Methods for analyzing blood to detect diseases associated with abnormal protein aggregation
A protein aggregation and protein technology, applied in proteomics, analytical materials, disease diagnosis, etc., can solve problems such as invasive, expensive, and unable to withstand high-throughput analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
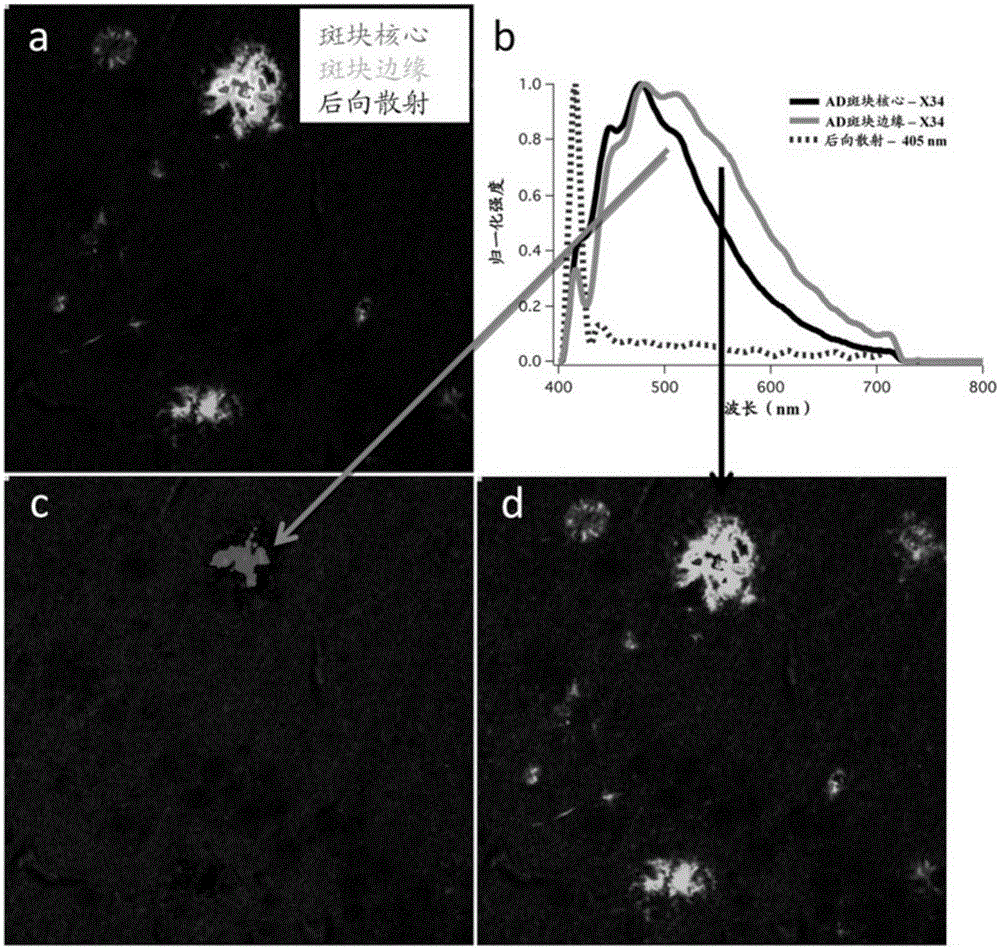
[0140] Example 1. Detection of Alzheimer's disease from blood using fluorescence spectroscopy
[0141] Many neurological diseases, such as AD, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease and prion diseases, are associated with the misfolding and aggregation of proteins from their soluble functional state into highly ordered fibrous assemblies with high β-sheet content. These pathologically unrelated diseases have in common a specific binding to the classic amyloid probe, Congo red, and are therefore termed "Congo red-ophilic" diseases. Conformational-sensitive fluorescent probes that specifically bind amyloid fibrils have been widely used to investigate protein aggregation (Styren et al., 2000; Klunk et al., 2002; Mathis et al., 2002; Aslund et al., 2009; Nilsson et al., 2005; Hammarstrom et al., 2010). Some newer probes have the additional property of detecting soluble oligomer species and altering their emission spectra based on the protein aggregates to which they bind, and ...
