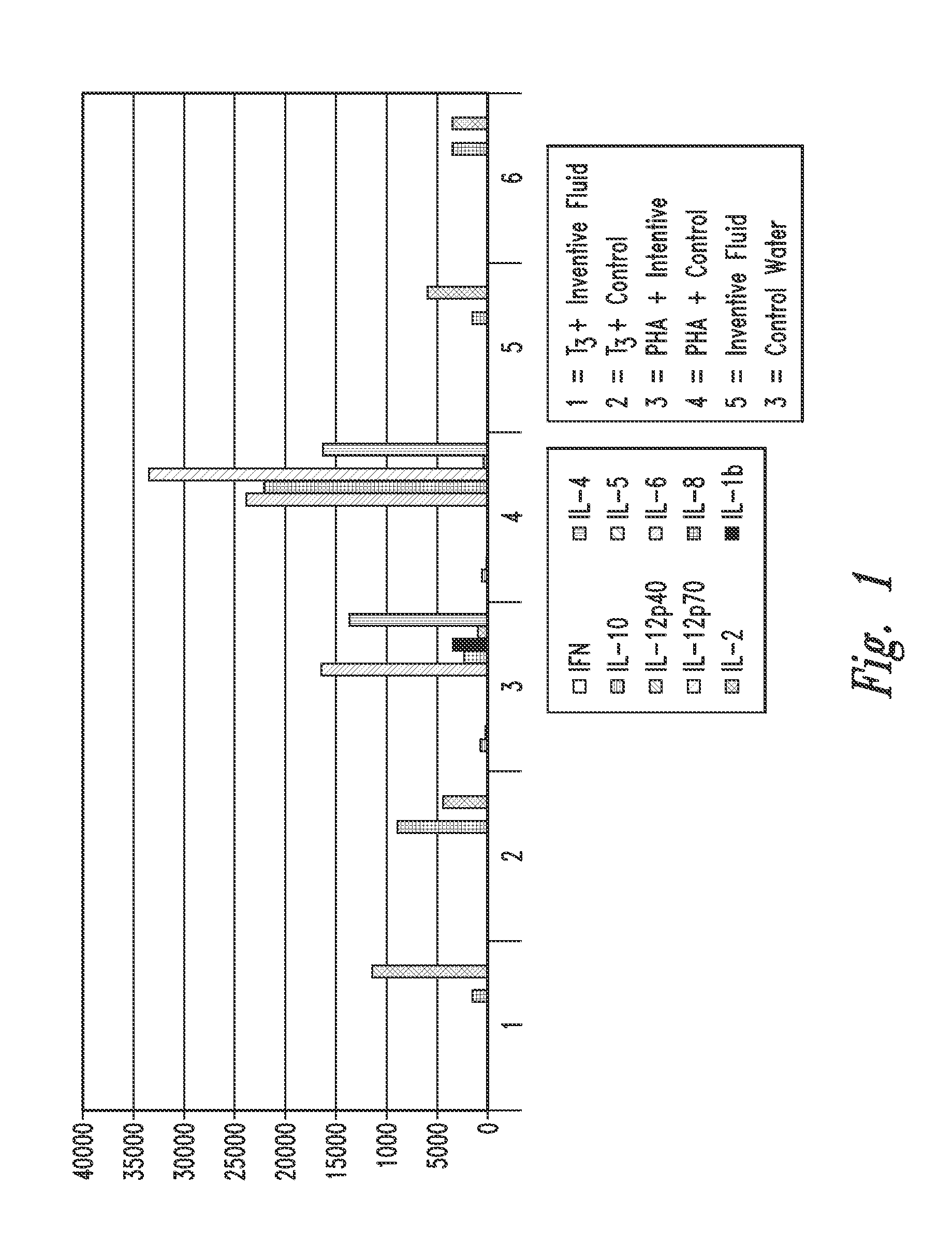
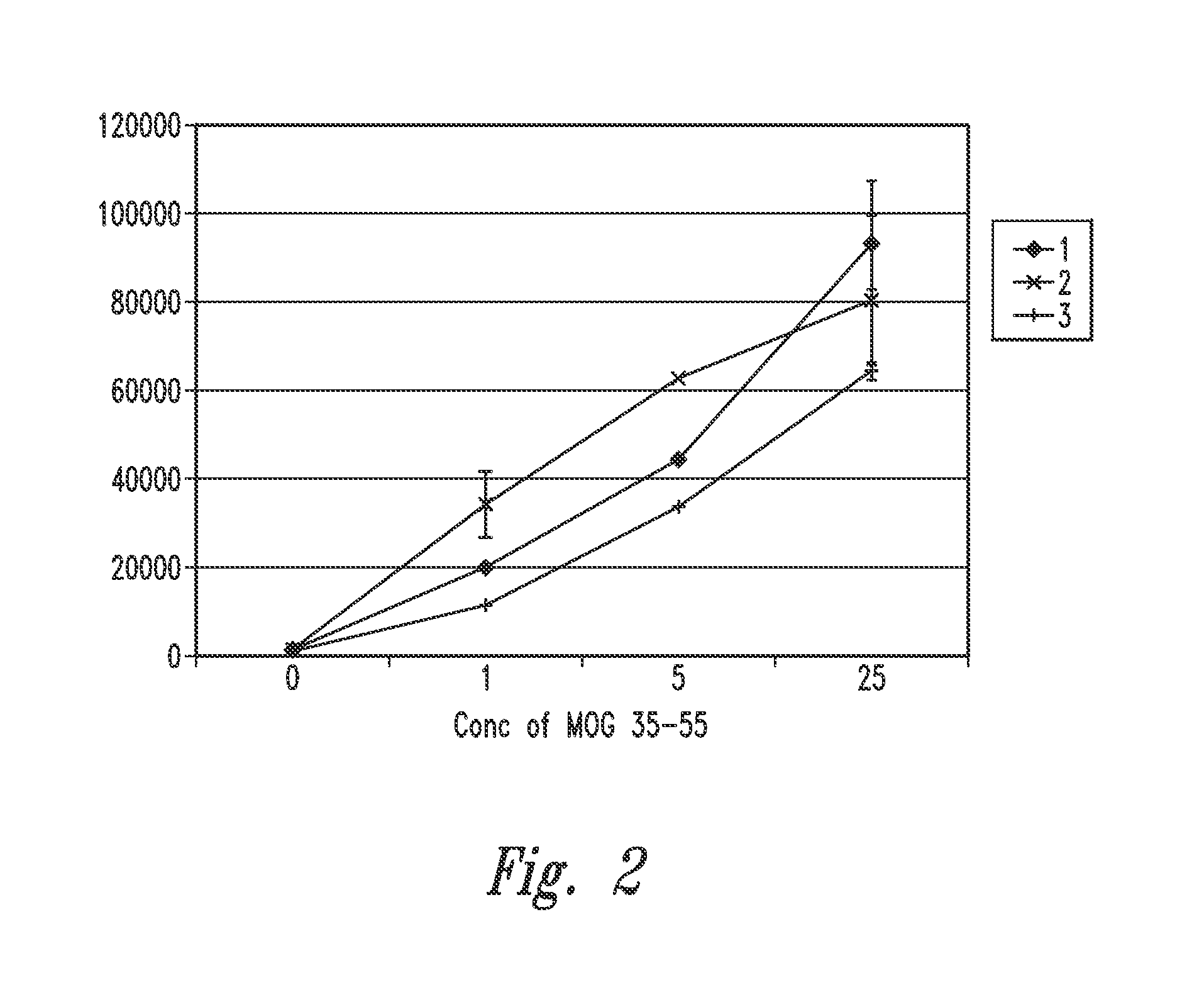
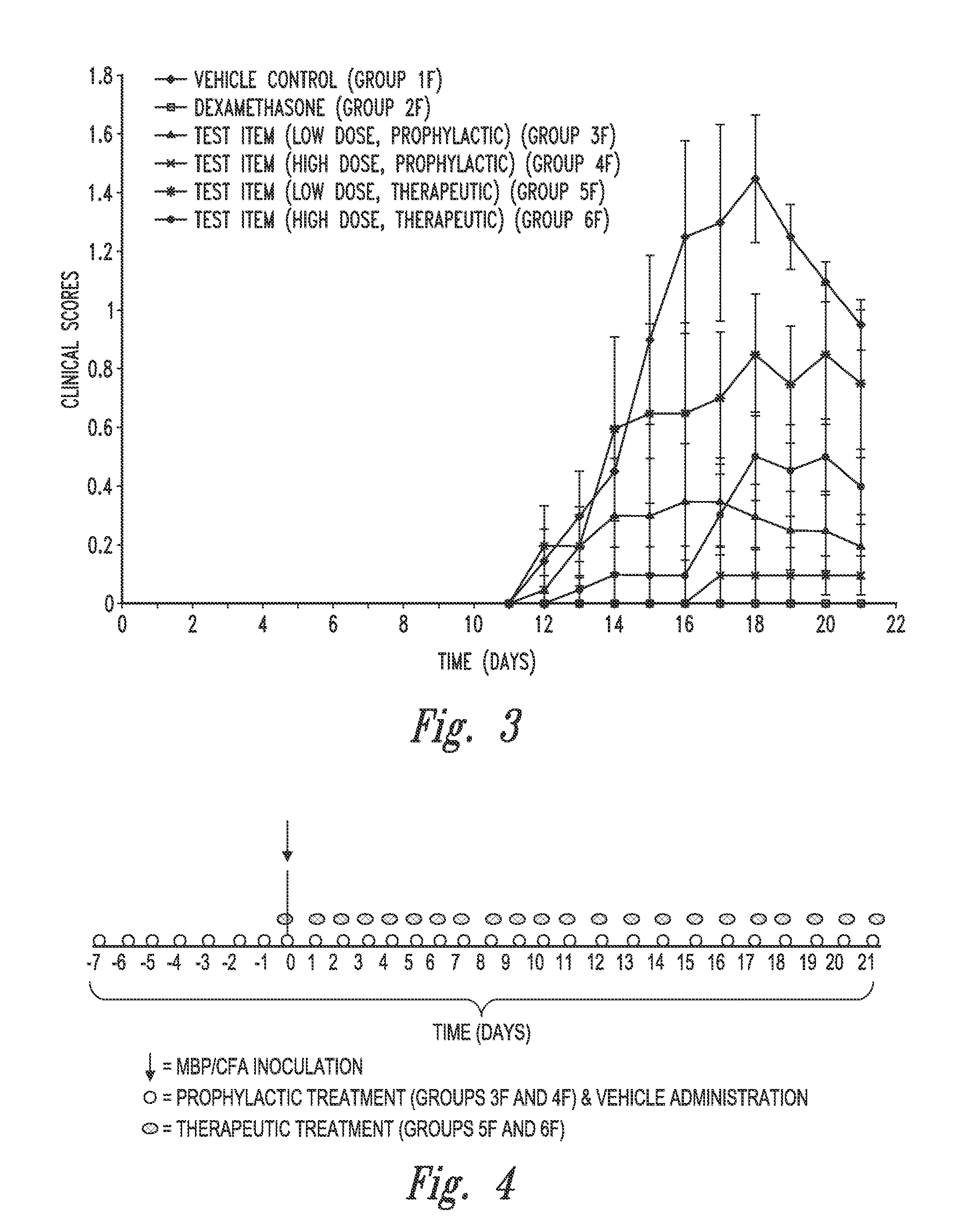
Patents
Literature
411 results about "Minimal cognitive impairment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI), also known as incipient dementia and isolated memory impairment, is a neurological disorder that occurs in older adults which involves cognitive impairments with minimal impairment in instrumental activities of daily living.
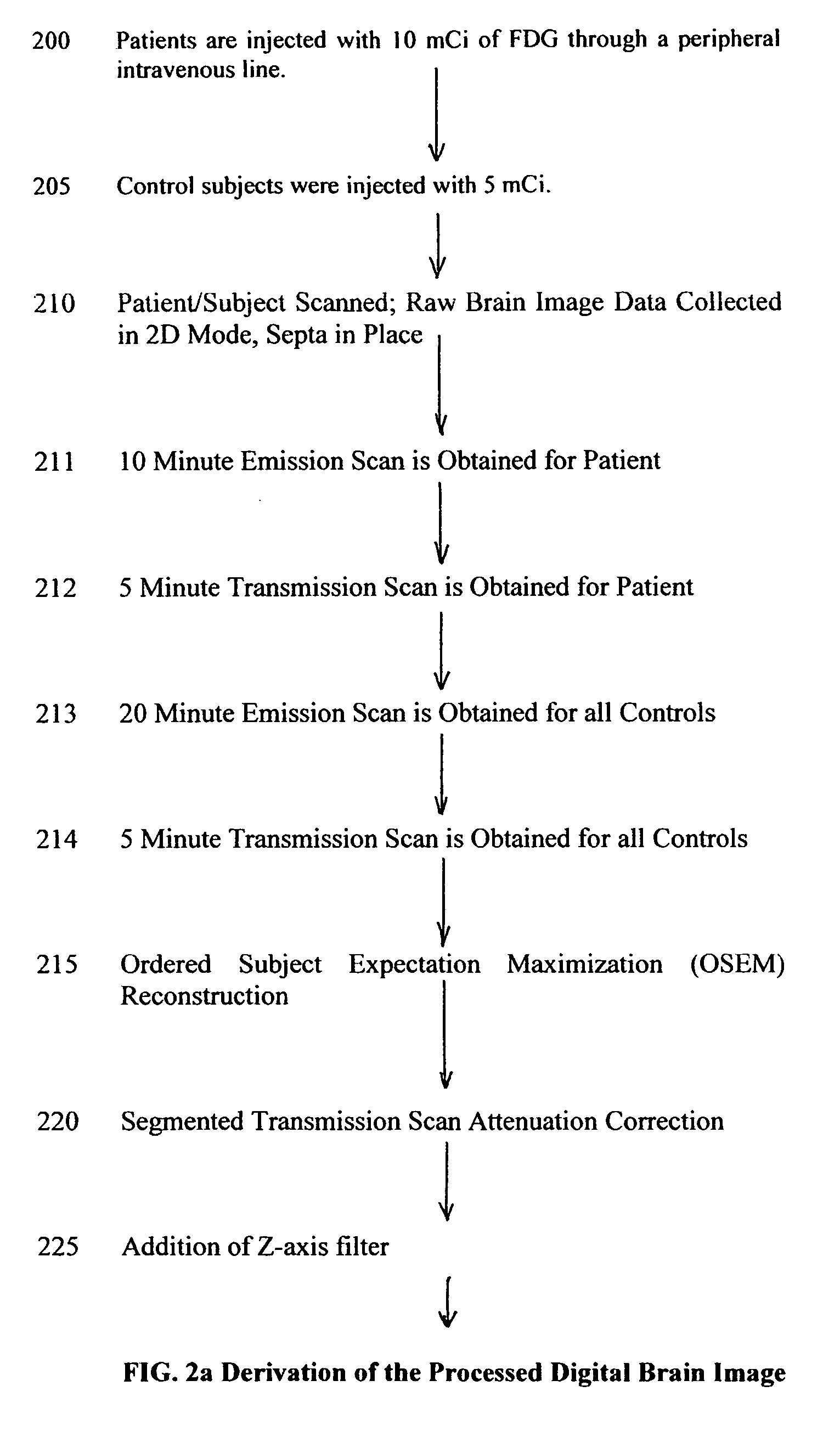
Methods for using pet measured metabolism to determine cognitive impairment
InactiveUS20050215889A1High sensitivityEarly detectionImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringNervous systemNon invasive
A non-invasive, early stage method to obtain quantitative measures of mild cognitive impairment useful in diagnosing and following degenerative brain disease or closed head injuries by utilizing the image data from individual patient positron emission tomographic scans to construct a cognitive decline index that serves as a diagnostic and screening tool to reveal the onset of mild cognitive impairment and nervous system dysfunction which are sequelae of degenerative brain diseases and closed head injury. The method involves using weighted values of brain region intensities derived from comparing scans of normal subjects to a scan of the patient to calculate a cognitive decline index that is useful as a diagnostic tool for mild cognitive impairment. The weights for the intensity values for each region are derived from the differences of intensity values from regions of the brain of the patient selected by comparing the patient to normal control subjects.
Owner:THE BIOMEDICAL RES FOUND OF NORTHWEST LOUSNA
Compositions and methods for improving or preserving brain function
InactiveUS20070179197A1Improve performancePrevent and reduce delayBiocideNervous disorderRegimenExercise performance
The present invention is related to mammalian nutrition and effects thereof in individuals with age associated cognitive decline such as Age Associated Memory Inpairment (AAMI) or a dementing illness such as Alzheimer's disease or related dementia, or Mild Cognitive Impairment, such as improving performance in, or reversal, prevention, reducing and delaying decline in, one or more of cognitive function, memory, behavior, cerebrovascular function, motor function, and / or brain physiology are seen. In particular, the present invention utilizes medium chain triglycerides, in one embodiment, administered as part of a long-term treatment regimen, to preserve or improve learning, attention, motor performance, cerebrovascular function, social behavior, and to increase activity levels, particularly in aging mammals.
