Alternative-boost-buck-circuit-based voltage equalizer
A technology of buck-boost circuit and voltage balancer, which is applied in the direction of instruments, electrical components, and adjustment of electric variables, etc. It can solve the problems of large current ripple, increased cost of voltage balancer, large filter capacitor, etc., and achieves the goal of reducing the size Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
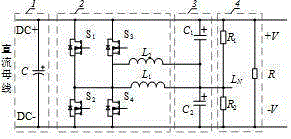
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, a voltage balancer based on an interleaved buck-boost circuit includes a DC link 1, a bidirectional interleaved buck-boost converter 2, an output filter circuit 3 and a load 4, and the bidirectional interleaved buck-boost converter 2 The positive terminal and the negative terminal are respectively connected to the positive potential link DC+ and the negative potential link DC- of the DC link 1, the common terminal of the bidirectional interleaved buck-boost converter 2 and the capacitor common terminal of the output filter circuit 3 The connection constitutes the neutral line and thus constitutes the distribution form of the bipolar busbar.
[0028] The DC link 1 includes a positive potential link DC+, a negative potential link DC- and a decoupling capacitor C , the decoupling capacitor C The anode and cathode are connected across DC+ and DC- respectively.
[0029] The bidirectional interleaved buck-boost converter 2 is composed of a first ...
Embodiment 2
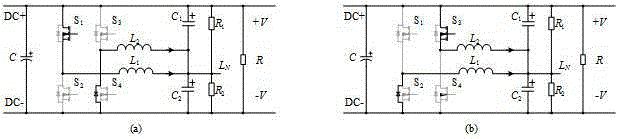
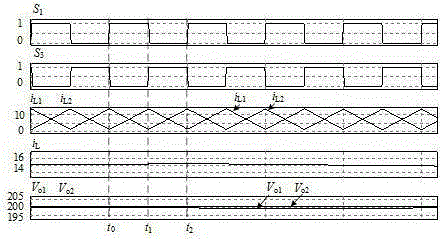
[0033] Combine below Figure 2-9 The specific working principle of this preferred embodiment is described: (the balancer based on the bidirectional interleaved buck-boost circuit adopts complementary PWM drive mode for interleaving control, the control signal of the first phase buck-boost circuit and the control signal of the second road buck-boost circuit The signals differ by 180o. Then the first switch tube S 1 and the third switching tube S 3 The drive signal difference of 180o, then the second switch tube S 2 and the fourth switching tube S 4 The difference between the drive signals is 180o; the first switch tube S 1 and the second switch tube S 2 The driving signals of the are complementary and have a certain dead zone, the third switch tube S 3 and the fourth switching tube S 4 The drive signals are complementary and have a certain dead zone. )
[0034] Such as figure 2 Shown, for this preferred embodiment load R 1 >R 2 , and the equivalent circuit diagram...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com