Embodiment 2
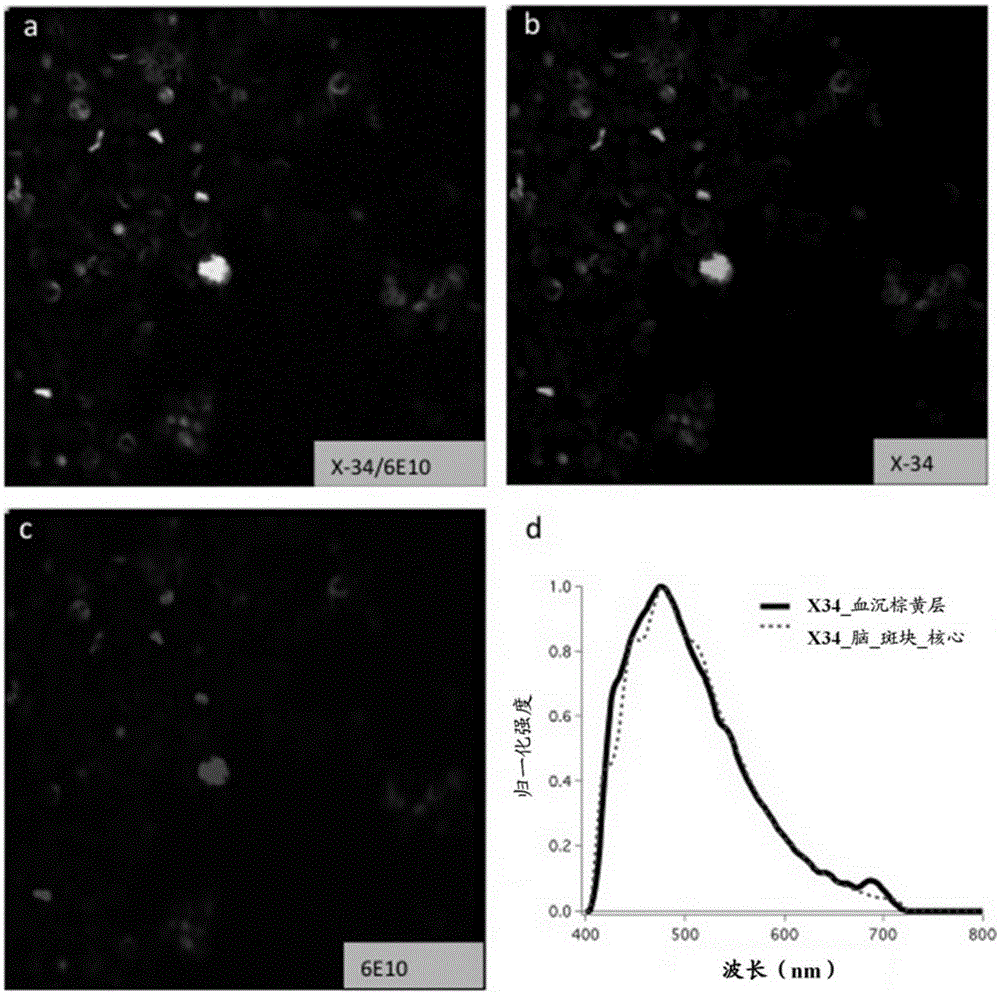
[0148] Example 2: Detection of protein aggregates in leukocytes using probe K114
[0149] Protein aggregates were detected in human leukocytes using the fluorescent probe K114, an amyloid-specific dye and an analog of Congo red. In addition, the fluorescent signal from labeled leukocytes is processed using an algorithm (e.g., an algorithm based on the Levenberg-Marquardt damped least squares nonlinear curve fitting algorithm) to separate the disease-specific signal from background and autofluorescence emission . Fluorescent emission-based counts are calculated, reflecting the likelihood that the test cell sample originated from a patient with a disease associated with abnormal protein aggregation.
[0150] Program
[0151] Blood was drawn from the patient into EDTA tubes and kept on ice. The buffy coat (white blood cells) was isolated using standard techniques. Briefly, the blood samples were centrifuged at 1700 RCF at room temperature to remove a band of concentrated leuk...
Embodiment 3
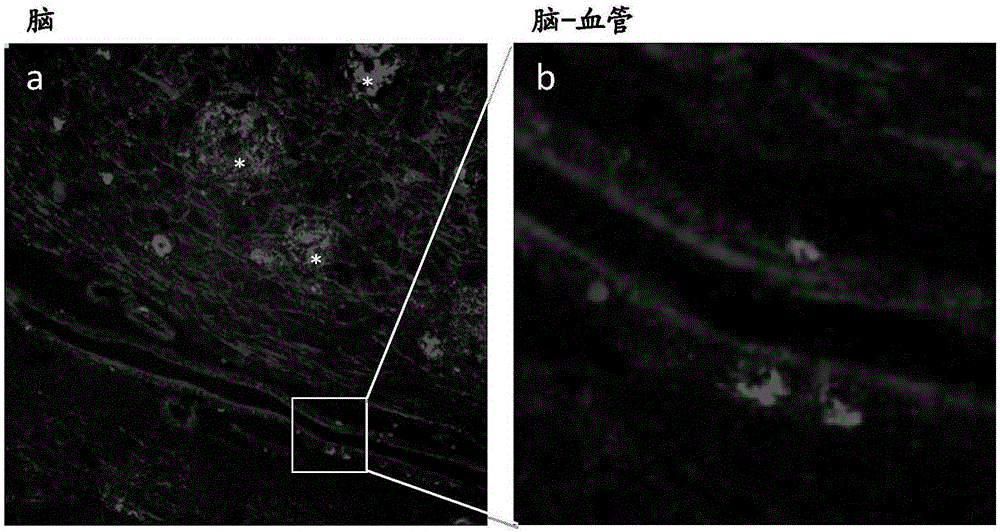
[0163] Example 3. Presence of amyloid in the brains of MS patients
[0164] AD is generally considered to be a neurodegenerative disorder with secondary innate inflammation, but the perspective on multiple sclerosis is less clear. Initially, the evidence strongly supported a primary autoimmune disorder, the resulting inflammatory attack triggering demyelination and cortical atrophy. However, recent data from detailed pathological examination and experience with effective anti-inflammatory treatments cast doubt on this conclusion (Stys et al., 2012).
[0165] Thus, the possibility exists that MS may also be a primary degenerative disorder, with an unusually prominent inflammatory secondary response. So what could be the root cause of MS? Whereas the pathology of later chronic MS (in which the inflammatory response is less prominent) shows the development of demyelinating lesions over time (possibly spreading from discrete foci in plaques?), the pathology of the periventricula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com