Owner:ACCERA INC
Use of glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors
ActiveUS20090068699A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Percent Diameter Stenosis
An inhibitor of a glutaminyl peptide cyclotransferase, and use thereof for the treatment and / or prevention of a disease or disorder selected from the group consisting of inflammatory diseases selected froma. neurodegenerative diseases, e.g. mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, neurodegeneration in Down Syndrome, Familial British Dementia, Familial Danish Dementia, multiple sclerosis,b. chronic and acute inflammations, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, restenosis, pancreatitis,c. fibrosis, e.g. lung fibrosis, liver fibrosis, renal fibrosis,d. cancer, e.g. cancer / hemangioendothelioma proliferation, gastric carcinomas,e. metabolic diseases, e.g. hypertension,f. and other inflammatory diseases, e.g. neuropathic pain, graft rejection / graft failure / graft vasculopathy, HIV infections / AIDS, gestosis, tuberous sclerosis.Additionally disclosed are a respective diagnostic method, assay and kit.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Methods and compositions for diagnosis, stratification, and monitoring of alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders in body fluids
InactiveUS20060094064A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Body fluid
The inventors have discovered a collection of proteinaceous biomarkers (“AD biomarkers) which can be measured in peripheral biological fluid samples to aid in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorders, particularly Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The invention further provides methods of identifying candidate agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease by testing prospective agents for activity in modulating AD biomarker levels.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
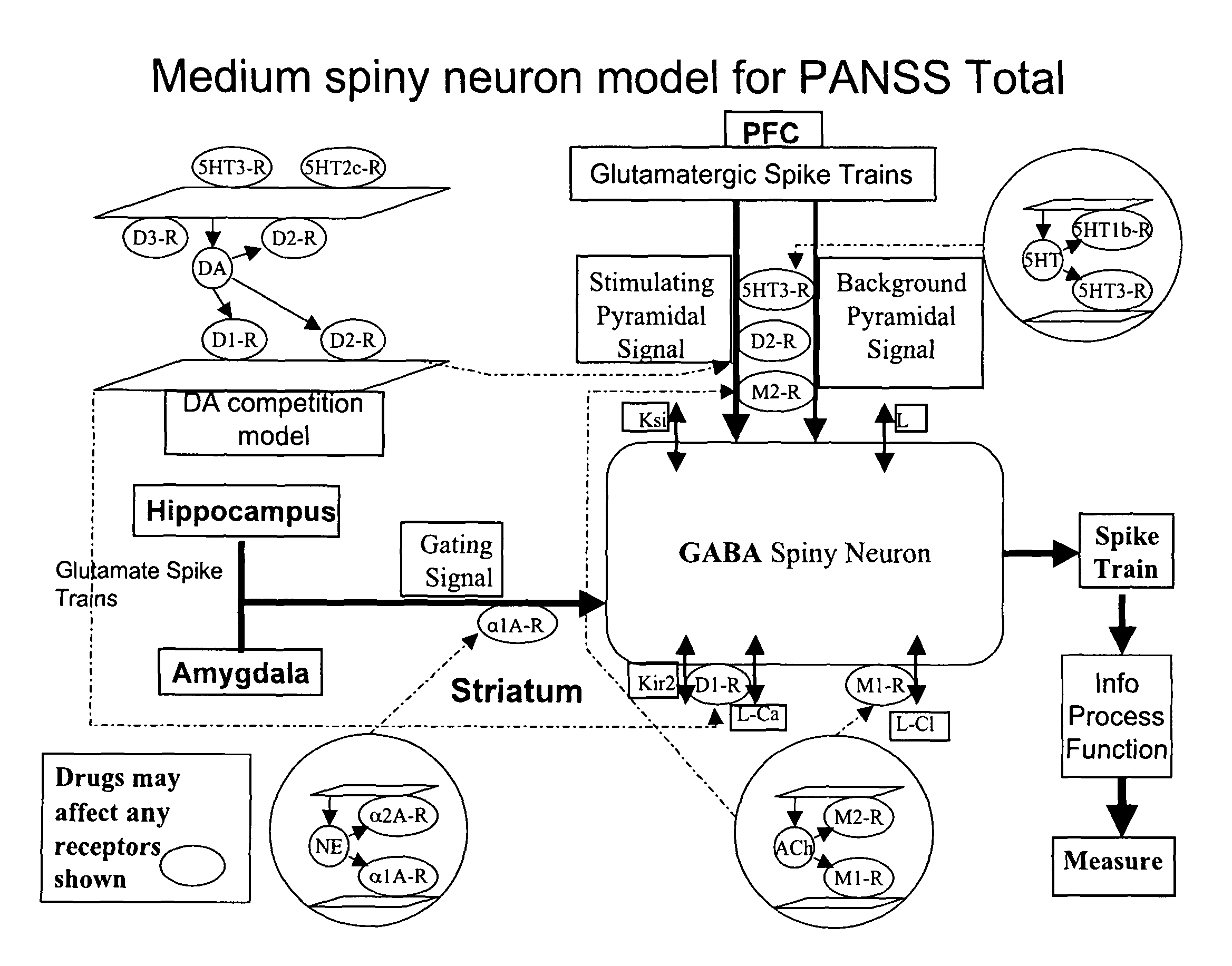
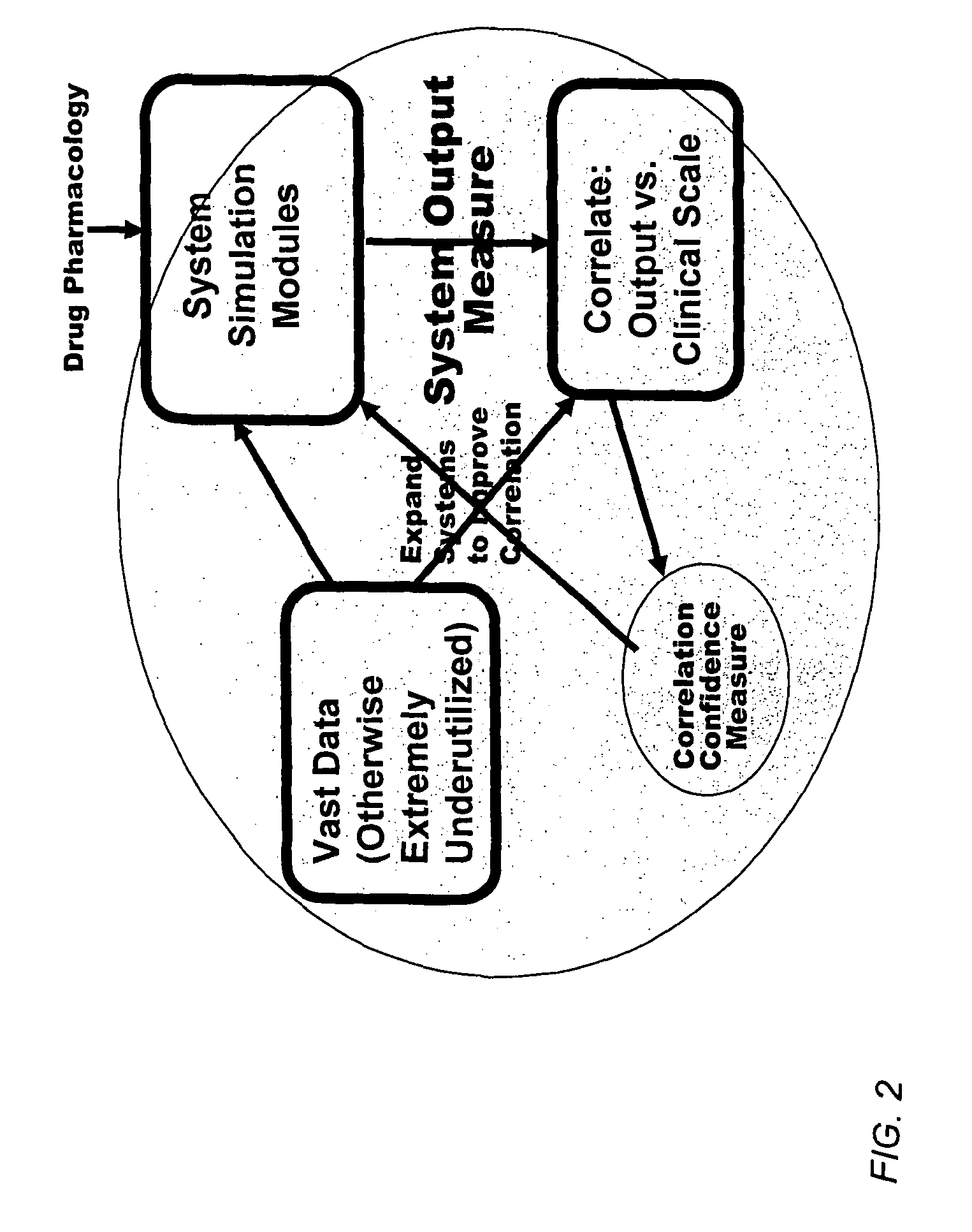
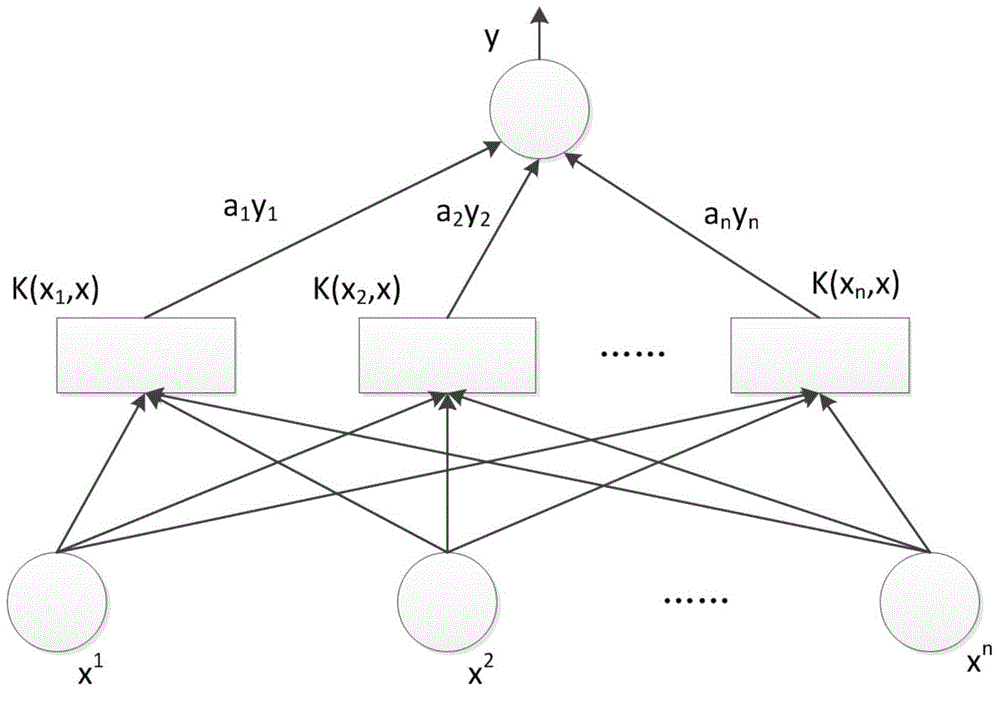
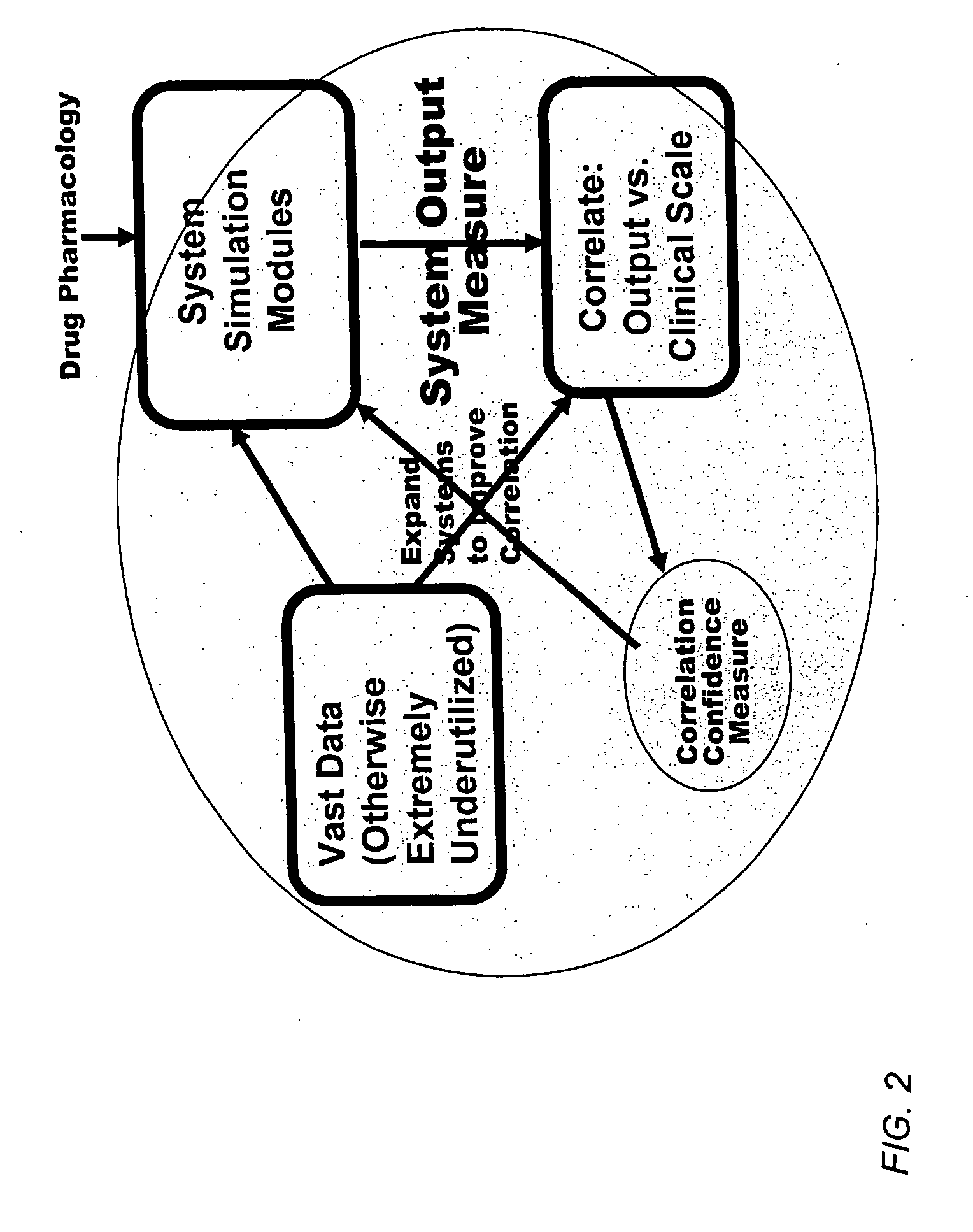
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases
ActiveUS8150629B2Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserAmygdala
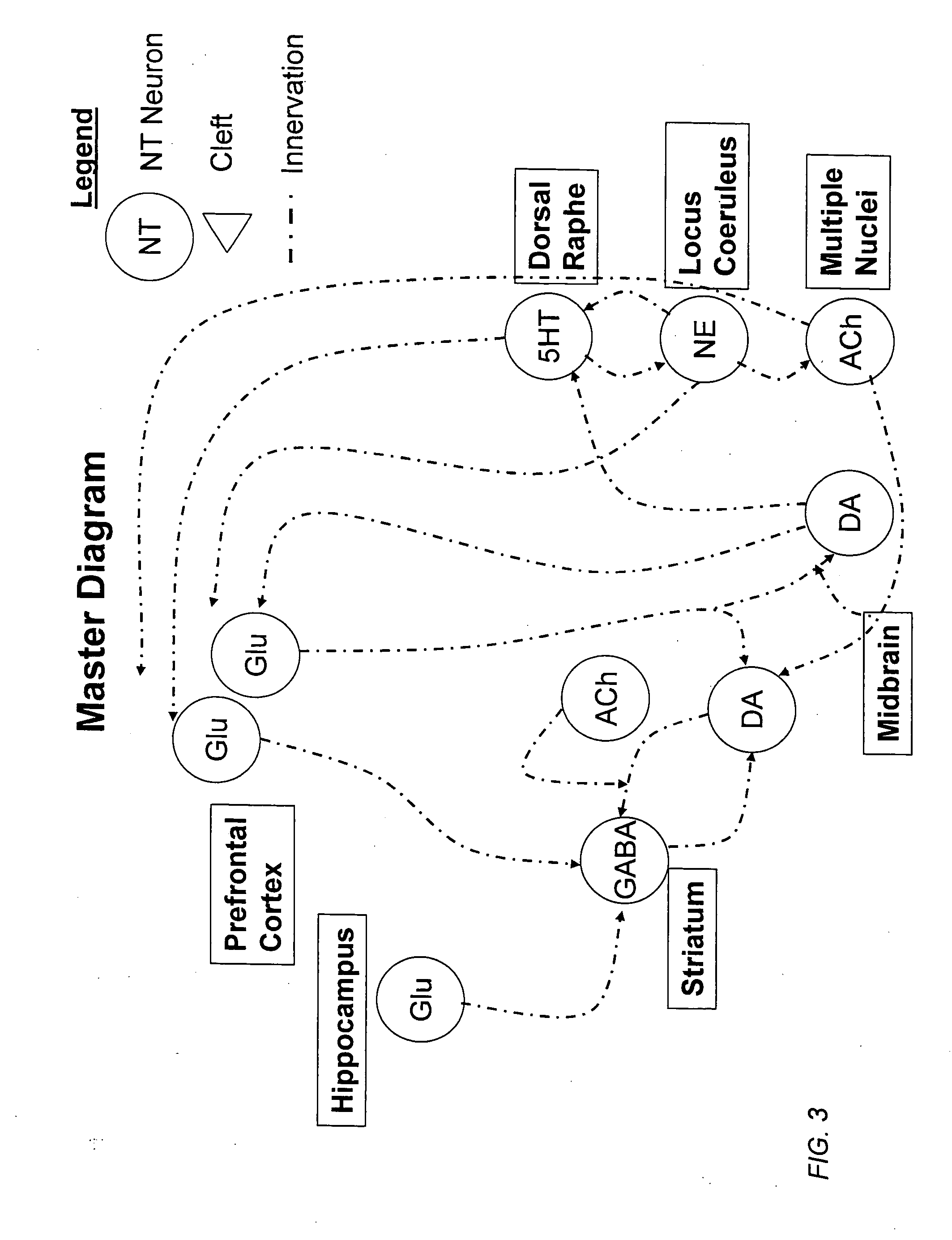
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases on one or more clinical scales. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. The computer model preferably uses the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, as well as certain mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
Methods to facilitate transmission of large molecules across the blood-brain, blood-eye, and blood-nerve barriers
InactiveUS7629311B2Reduce deliveryImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTrendelenburg positionGolimumab
A method for delivering a biologic to a human with Alzheimer's-related dementia, comprising administering the biologic parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human's head below the horizontal. The method further includes delivering a TNF antagonist to the brain of a human for treating mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's related dementia, or vascular dementia, comprising administering the TNF antagonist golimumab parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human in a Trendelenburg position, for delivery of the golimumab to the brain via the human's vertebral venous system.
Owner:EDWARD LEWIS TOBINICK M D
Novel compounds for the treatment of neurological disorders
The present invention relates to novel inhibitors of prolyl endopeptidase of formula 1 W—KCONH—X—CON—Y—CO—Z (1) wherein K, W, X, Y and Z are specified in the description. The compounds are useful for the treatment of diseases such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome, Parkinson disease and Chorea Huntington.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Method for extracting and fusing time, frequency and space domain multi-parameter electroencephalogram characters
ActiveCN104586387AEfficient extractionAll-round extractionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSingular value decompositionFunctional disturbance
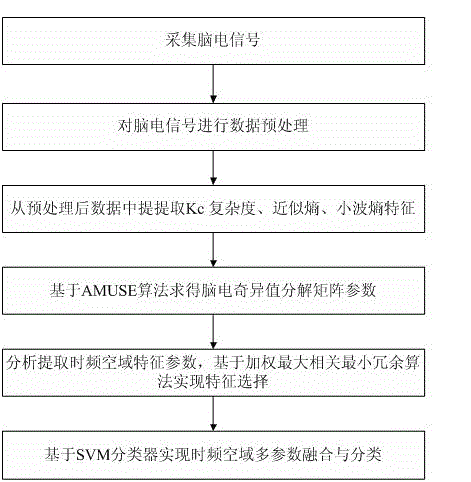
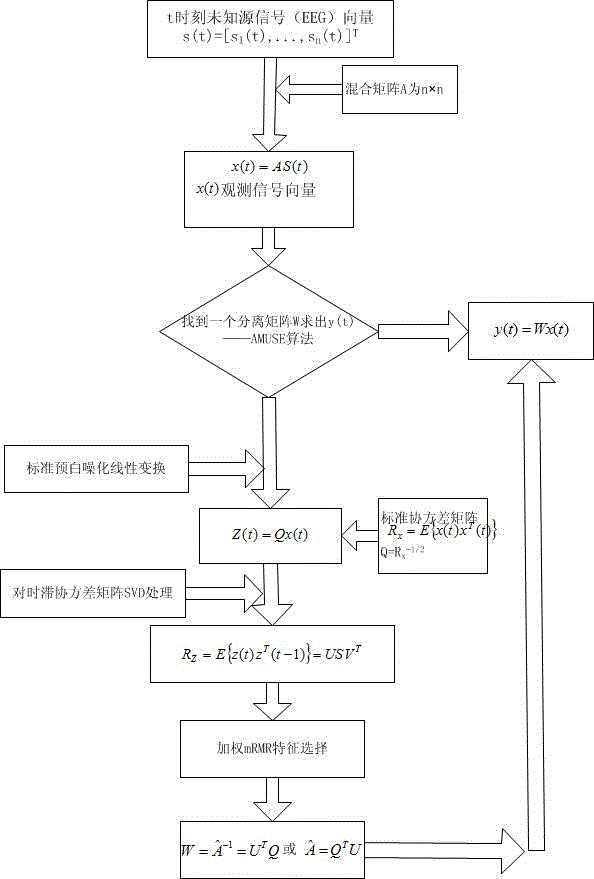
The invention relates to a method for extracting and fusing time, frequency and space domain multi-parameter electroencephalogram characters, which comprises the following steps: 1) collecting an electroencephalogram signal; 2) performing data pre-processing on the electroencephalogram signal; 3) extracting Kc complexity, approximate entropy and wavelet entropy from the pre-processed data; 4) on the basis of AMUSE algorithm, acquiring an electroencephalogram singular value decomposition matrix parameter; 5) performing character selection on the time, frequency and space domain character parameters for the extracted Kc complexity, approximate entropy, wavelet entropy and electroencephalogram singular value decomposition matrix parameters; 6) utilizing a SVM classifier to fuse and classify the four parameters of the time, frequency and space domains after the character selection. According to the method provided by the invention, the Kc complexity, the approximate entropy, the wavelet entropy and the electroencephalogram singular value decomposition matrix parameter can be selected for comprehensively presenting electroencephalogram character information, and then subsequent effective fusion is performed, so that effective support and help can be supplied to early diagnosis assessment for the brain functional disordered diseases, such as, Alzheimer disease, mild cognitive impairment, and the like.
Owner:秦皇岛市惠斯安普医学系统股份有限公司 +1
Methods and compositions for diagnosis, stratification, and monitoring of alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders in body fluids
InactiveUS20050221348A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNeuro-degenerative diseaseBody fluid
The inventors have discovered a collection of proteinaceous biomarkers (“AD biomarkers) which can be measured in peripheral biological fluid samples to aid in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorders, particularly Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The invention further provides methods of identifying candidate agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease by testing prospective agents for activity in modulating AD biomarker levels.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Methods to facilitate transmission of large molecules across the blood-brain, blood-eye, and blood-nerve barriers
InactiveUS20070196375A1Reduction in rate of progressHalt in progression of illnessOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSpinal cordTnf antagonists
A method for delivering a biologic to a human with Alzheimer's-related dementia, comprising administering the biologic parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human's head below the horizontal. The method further includes delivering a TNF antagonist to the brain of a human for treating mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's related dementia, or vascular dementia, comprising administering the TNF antagonist golimumab parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human in a Trendelenburg position, for delivery of the golimumab to the brain via the human's vertebral venous system.
