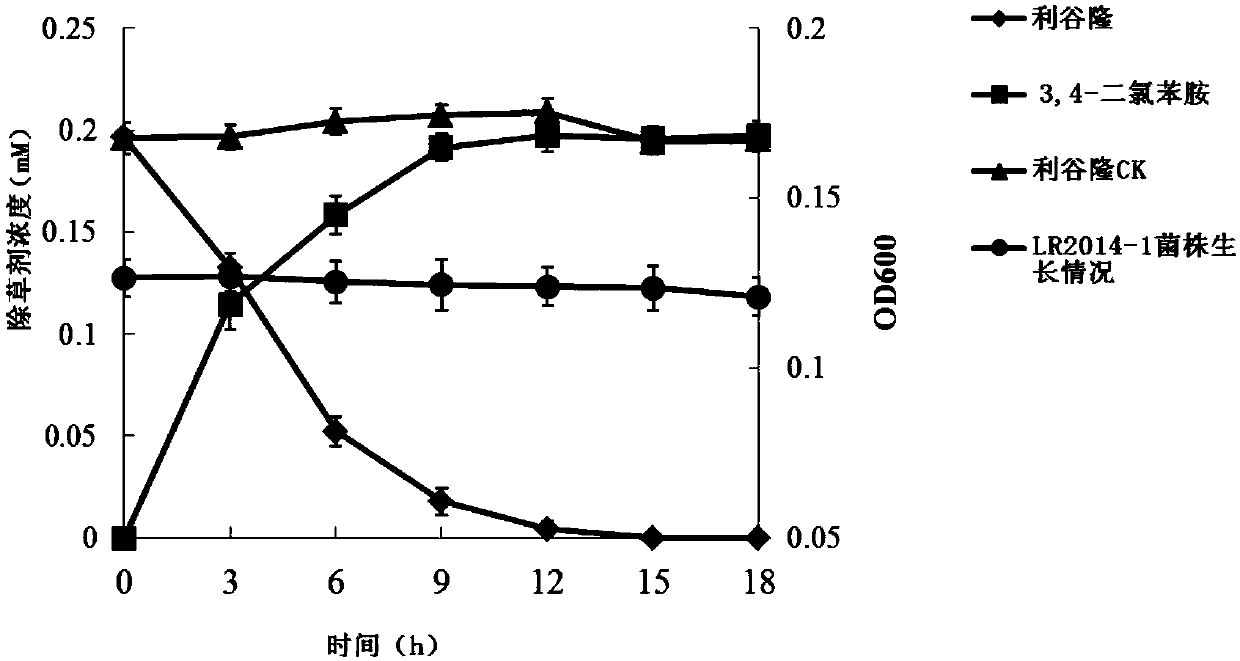
[0048] 2.2 Degradation of the herbicide Liguron by strain LR2014-1
[0049] The strain LR2014-1 was inoculated into 100mL MM containing 0.2mM Liguron at 5% inoculation amount, cultured on a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm, and 5mL was sampled every 3 hours for up to 24 hours. The residual amount of Riguron was detected, the degradation rate was calculated, and the time-degradation curve of strain LR2014-1 to Riguron herbicide was drawn. Such as figure 2 , strain LR2014-1 can completely degrade 0.2mM Riguron within 24h.
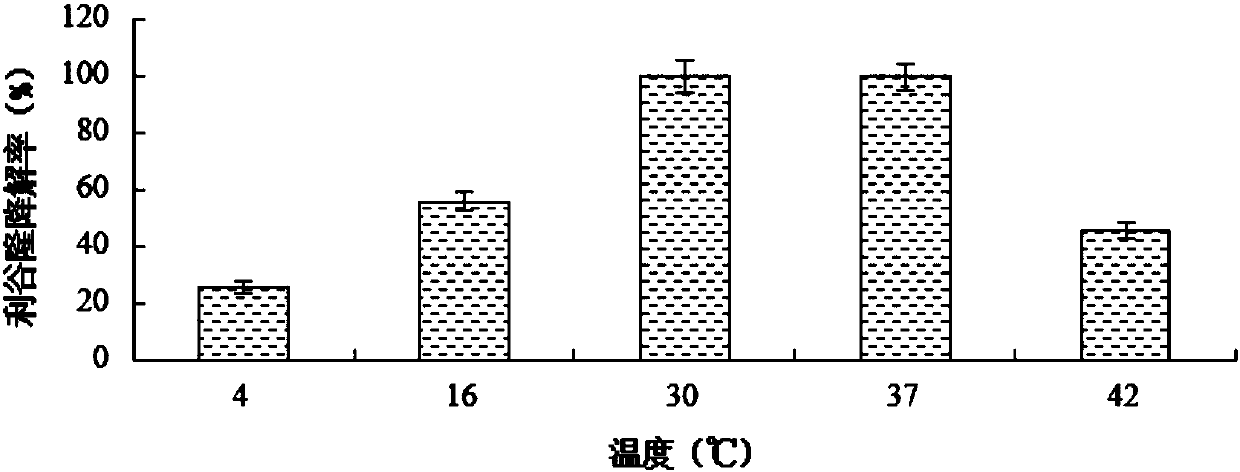
[0050] 2.3 Effect of temperature on degradation of Ligulong by strain LR...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3, soil degradation experiment
[0067] The vegetable garden soil was taken as the test soil sample. Pass the soil sample through a 2mm sieve, take a certain amount of Liguron, Diuron and Propannil powders and dissolve them in 10mL of methanol, and then soak in diatomaceous earth to completely absorb the pesticides. The soaked diatomaceous earth is placed in a fume hood to dry, and it is mixed into the soil so that the concentration of the pesticide in the soil is about 2mg / kg. 500g of each soil sample was cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C, and the inoculum was inserted into the seed solution at an inoculation amount of 10%, and the soil without inoculation was used as a control, and the water holding capacity of the soil was maintained at 60%. After culturing for 7 days, the residual amount was determined by HPLC. The measurement results are shown in Table 3.
[0068] It can be concluded from Table 3 that after 7 days of cultivation, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com