Owner:EDWARD LEWIS TOBINICK M D
Rapid improvement of cognition in condition related to abeta
InactiveUS20060073149A1Rapid improvement of cognitionRapid of cognitionNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCognition.knowledgeS syndrome
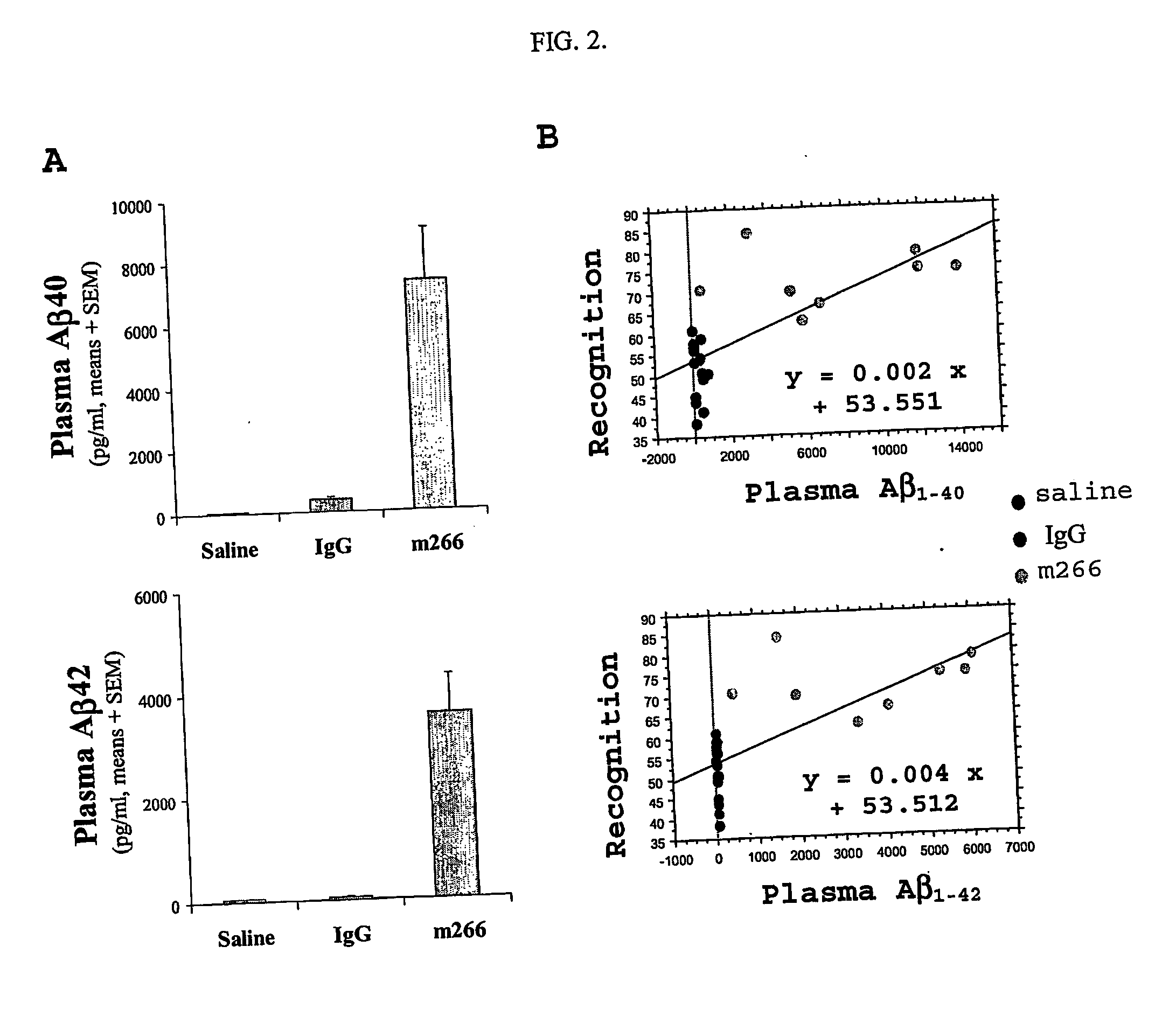
The present invention is a method for effecting rapid improvement in cognition in subjects suffering from conditions or diseases related to the Aβ peptide, including Alzheimer's disease, Down's syndrome, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, mild cognitive impairment, and the like. The method comprises administering anti-Aβ antibodies to the subject, especially antibodies having a high affinity for soluble forms of Aβ. X-15240
Owner:BALES KELLY +2
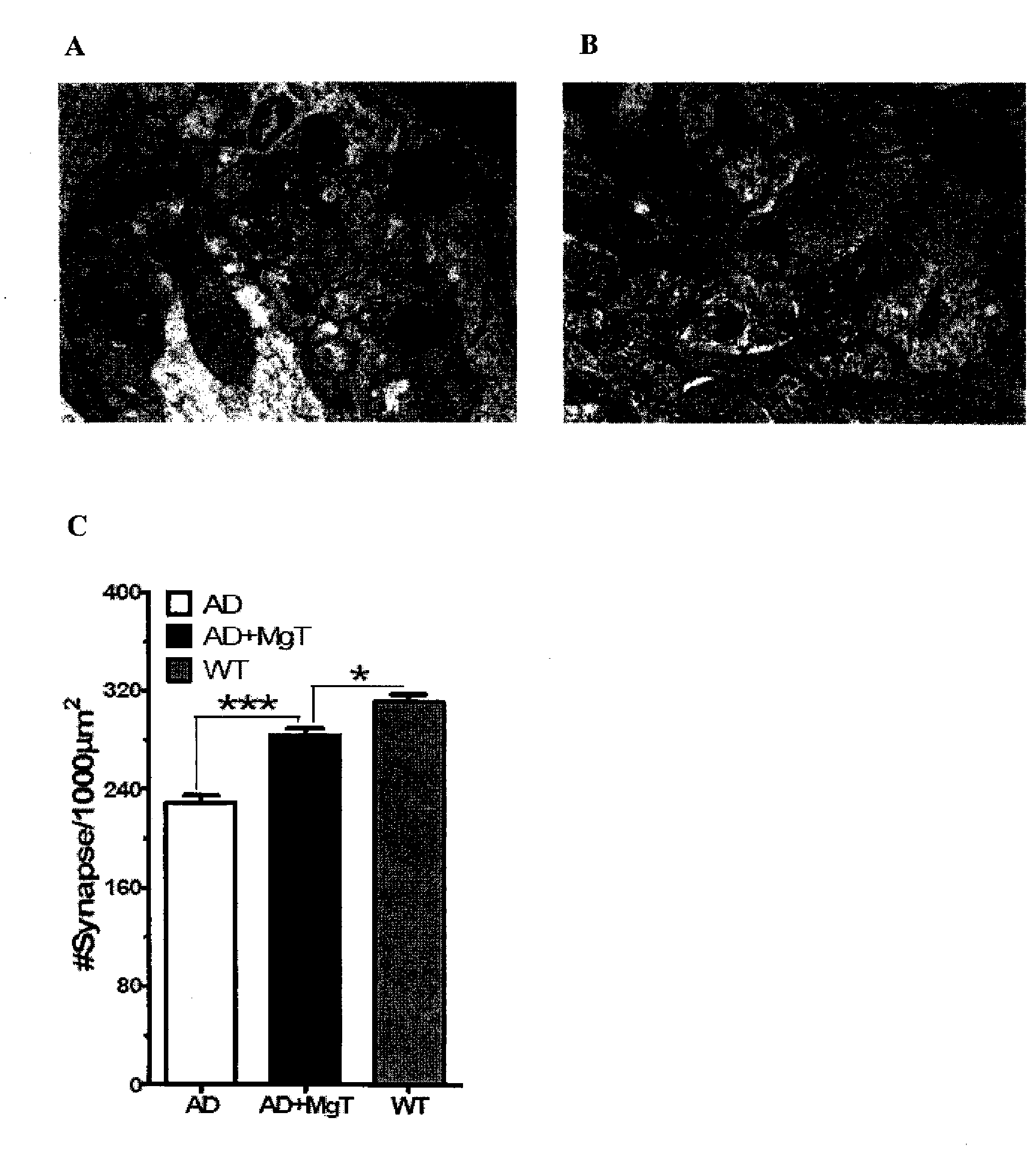
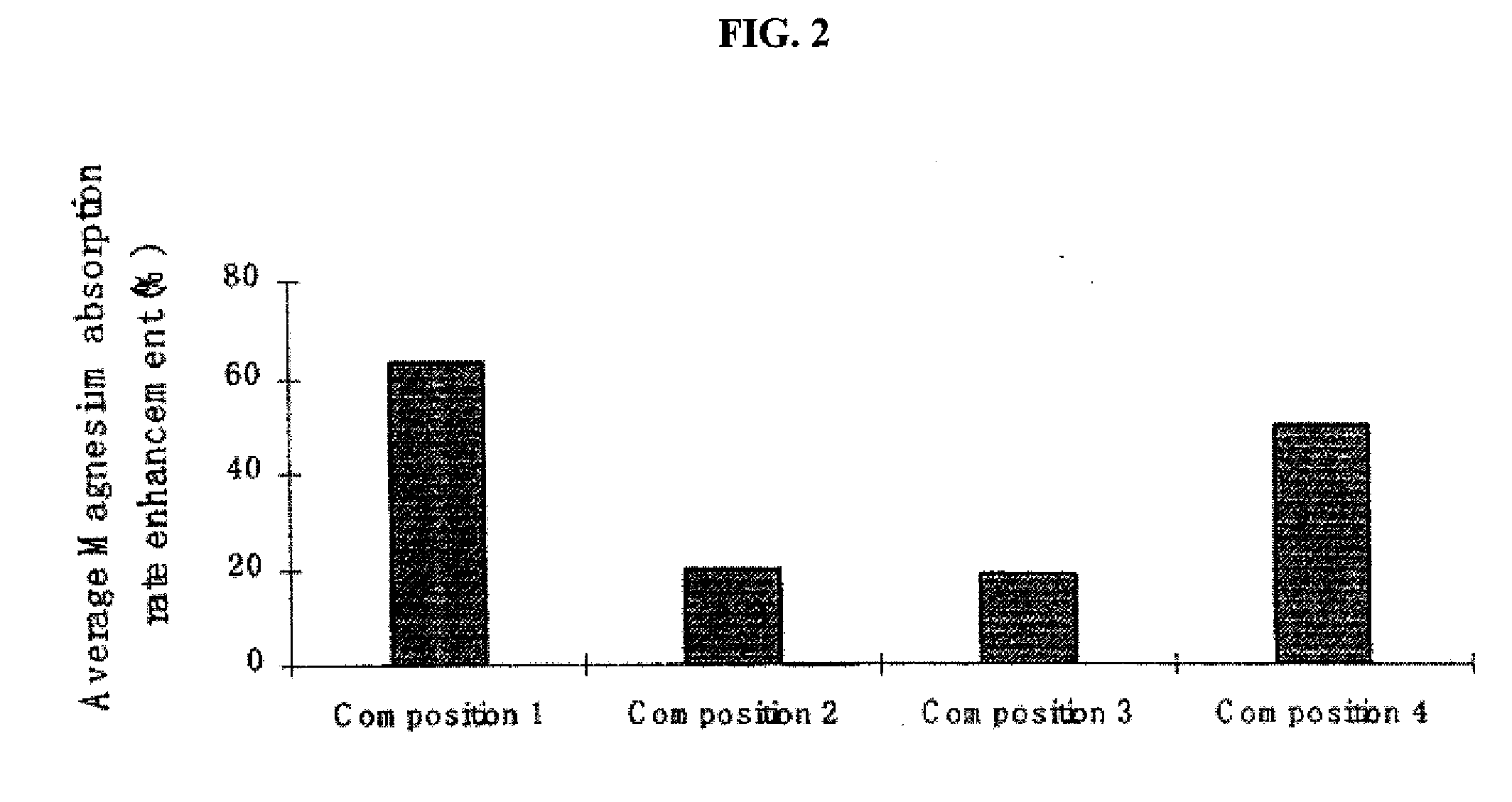
Magnesium compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080248100A1Increase in physiological concentrationImprove depressionPowder deliveryBiocideAttention deficitsMigraine
A composition for administration to a subject, such as oral administration to a subject, for example, has been provided. Such a composition may comprise at least one magnesium-counter ion compound. A magnesium-counter ion composition described herein may be useful for any of a variety of applications provided herein, such as maintaining, enhancing, and / or improving health, nutrition, and / or another condition of a subject, and / or cognitive, learning, and / or memory function. A magnesium-counter ion composition provided herein may be useful for administration to a subject presenting magnesium deficiency, mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, ALS, Parkinson's disease, diabetes, migraine, anxiety disorder, mood disorder, and / or hypertension. A kit, method, and other associated technology are also provided.
Owner:NEUROCENTRIA INC
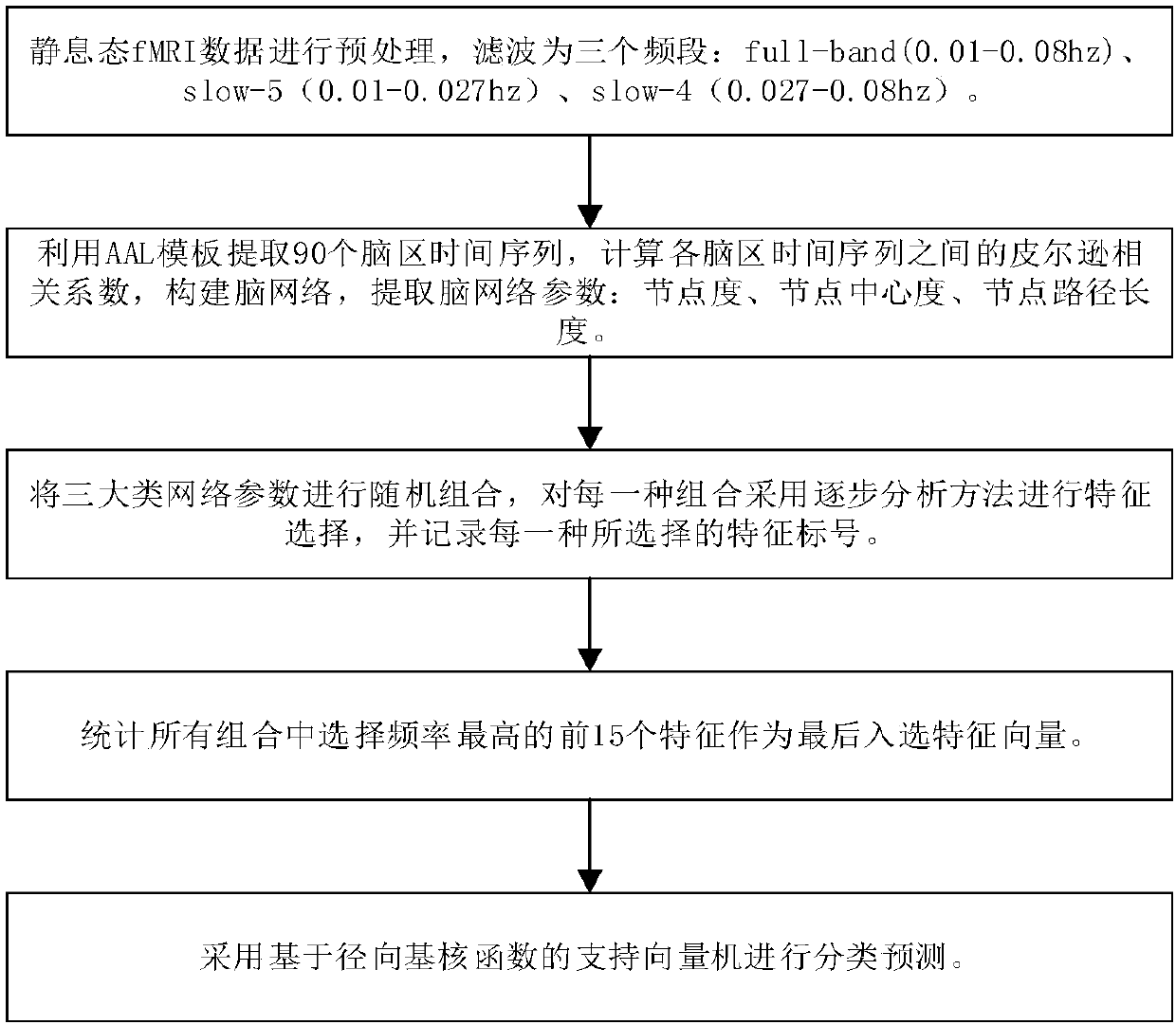
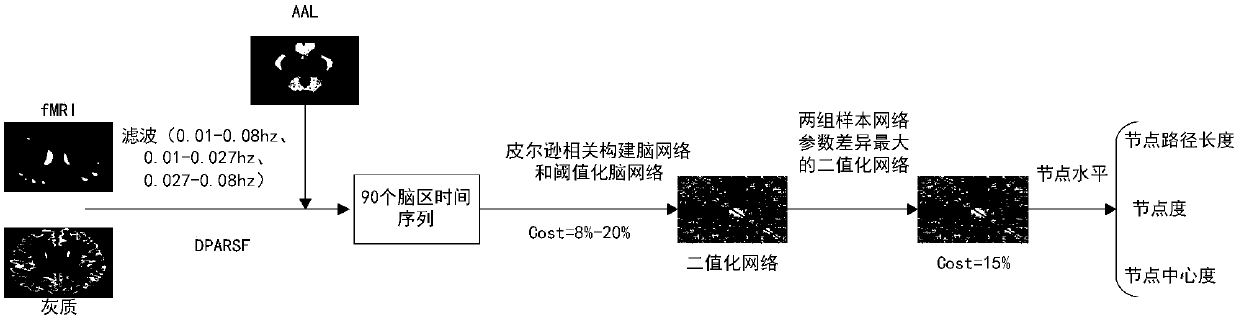
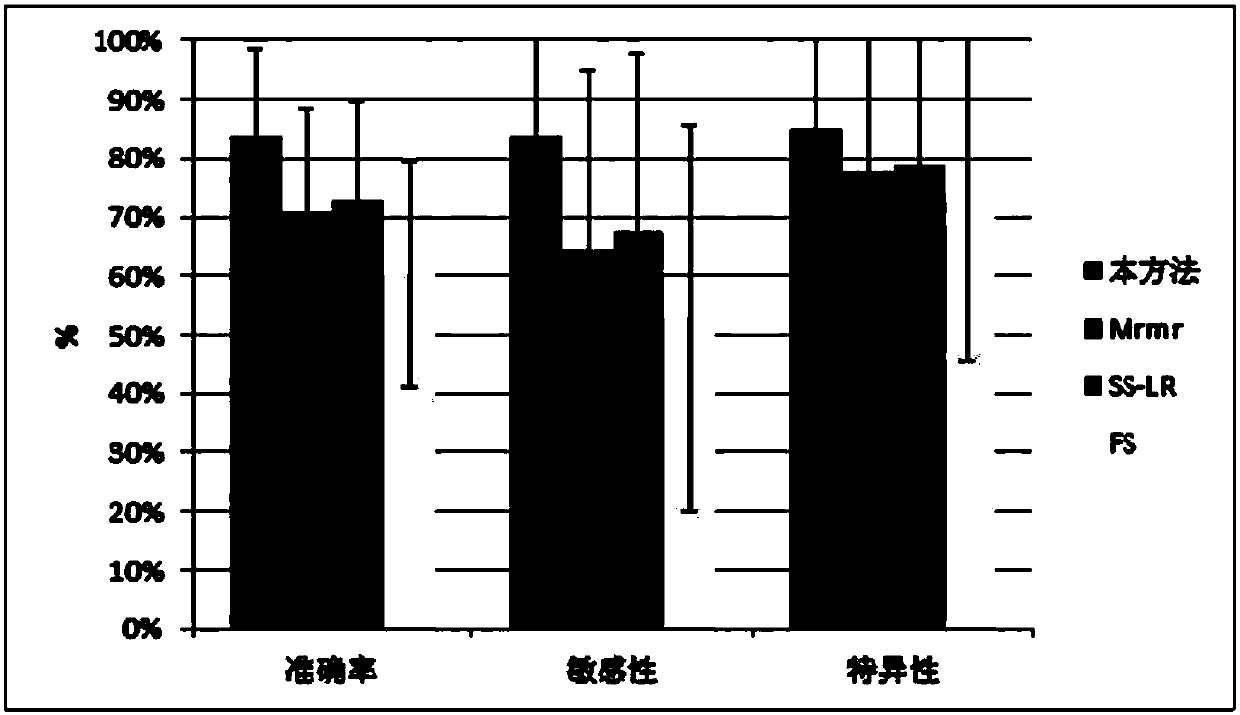
Early and late mild cognitive impairment classification method and device based on brain function network characteristics
ActiveCN107909117AImprove classification accuracyIncreased sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsCognitive disorder
The invention discloses an early and late mild cognitive impairment classification method and device based on brain function network characteristics and belongs to the medical image processing technology field. According to the method, firstly, sample data is pre-processed, multiple brain region time series are extracted, the brain function network is constructed by utilizing a correlation coefficient between the Pearson's correlation calculation brain area time series, and brain network parameters are calculated; secondly, the stepwise analysis method is utilized to extract characteristics, abinary classifier is trained, corresponding characteristic vectors are extracted from to-be-classified resting state functional magnetic resonance data and are inputted to the trained binary classifier, and the medical image classification result is acquired. Compared with a method in the prior art, the method is advantaged in that classification accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are better.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods and compositions for diagnosis, stratification, and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders in body fluids
InactiveUS20070037200A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Body fluid
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
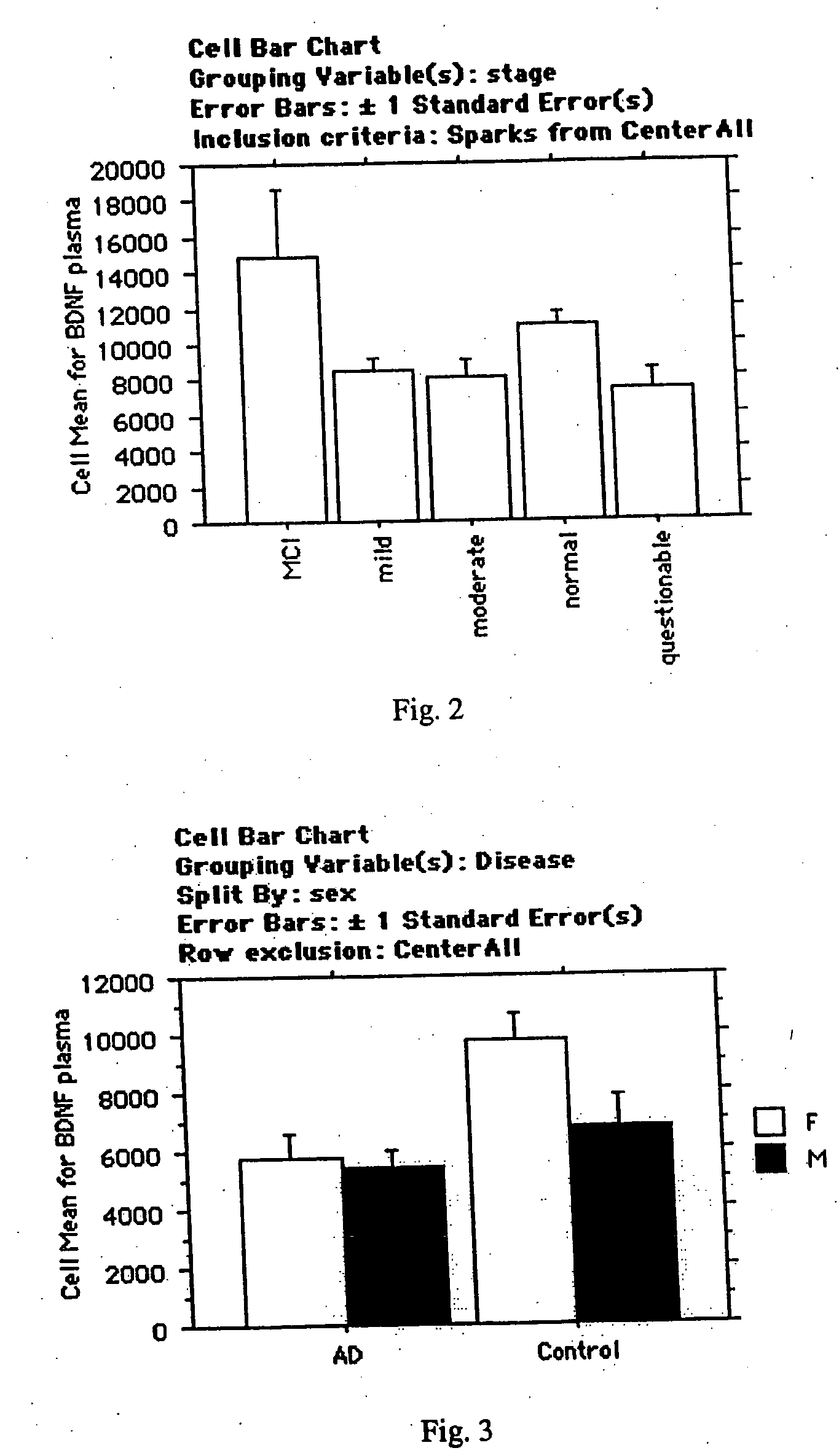
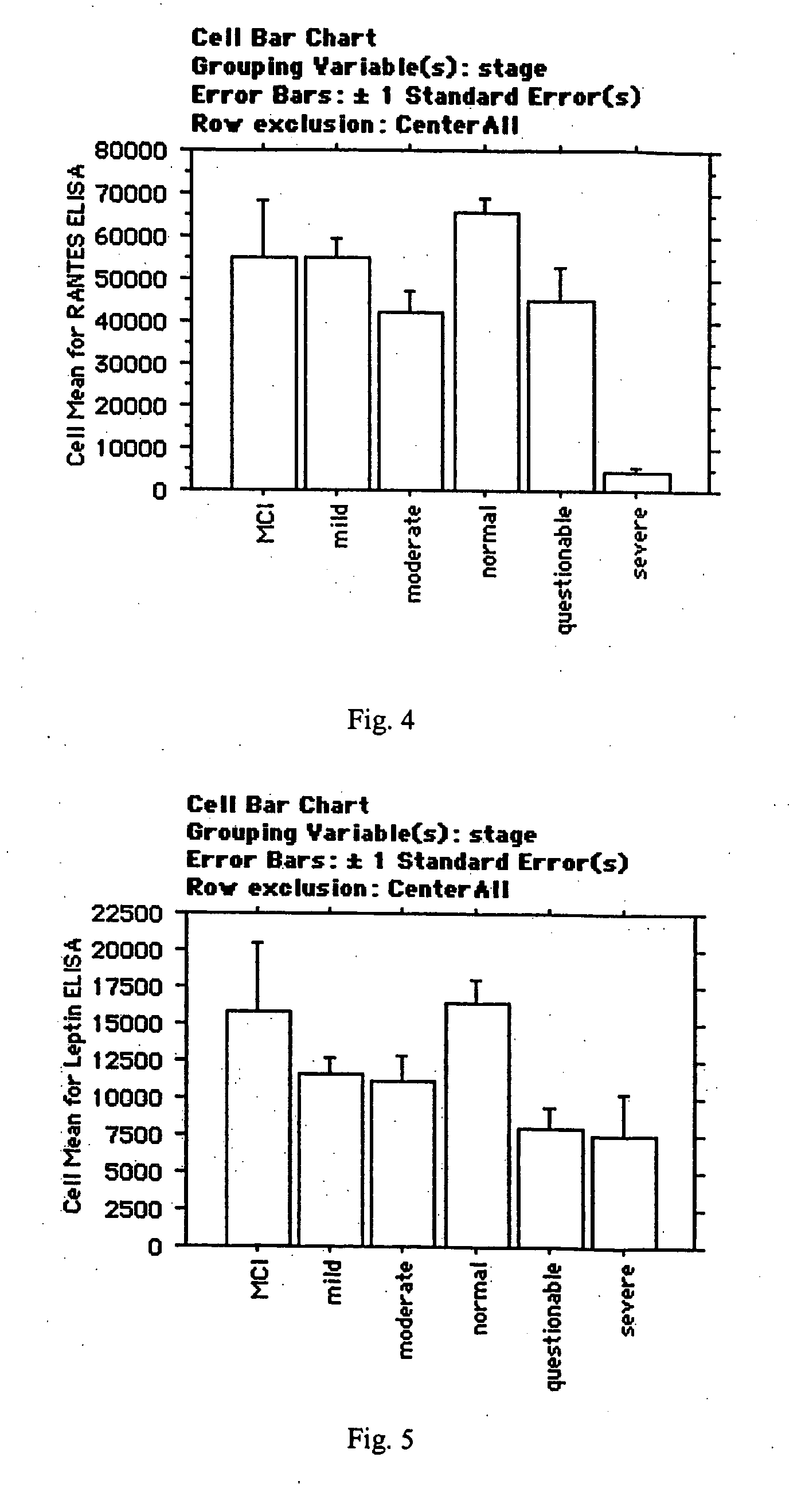
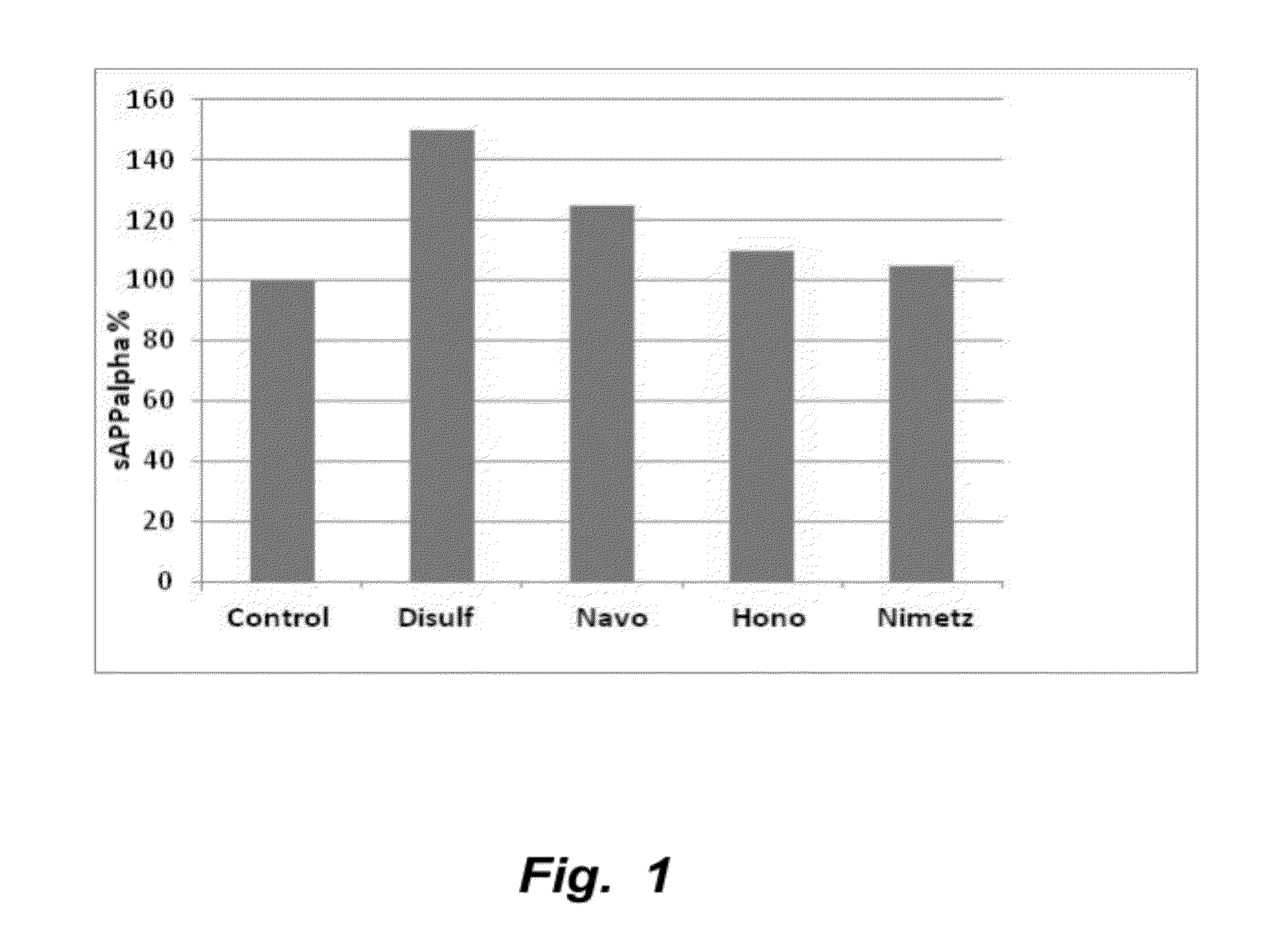
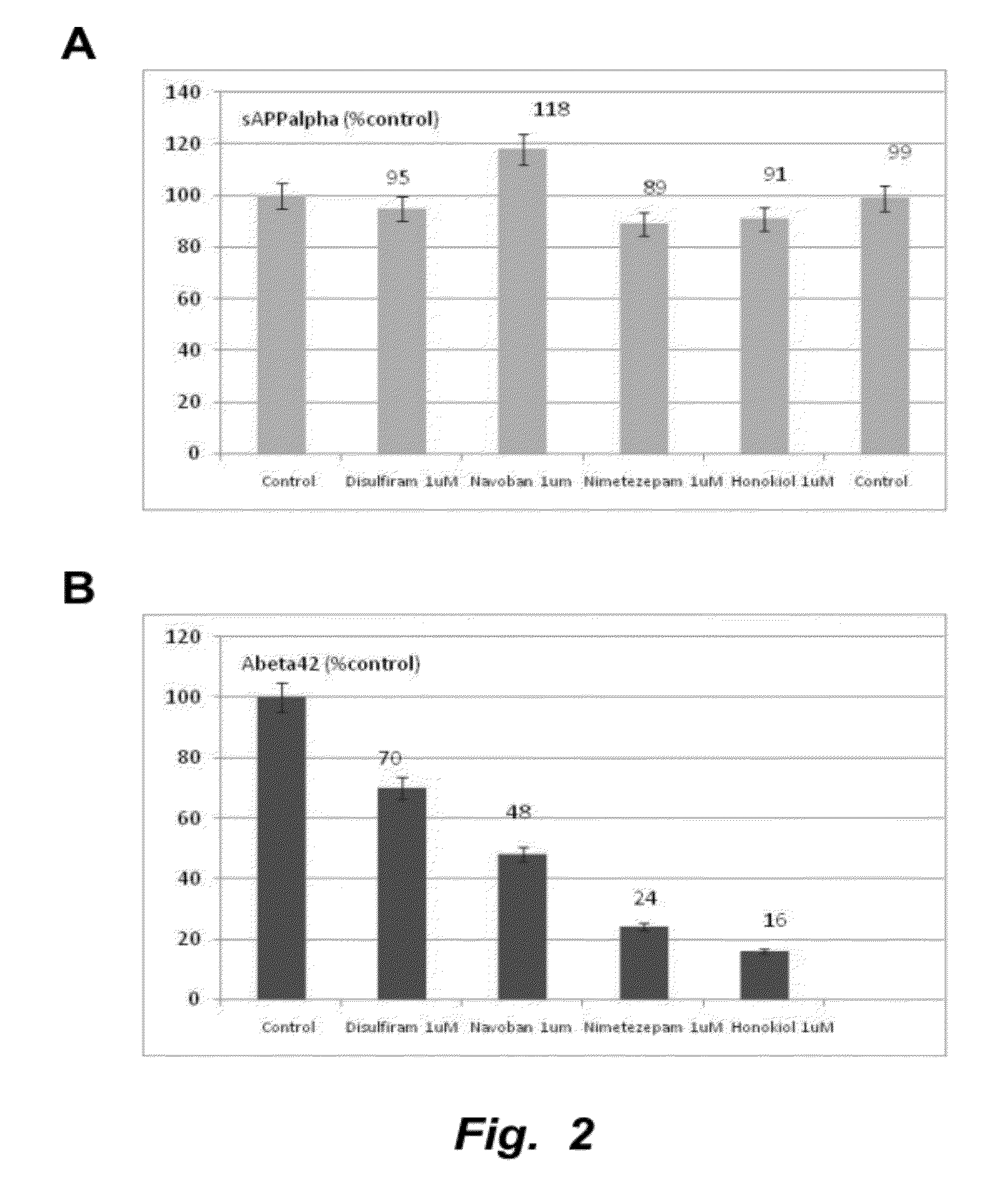
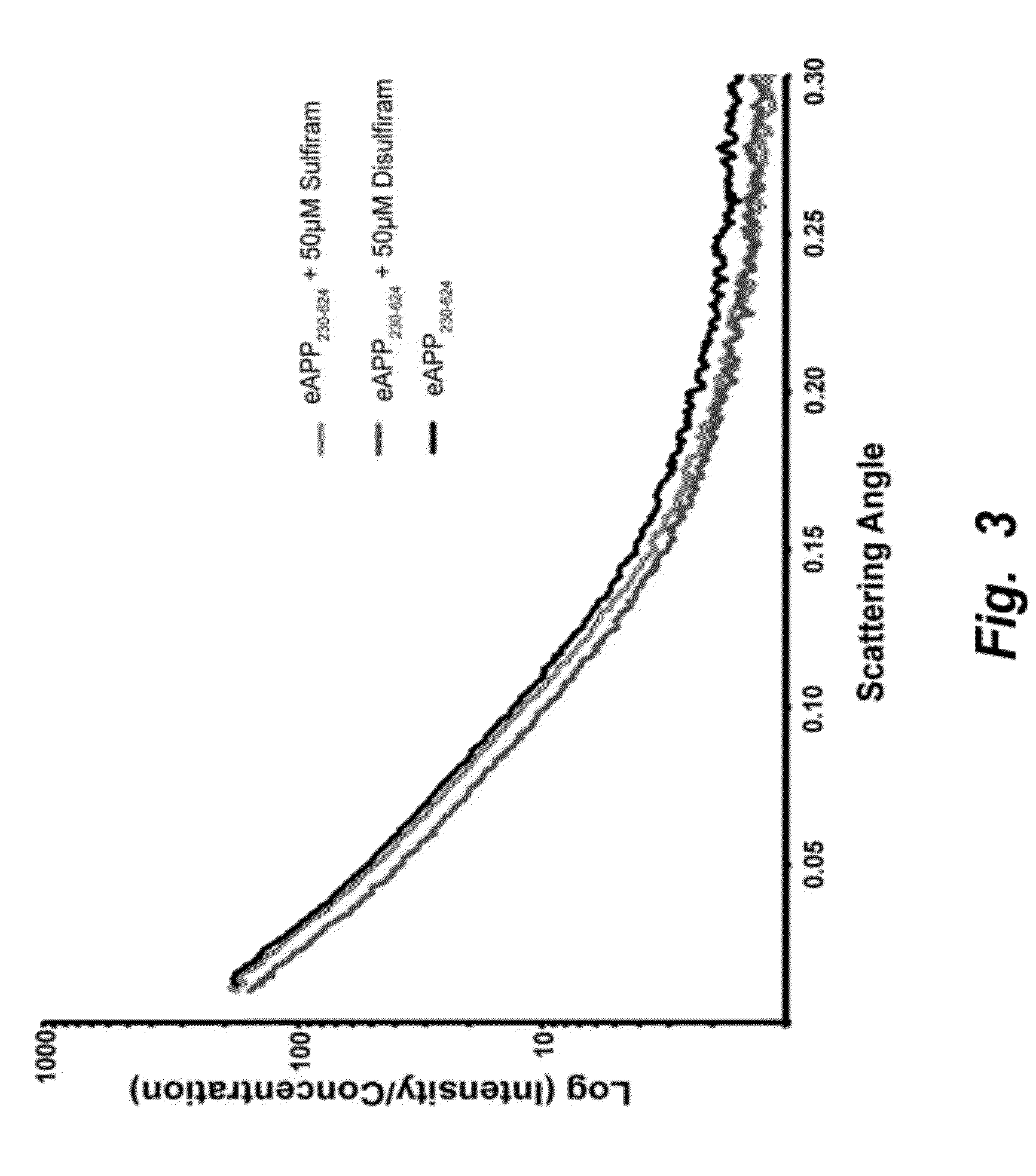
Methods of treating mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and related disorders
ActiveUS20120071468A1Progression from an asymptomatic state to a symptomatic state is prevented or delayedBiocideNervous disorderHonokiolMedicine
The invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and for inhibiting, reducing, delaying and / or preventing the progression of MCI to Alzheimer's disease. The methods entail administering an effective amount of one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of tropisetron, disulfuram, honokiol and nimetazepam. The methods also are useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of amyloidogenic diseases, including Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
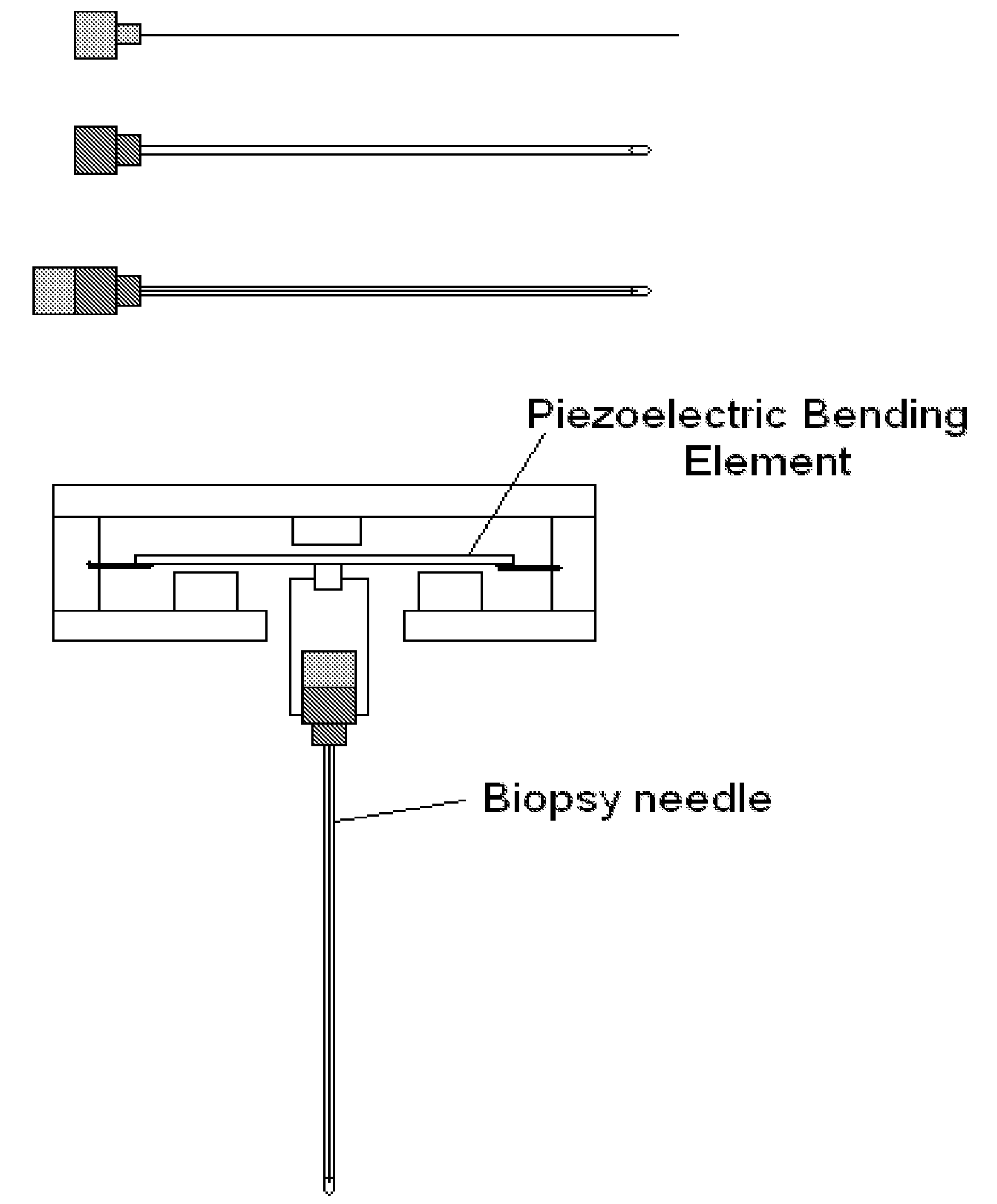
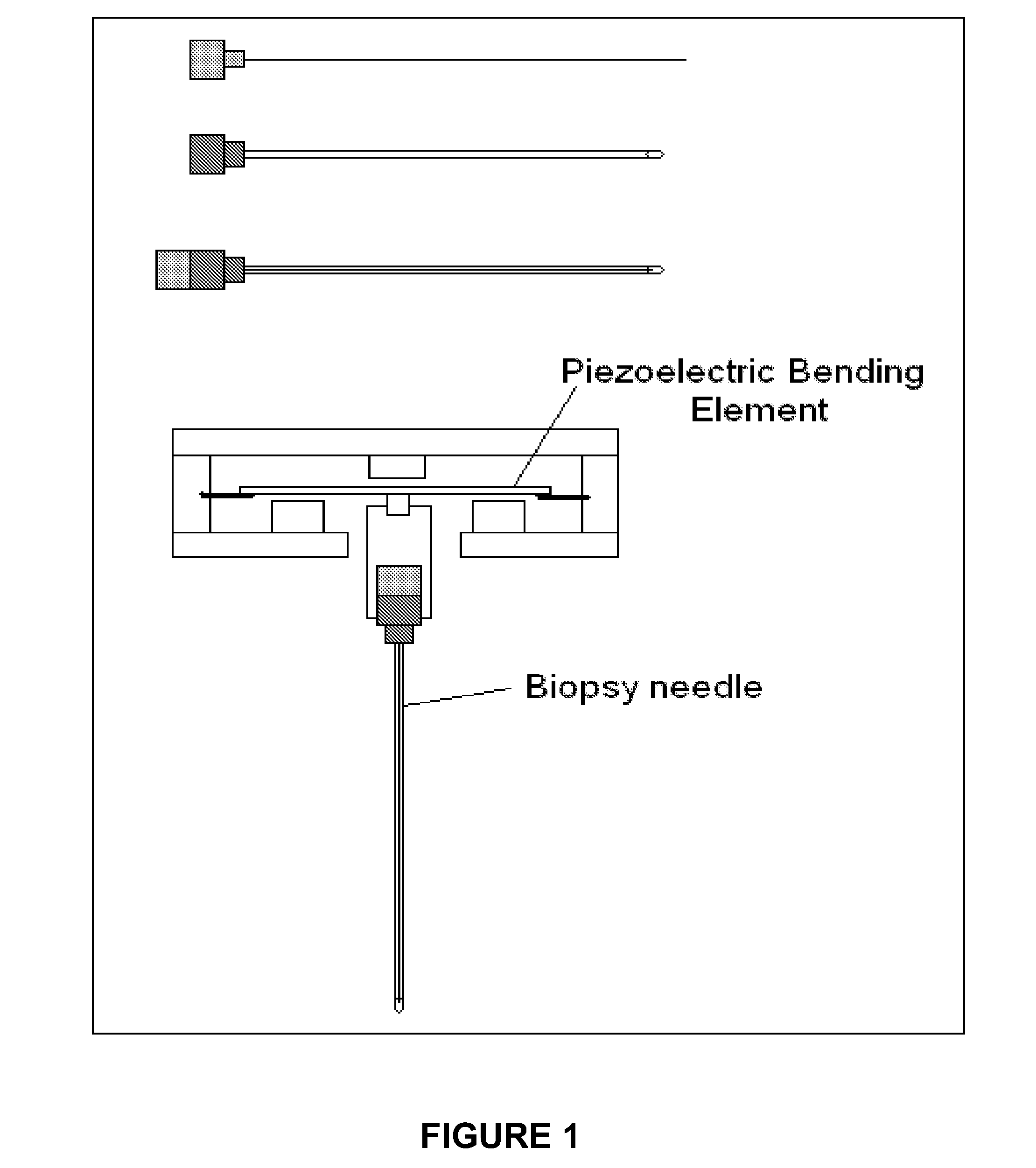
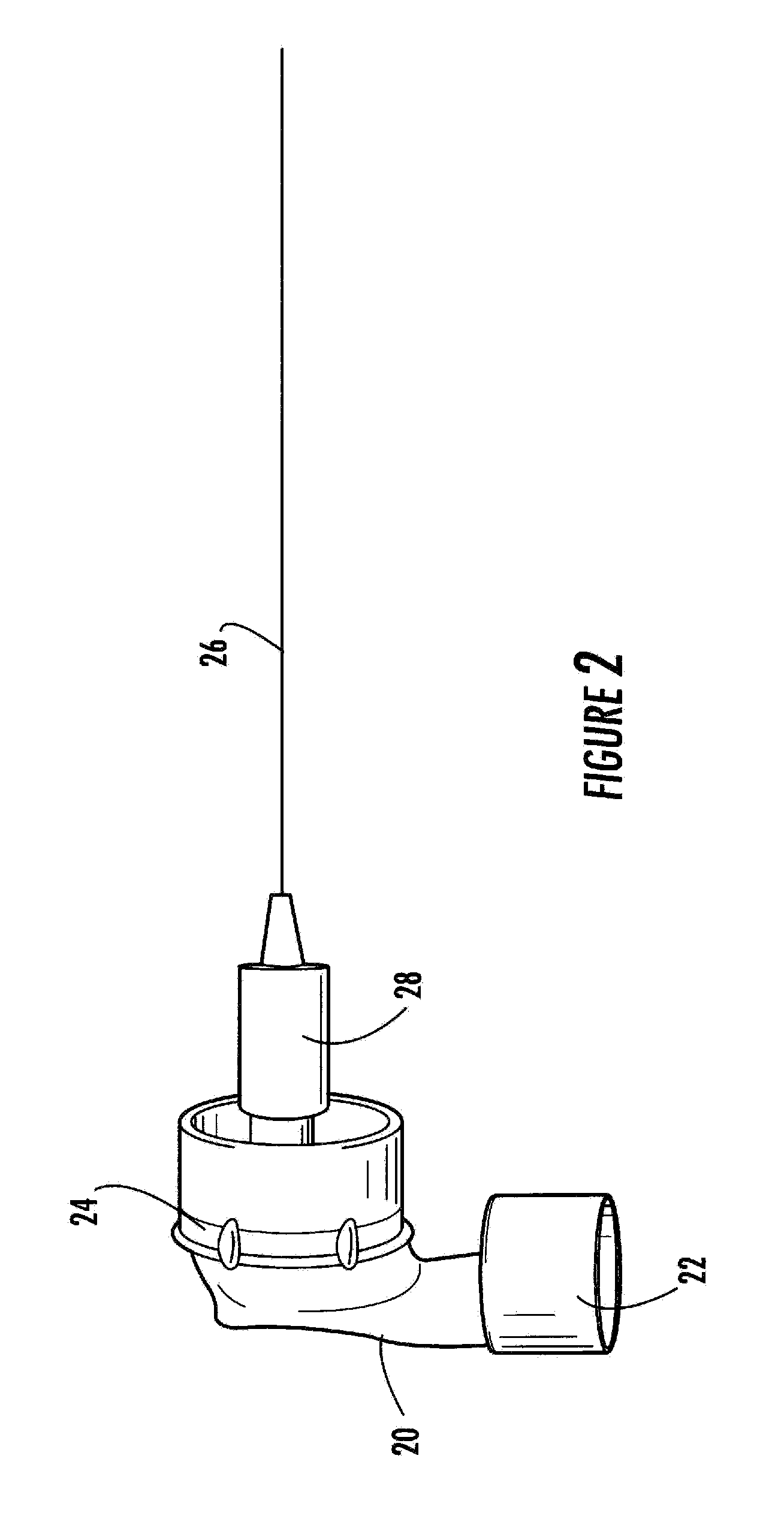
Novel needle driver for magnetic resonance elastography
ActiveUS20080255444A1Accurately determineReduce decreaseDiagnostics using vibrationsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAcupuncture needlesMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Owner:LAWRENCE GROUP MEDICAL DEVICE TRUST
Compositions and methods for inhibiting and/or modulating effector t-cells involved in inflammatory neurodegenerative disease
Provided are methods for treating inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke / cerebral ischemia, head trauma, spinal cord injury, Huntington's disease, migraine, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, inflammatory neurodegenerative condition associated with AIDS, age-related cognitive decline; mild cognitive impairment and prion diseases in a mammal), or at least one symptom thereof in a subject by administering a therapeutic composition comprising at least one electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-generated oxygen-enriched fluids) of the present invention. Particular aspects provide methods for inhibiting and / or modulating the function and / or activity of effector T-cells, and / or for cell-based tolerogenic therapy (e.g., by modulating development and / or function and / or activity of TREG cells and / or dendritic cells (DCs) and / or TH17 cells (e.g., RORγt+ TH17 cells). In certain aspects such methods comprise ex vivo exposure of T-cells and / or APC (e.g., dendridic cells) to at least one electrokinetically-altered fluid as disclosed herein. Combination therapies are additionally provided.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
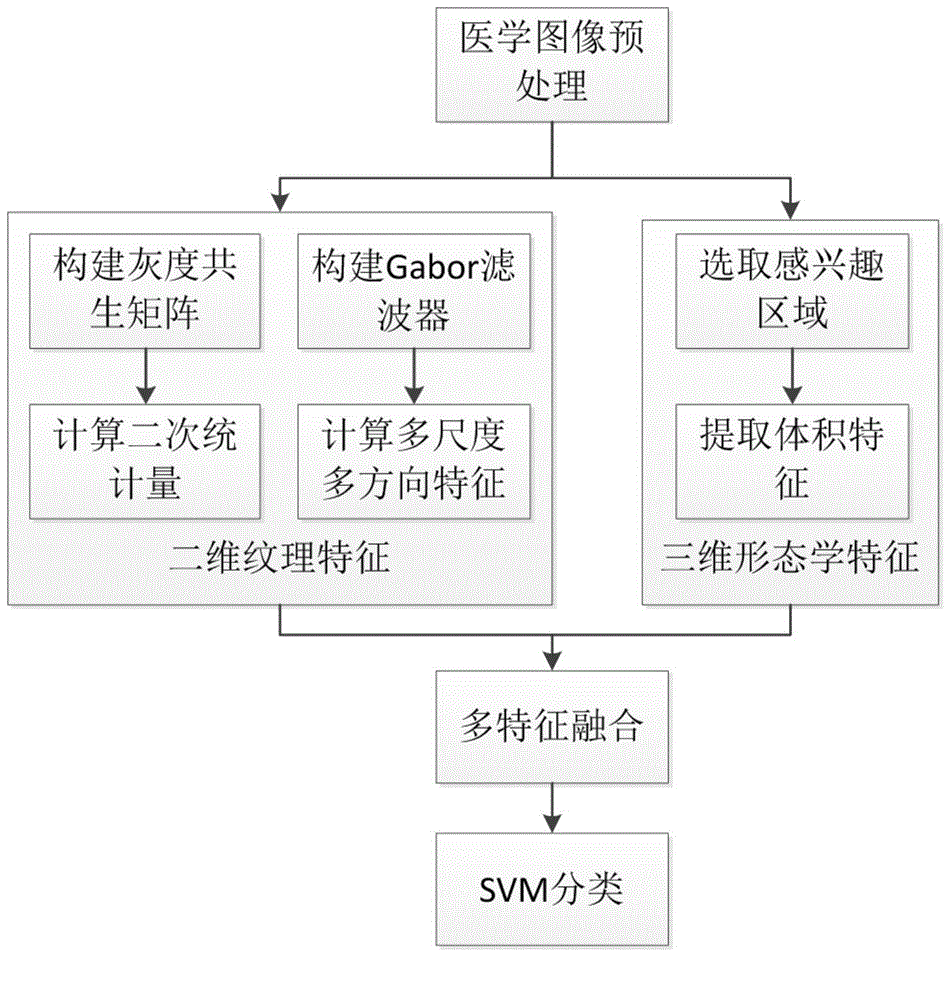
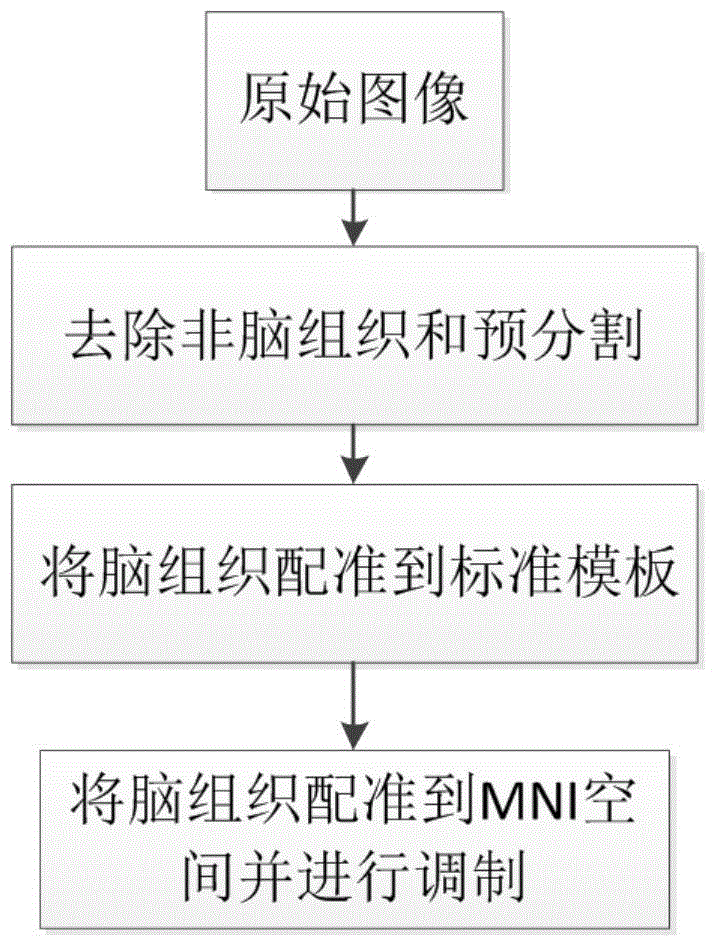
Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment identification method based on two-dimension features and three-dimension features
InactiveCN104881680AImprove recognition rateMature thinkingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseSupport vector machine classifier
The invention provides an Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment identification method based on two-dimension features and three-dimension features. The method particularly comprises a step of performing pretreatment of a medical image, wherein the pretreatment comprises pre-segmentation, registration and other processes; a step of performing two-dimension textural feature extraction of the medical image, wherein features comprise the quadratic statistic of a gray-level co-occurrence matrix and a multiscale and multidirectional feature value of Gabor wavelet transformation; a step of performing three-dimension morphological feature extraction of the medical image, i.e., extracting volume features of an area of interest; a step of performing feature fusion of three-dimension morphological features and two-dimension textural features; and a step of constructing a support vector machine to achieve identification of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. According to the method provided by the invention, the three-dimension morphological features and the two-dimension textural features are combined, so that the content of the medical image can be expressed in a comprehensive and accurate manner. The method can improve identification of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment, thereby providing a more effective clinic assistant diagnosis.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric & cognitive diseases
ActiveUS20070106479A1Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserHuntingtons chorea
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases. A method is provided for developing a computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain which comprises the steps of identifying data relating to a biological state of a generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex; identifying biological processes related to the data, these identified biological processes defining at least one portion of the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala, and cortex; and combining the biological processes to form a simulation of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. A resulting computer model is of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, comprising code to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, and code to define the mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes. At least two of the biological processes are associated with the mathematical relationships. A combination of the code to define the biological processes and the code to define the mathematical relationships define a simulation of the biological state of the interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Computer executable software code is provided comprised of code to define biological processes related to a biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain including code to define mathematical relations associated with the biological processes. A computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain is provided, comprising a computer-readable memory storing codes and a processor coupled to the computer-readable memory, the processor configured to execute the codes. The memory comprises code to define biological processes related to the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, and code to define mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
New compounds 575
InactiveUS20100125087A1Shorten the progressReduce in patientBiocideNervous disorderPre-Senile DementiaAttention deficits
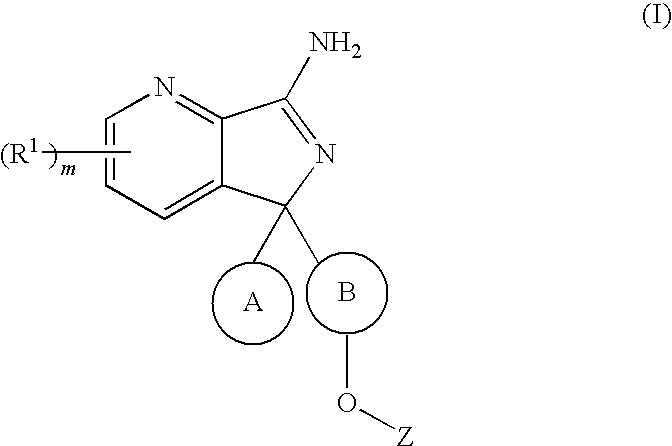
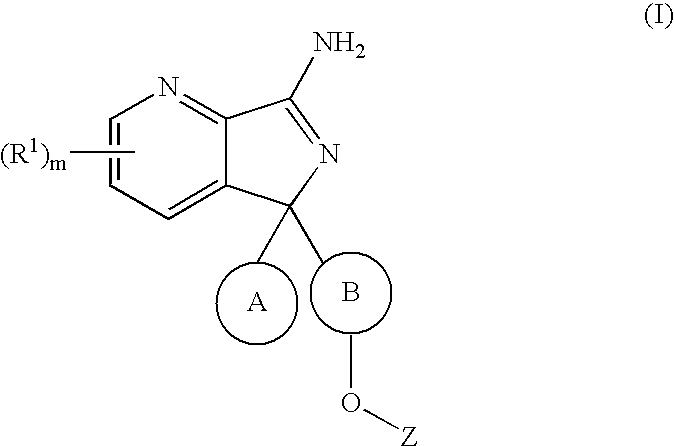
The present invention relates to novel compounds of formula (I) and their pharmaceutical compositions. In addition, the present invention relates to therapeutic methods for the treatment and / or prevention of Aβ-related pathologies such as Downs syndrome, β-amyloid angiopathy such as but not limited to cerebral amyloid angiopathy or hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, disorders associated with cognitive impairment such as but not limited to MCI (“mild cognitive impairment”), Alzheimer Disease, memory loss, attention deficit symptoms associated with Alzheimer disease, neurodegeneration associated with diseases such as Alzheimer disease or dementia including dementia of mixed vascular and degenerative origin, pre-senile dementia, senile dementia and dementia associated with Parkinson's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy or cortical basal degeneration.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Method and composition for treating neurodegenerative disorders
InactiveUS20050288375A1Delay and slow onsetImprove the level ofBiocideNervous disorderNeuro-degenerative diseaseCYP2C9
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating neurodegenerative disorders. A method of the invention involves administering to an individual in need of treatment a composition having an R-NSAID and an NMDA antagonist. Another method of the invention involves administering to an individual in need of treatment a composition having at least two compounds that are capable of interacting with CYP2C9, wherein at least one of said compounds is an Aβ42 lowering agent. The methods and compositions of the invention are useful for treating and preventing neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease, dementia, mild cognitive impairment.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
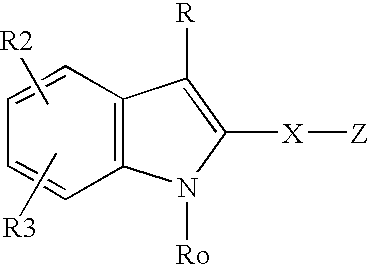
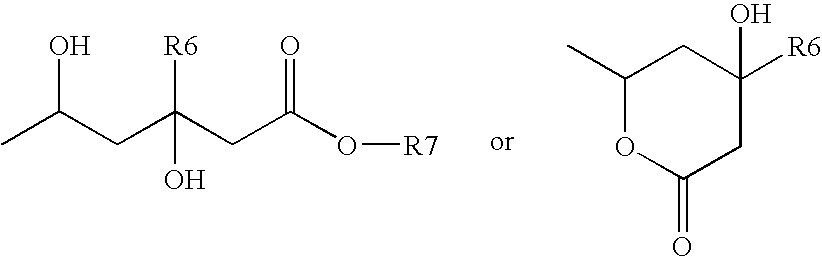
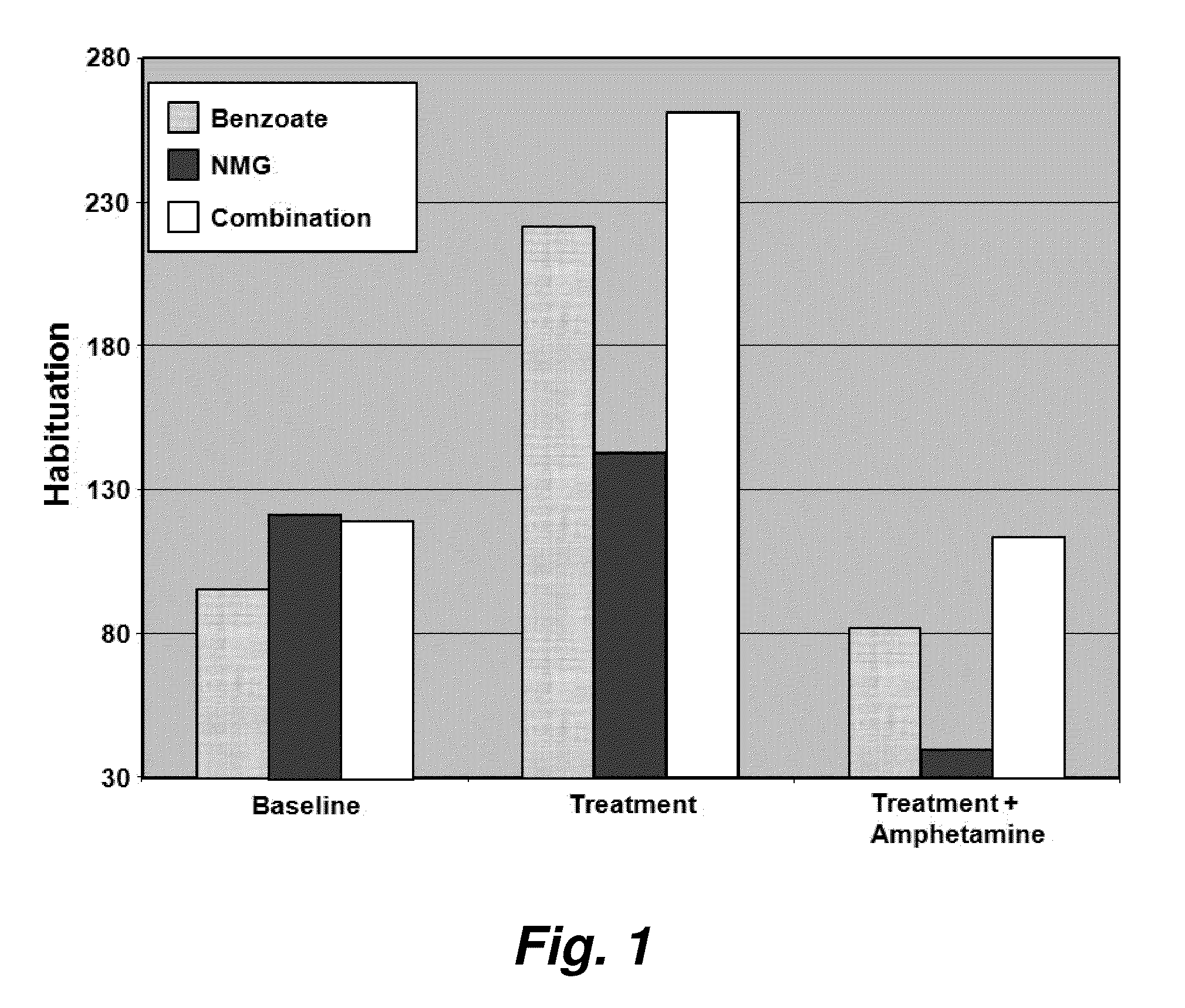
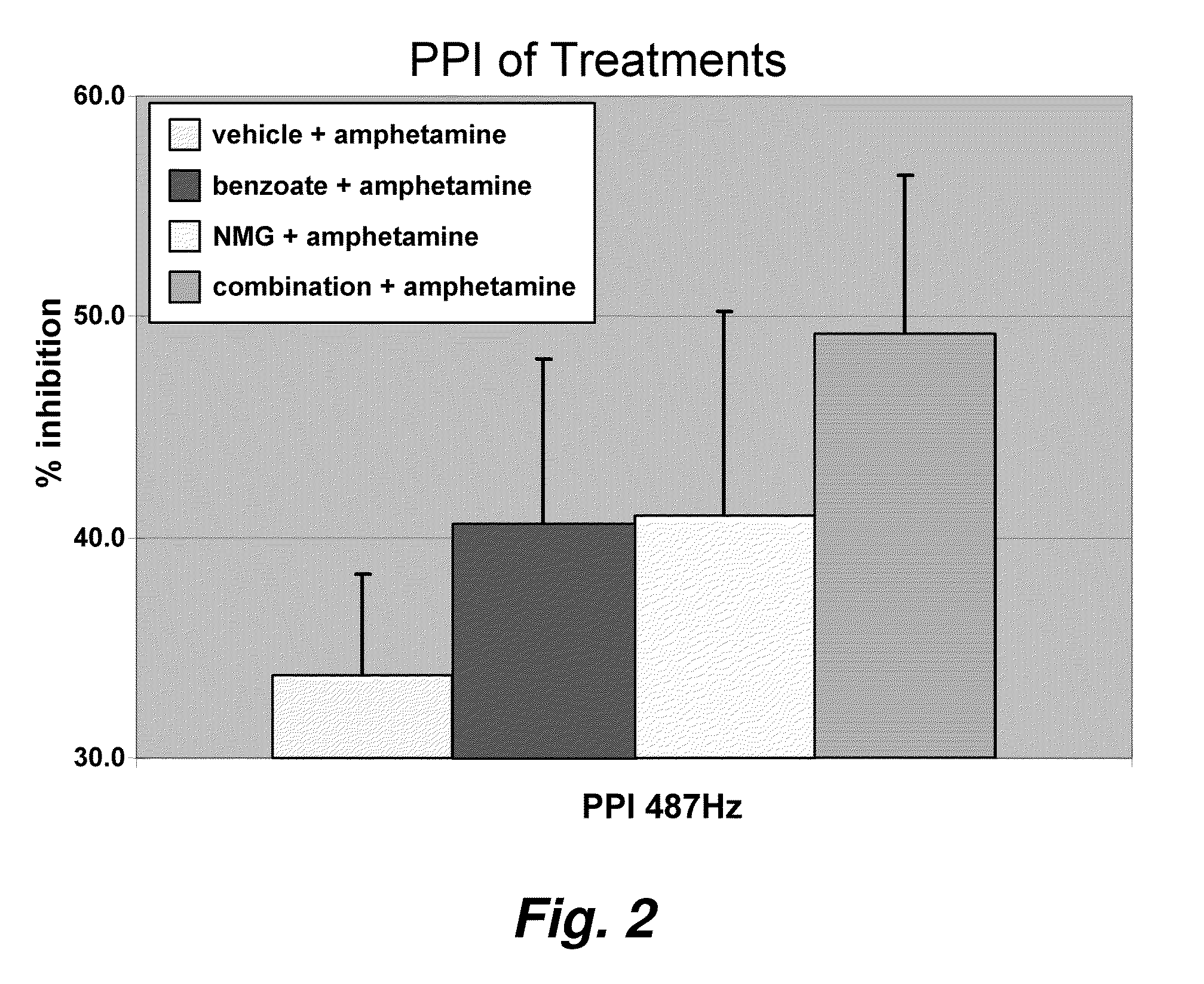
Sorbic and benzoic acid and derivatives thereof enhance the activity of a neuropharmaceutical
Methods and compositions are provided for treating neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, attention deficit disorder, mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and bipolar disorder. The methods entail administering to a patient diagnosed as having a neuropsychiatric disorder (e.g., schizophrenia, depression, attention deficit disorder, mild cognitive impairment, dementia bipolar disorder, etc.) or as at risk for a neuropsychiatric disorder a benzoic acid, benzoic acid salt, and / or benzoic acid derivative, and / or a sorbic acid, sorbic acid salt, and / or sorbic acid derivative, in combination with a neuropharmacological agent (e.g., an antipsychotic, an antidepressant, medications for attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder, cognitive impairment, or dementia, etc.) where the benzoic acid, benzoic acid salt, or benzoic acid derivative, and / or a sorbic acid, sorbic acid salt, and / or sorbic acid derivative, is in an amount sufficient to increase the efficacy of the neuropharmacological agent.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
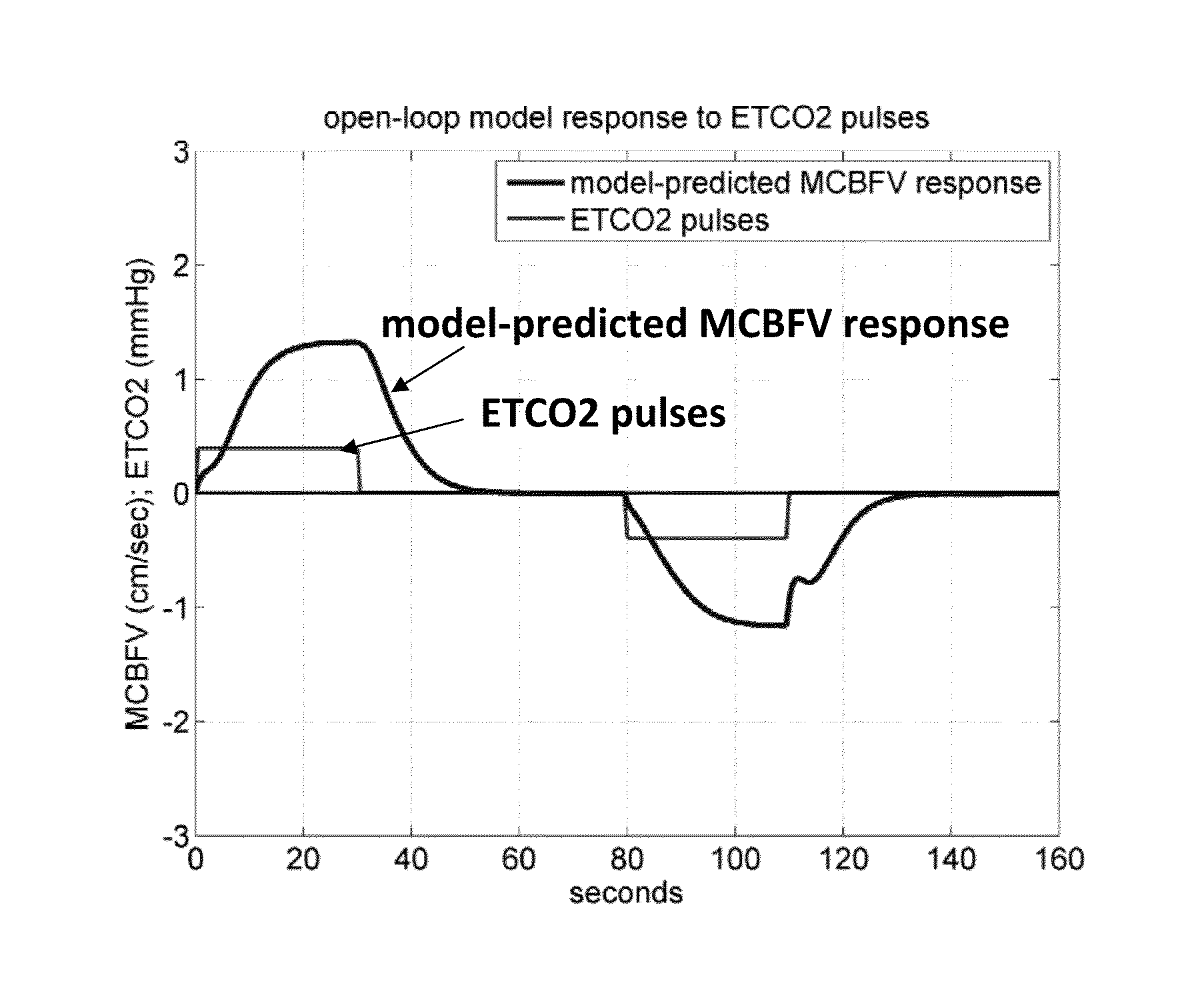
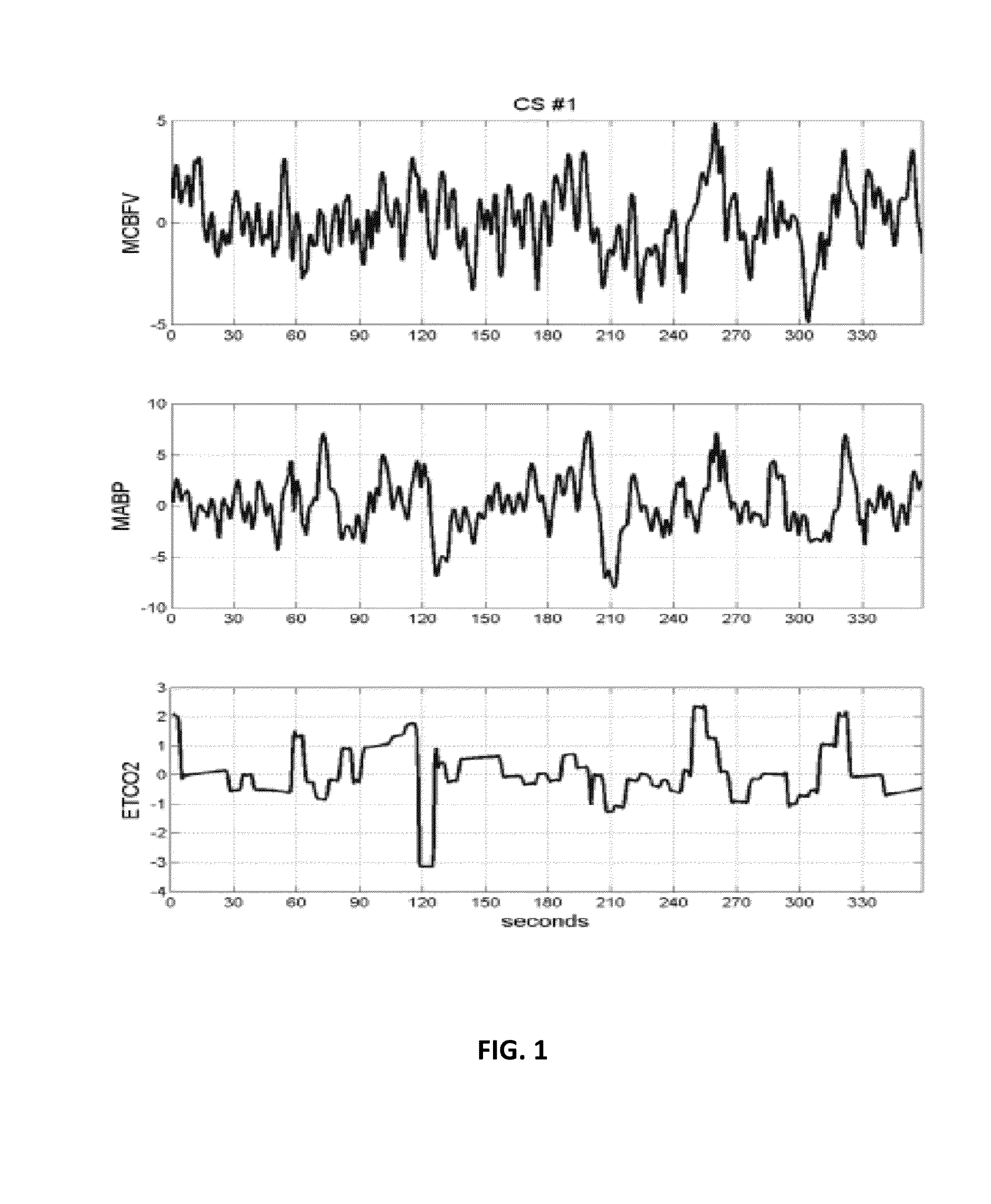
Method for Quantitative Diagnosis of Cerebrovascular, Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases via Computation of a CO2 Vasomotor Reactivity Index based on a Nonlinear Predictive Model
InactiveUS20140278285A1Sensitive and reliableMedical simulationHealth-index calculationComputational modelComputer aid
The present invention relates generally to a method for computer-aided quantitative diagnosis of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's, vascular dementia, mild cognitive impairment, transient ischemia, stroke etc.) via a vasomotor reactivity index (VMRI) which is computed on the basis of a computational model of the dynamic nonlinear inter-relationships between beat-to-beat time-series measurements of cerebral blood flow velocity, arterial blood pressure and end-tidal CO2. This model is obtained by means of a method pioneered by the inventors and may incorporate additional physiological measurements from human subjects. Its purpose is to provide useful information to physicians involved in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases with a significant neurovascular component by offering quantitative means of assessment of the effects of the disease or medication on cerebral vasomotor reactivity. Initial results from clinical data have corroborated the diagnostic potential of this approach.
Owner:MARMARELIS VASILIS Z +2
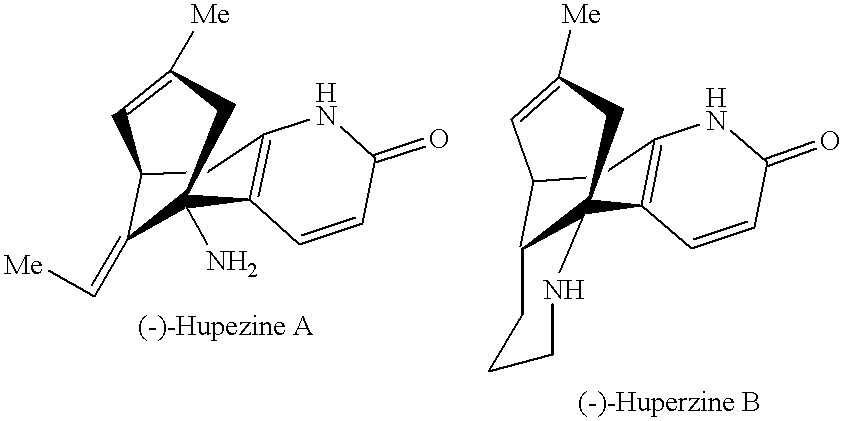
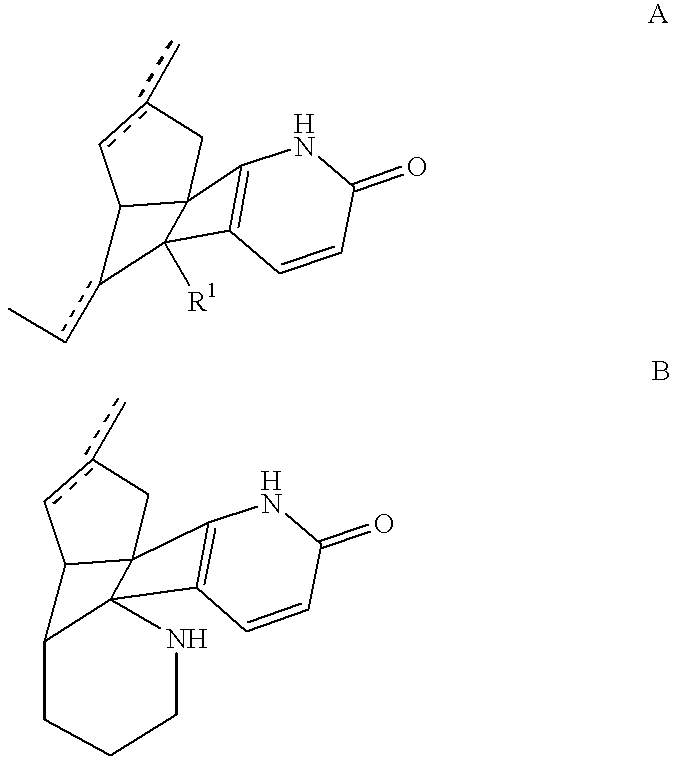
Combination of huperzine and nicotinic compounds as a neuroprotective agent
InactiveUS6369052B1Enhance memoryPrevent and reverse memory declineBiocideNervous disorderRisk strokeDisease cause
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, or reversing neuronal dysfunction including cognitive decline, such as cognitive decline associated with aging and minimal cognitive impairment; severe neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease; and neuronal dysfunction associated with loss of motor skills, such as Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The compositions and methods of the invention can also treat or prevent neuronal dysfunction resulting from CNS injury, such as stroke, spinal-cord injury, and peripheral-nerve injury. The compositions of the invention comprises a huperzine compound and a nicotinic compound.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
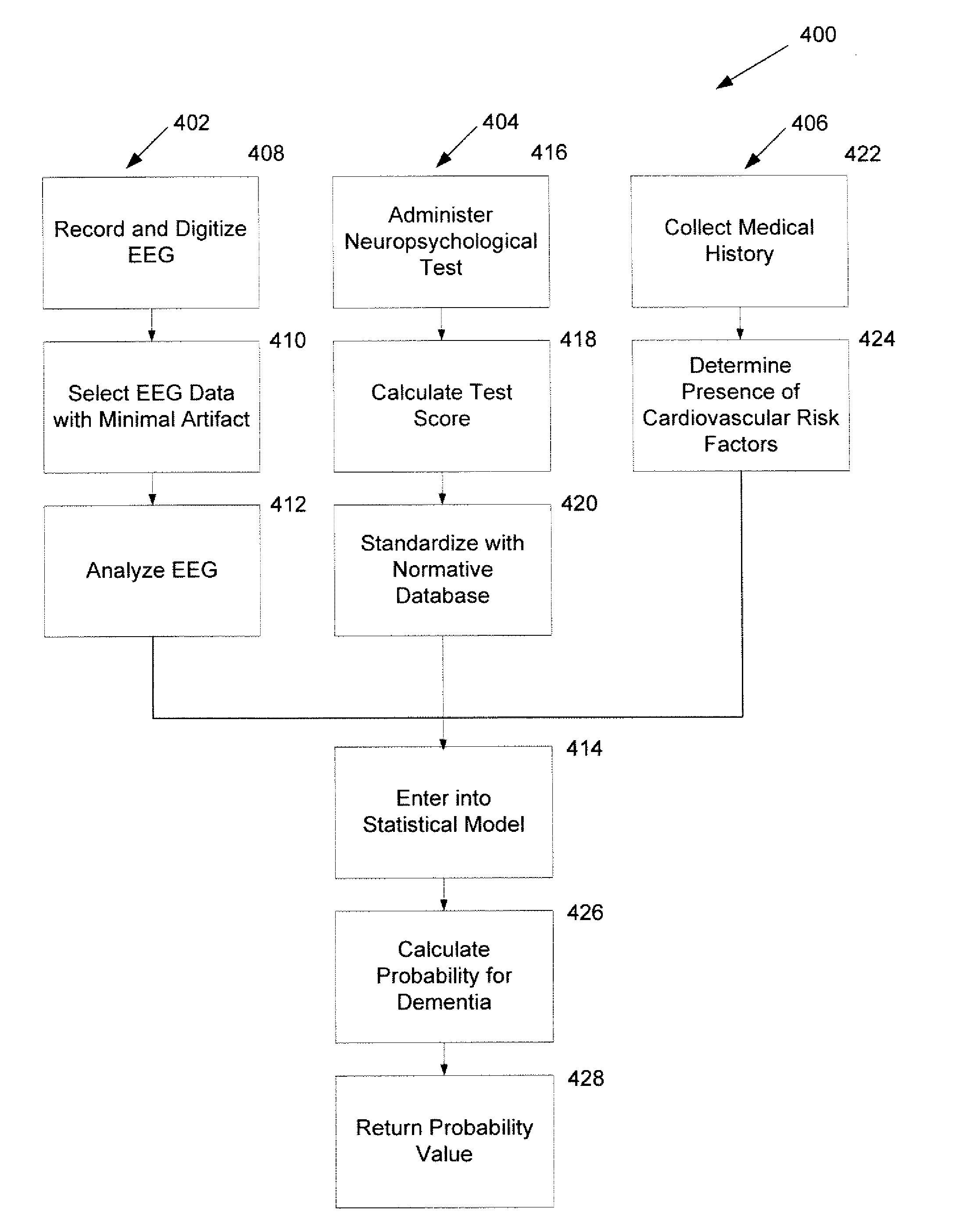
Systems and Methods for Analyzing and Assessing Dementia and Dementia-Type Disorders
InactiveUS20070299360A1High sensitivityStrong specificityElectroencephalographyMedical automated diagnosisMixed dementiaElectroencephalography
Embodiments of the invention can provide systems and methods for analyzing and assessing dementia and dementia-type disorders by integrating the use of electroencephalography (EEG), neuropsychological or cognitive testing data, and cardiovascular risk factor data. Embodiments of the invention can provide systems and methods for early detection of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), vascular dementia (VAD), mixed dementia (AD and VAD), MCI, and other dementia-type disorders. Embodiments of the invention can provide some or all of the following improvements over conventional systems and methods, including: (1) Increased sensitivity, specificity, and overall accuracy; (2) Detection of AD, VAD and mixed dementia; and (3) Accurate detection of mild dementia and some cases of mild cognitive impairment in addition to the detection of moderate to severe dementia.
Owner:LEXICOR MEDICAL TECH
Methods and compositions for improving cognitive function
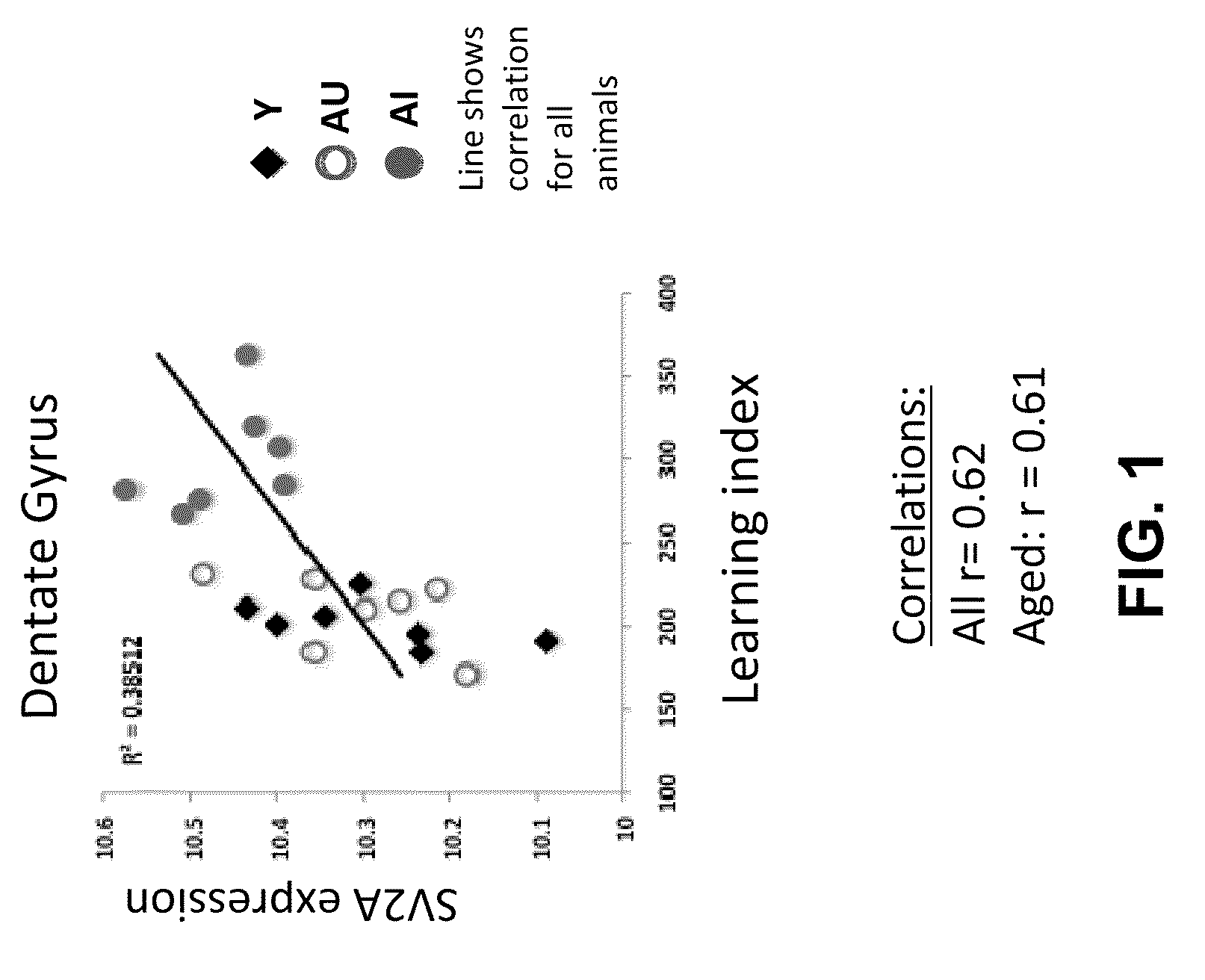
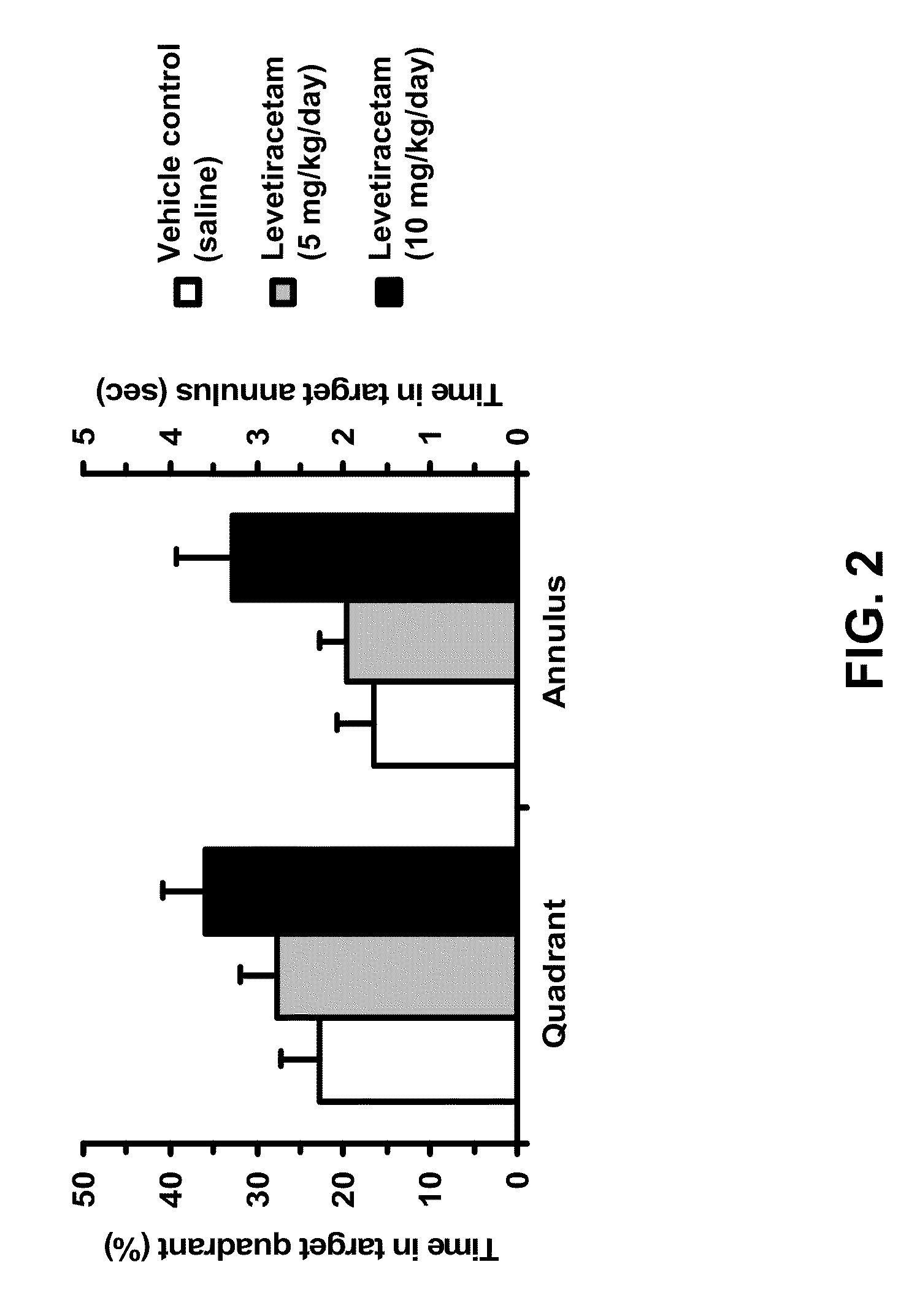
InactiveUS20100099735A1Improve cognitive functionBiocideNervous disorderMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Memory disorder
This invention relates to treating age-related cognitive impairment. This invention in particular relates to the use of inhibitors of synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A), such as levetiracetam, seletracetam, and brivaracetam, in improving cognitive function in subjects that exhibit age-related cognitive impairment or are at risk thereof, including, without limitation, subjects having or at risk for Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Age-related Cognitive Decline (ARCD) or Age-Associated Memory Impairment (AAMI).
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
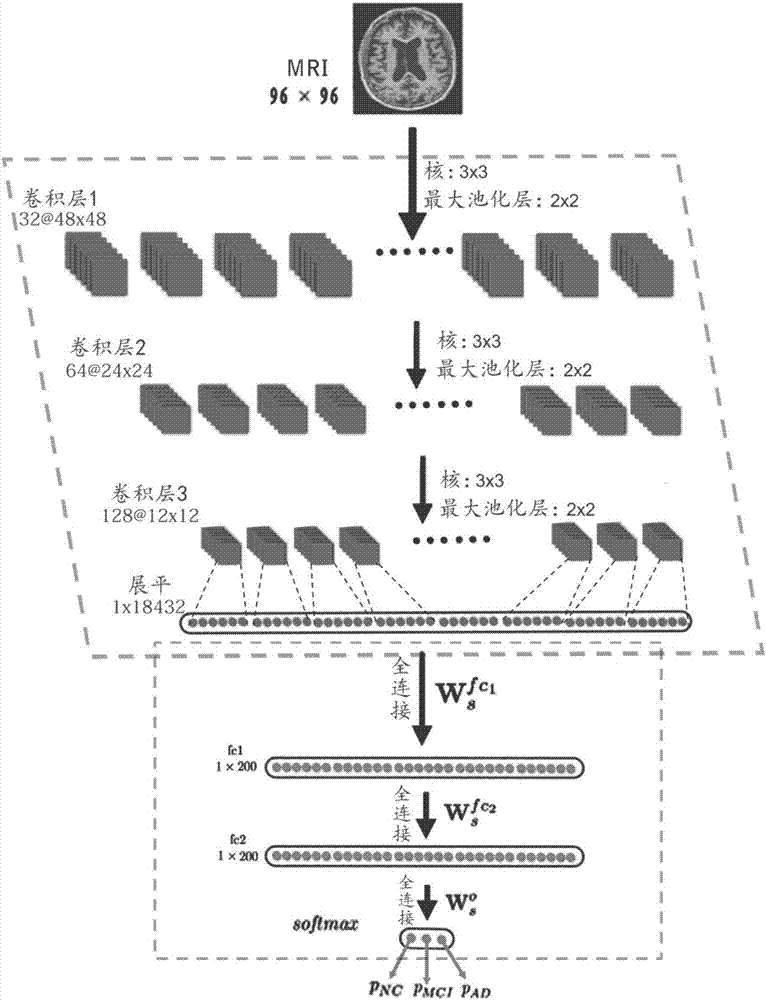
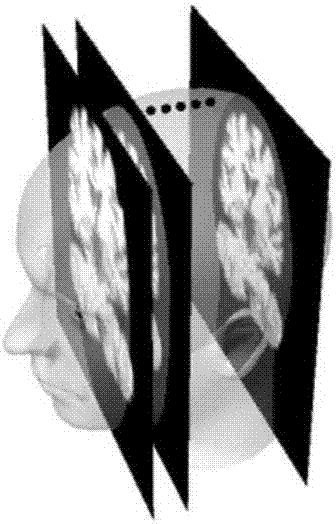
Nuclear magnetic resonance image processing device and method based on convolutional neural network
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance image processing device and method based on a convolutional neural network, and relates to a method for carrying out computer-assisted identification on a hippocampal head of a hippocampus, CA1, CA2, CA3, CA4 / dentate gyrus, hippocampal fimbria and a hippocampus tail, and a classification method for realizing three classification of three groups of a normal old age group, a clinically-diagnosed amnestic mild cognitive impairment group and a clinically-diagnosed Alzheimer's disease group through the deep learning convolution neural network of artificial intelligence. The method determines a training set, a verification set and a test set for deep learning of the artificial intelligence by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance image data of the normal old age group, the clinically-diagnosed amnestic mild cognitive impairment group and the clinically-diagnosed Alzheimer's disease group, and can convert nuclear magnetic resonance three-dimensional data into two-dimensional data by utilizing selected two-dimensional slices.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
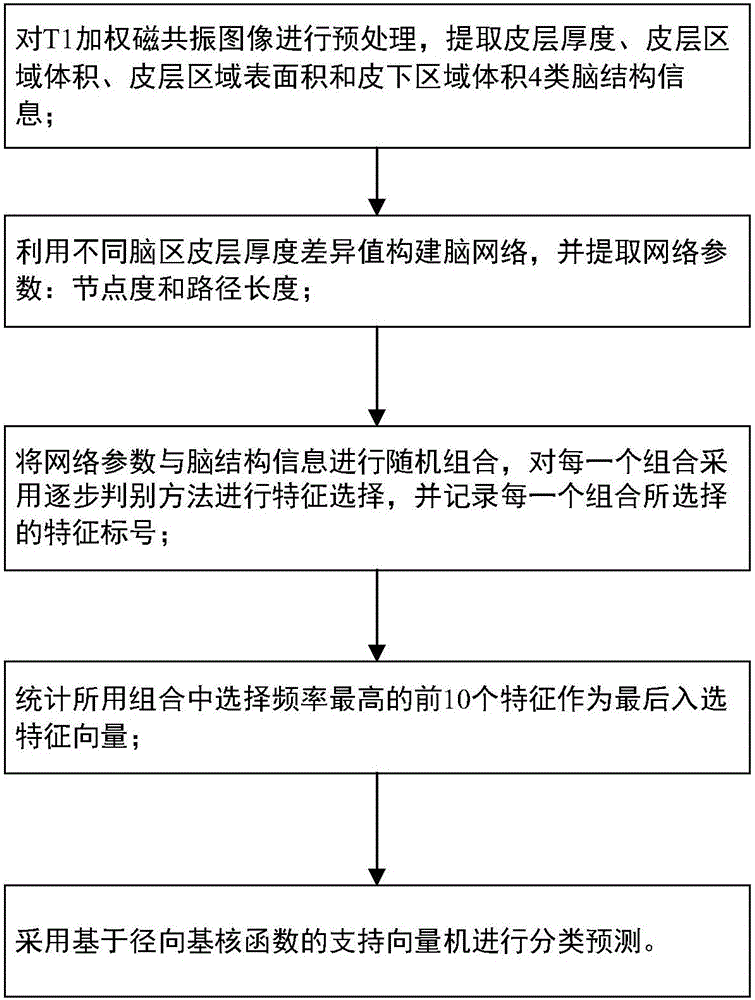
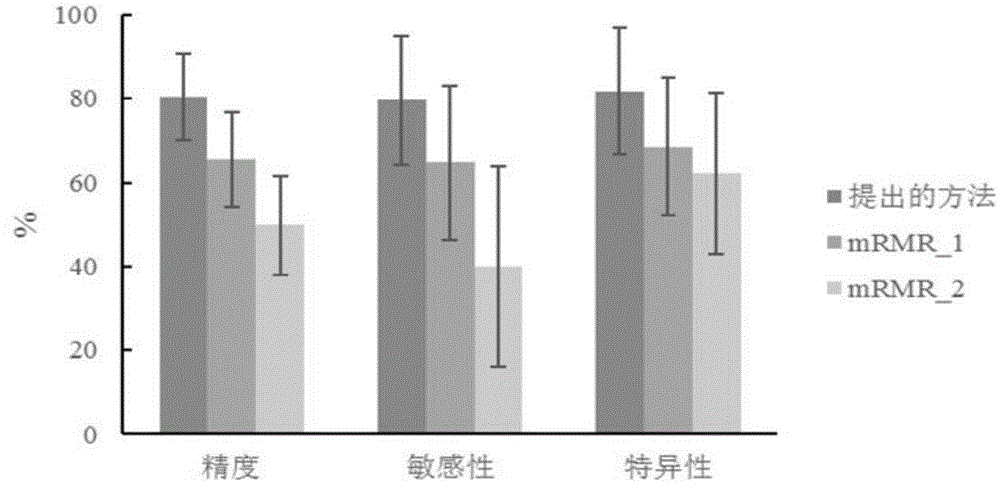
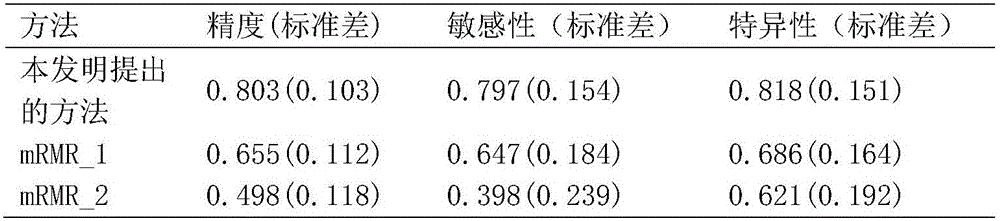
Mild cognitive impairment disease classifying method based on brain network and brain structure information
InactiveCN105726026AQuick and efficient selectionIncreased sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSupport vector machineClassification methods
The invention discloses a mild cognitive impairment disease classifying method based on a brain network and brain structure information, and belongs to the field of medical image disease classification. The method includes the steps that individual cortex characteristics are calculated first, and difference between individual cortices is calculated with a specific kernel function to construct the structural brain network; any number of parameter types are selected from network characteristics and original MRI data to be combined, characteristics are selected from each combined datum through a stepwise judgment method, and the top ten characteristics appearing the most frequently are used as classification characteristics; a support vector machine based on a radial basis function is adopted for classification. The interference on characteristic selection by different combining modes of the cortex characteristics and network characteristics is fully considered, and robustness and stationarity of characteristic selection are ensured. The characteristics with high sensitivity can be selected fast and effectively, and classification precision is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
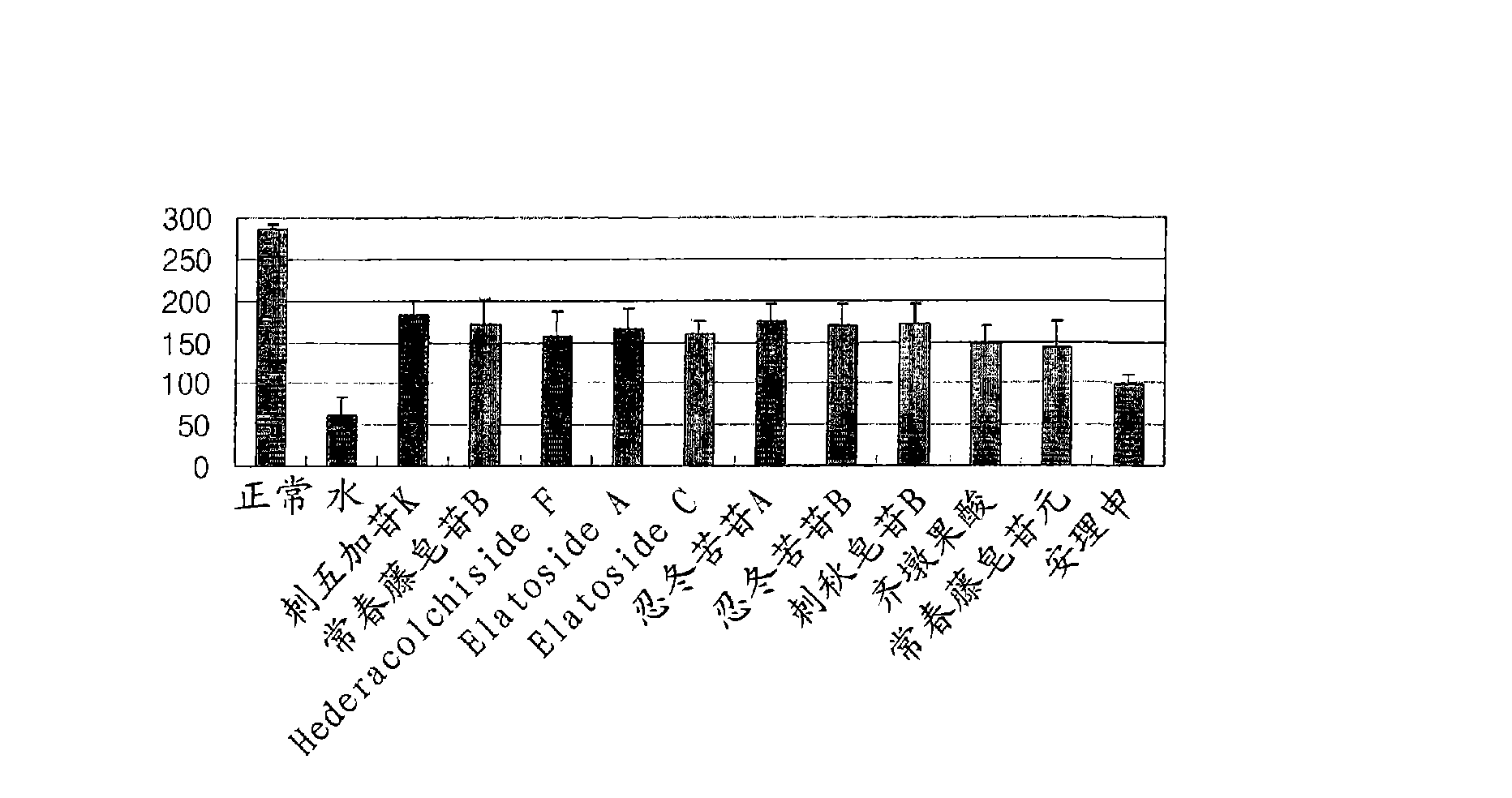
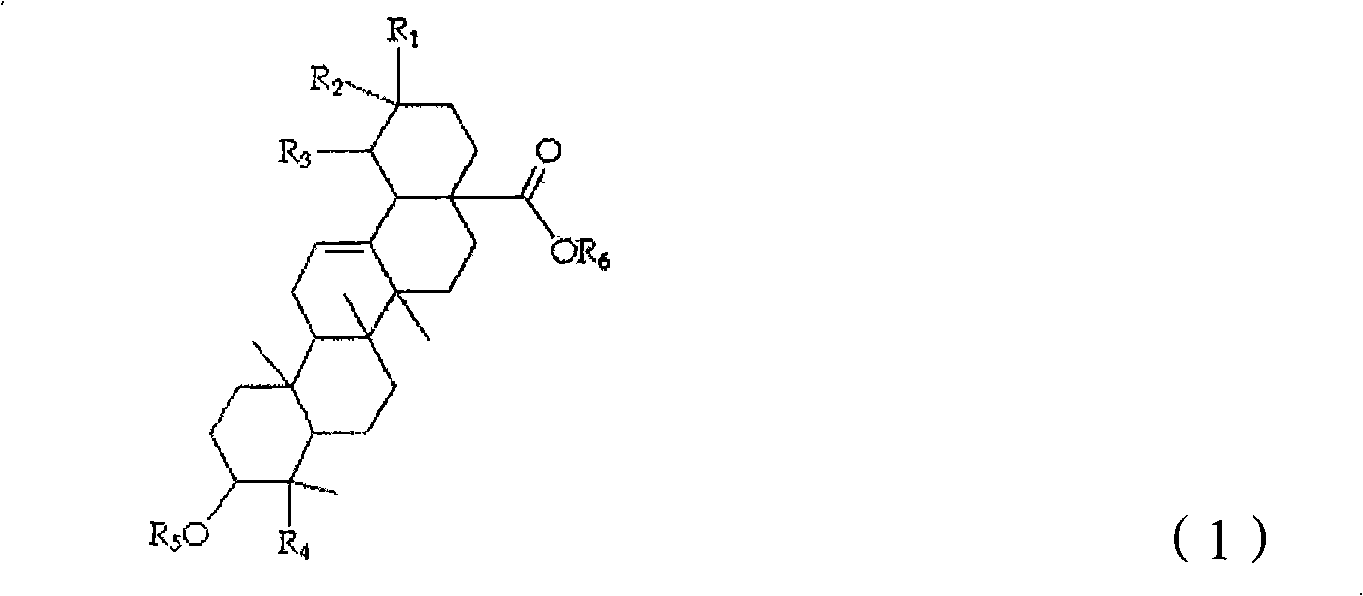
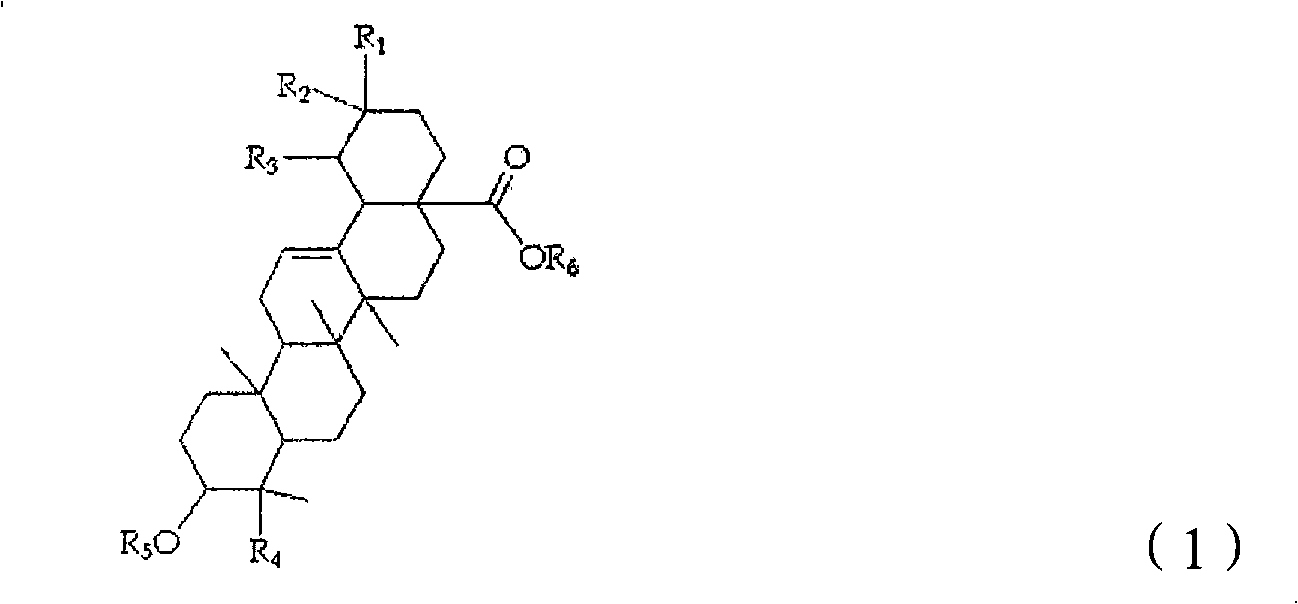
Oleanane triterpene saponin compounds which are effective on treatment of dementia and mild cognitive impairment(MCI), and improvement of cognitive function
InactiveCN101528209AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugTriterpenoid saponin
The present invention relates to the use of oleanane-type triterpene saponin compounds, which are effective for improving memory and learning ability, as an effective ingredient of drugs for the treatment and prevention of dementia and mild cognitive impairment and health foods for the improvement of brain functions including cognitive function.
Owner:SK CHEM CO LTD
Magnesium compositions and uses thereof for cognitive function
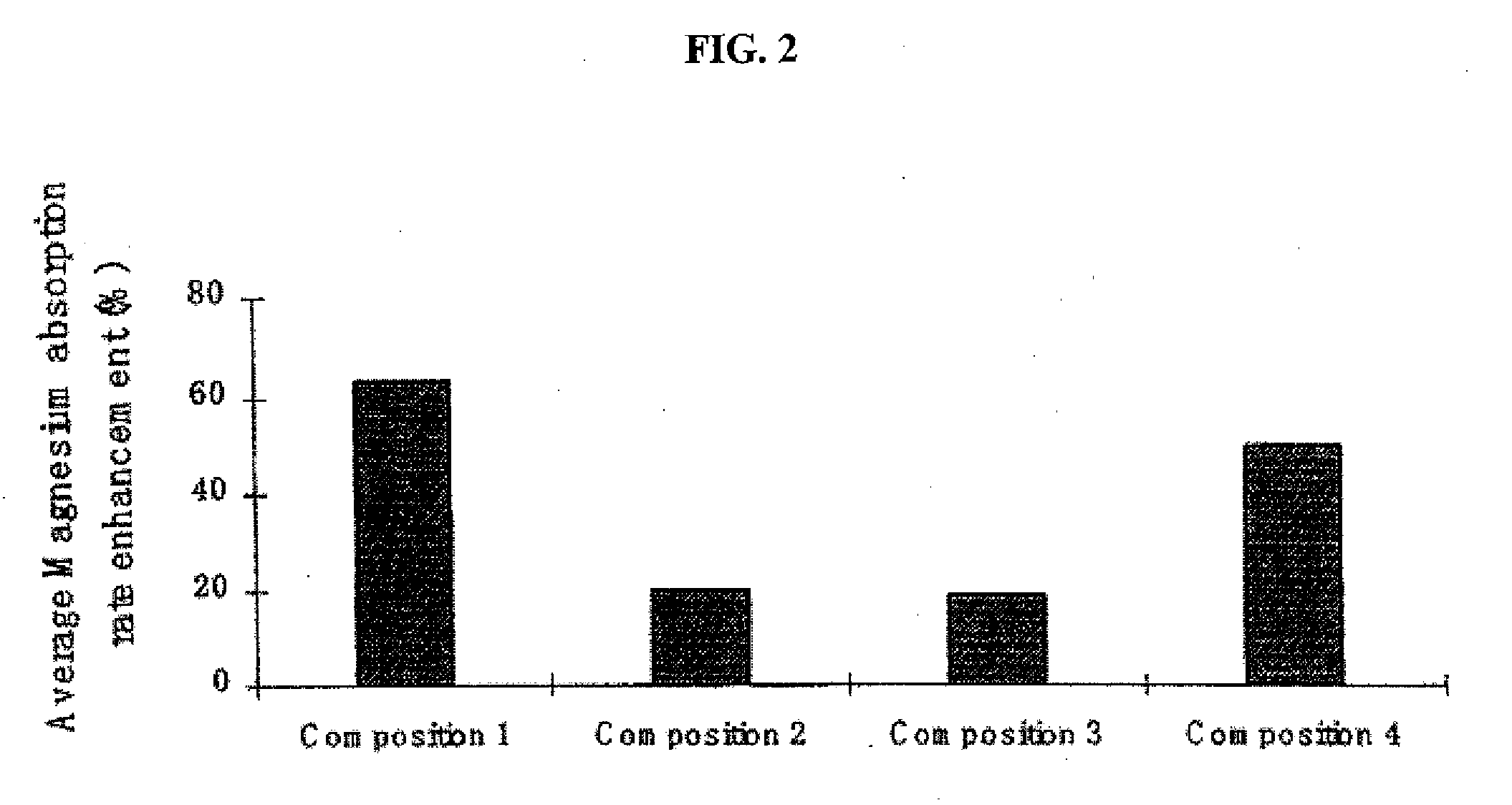
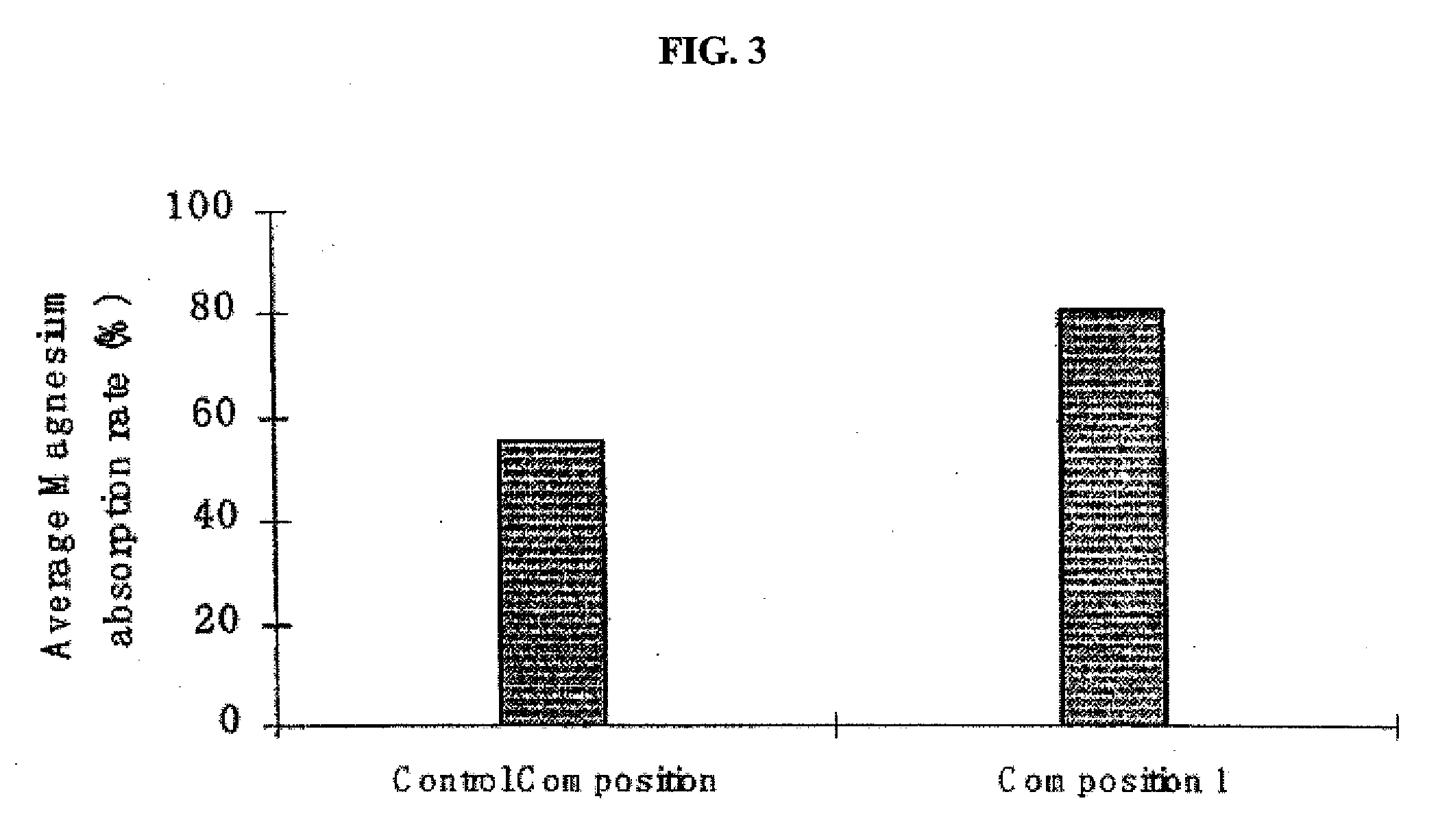
ActiveUS20080269327A1Improve cognitive functionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsAttention deficitsMigraine
Owner:NEUROCENTRIA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com