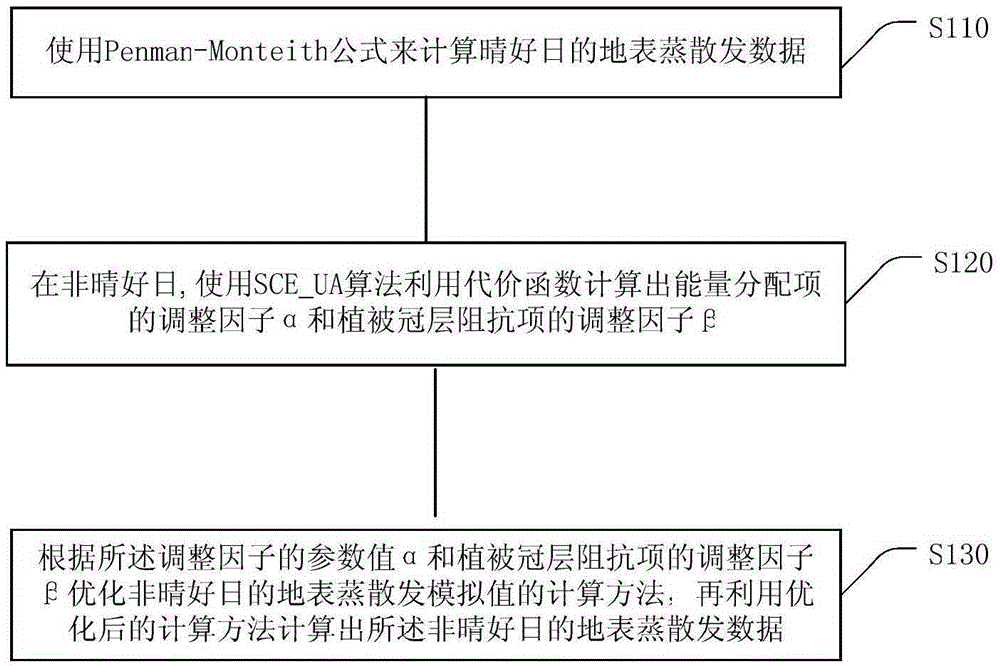
Method for calculating time-continuous surface evapotranspiration data
A calculation method and time-continuous technology, applied in the calculation field of surface evapotranspiration data, can solve the problems of not considering the observation error of remote sensing observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Data assimilation refers to the method of fusing new observation data during the operation of the numerical model on the basis of considering the temporal and spatial distribution of data and the errors of observation field and background field. This algorithm is dedicated to solving the problem of time scale expansion in remote sensing estimation of surface evapotranspiration, combining the assimilation method and the Penman-Monteith formula to expand the time scale of daily evapotranspiration from day to month / year to generate a time-continuous area with a resolution of 1km The evapotranspiration data set promotes the wide application of remote sensing estimation ET products in fields related to hydrological cycle and land surface energy.
[0055] The embodiment of the present invention constructs a complete assimilation system for evapotranspiration data assimilation of the surface by remote sensing, mainly including: model operator, observation operator, assimilation...
Embodiment 2
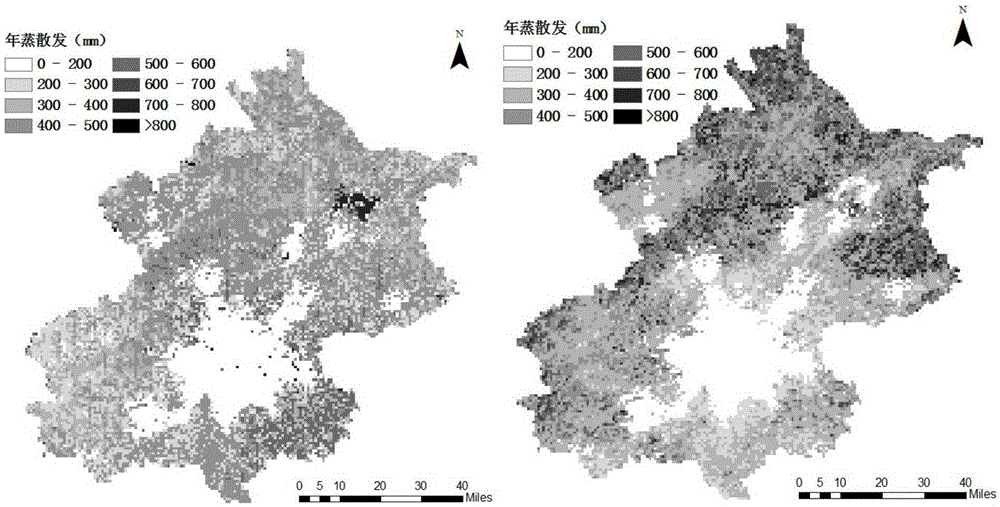
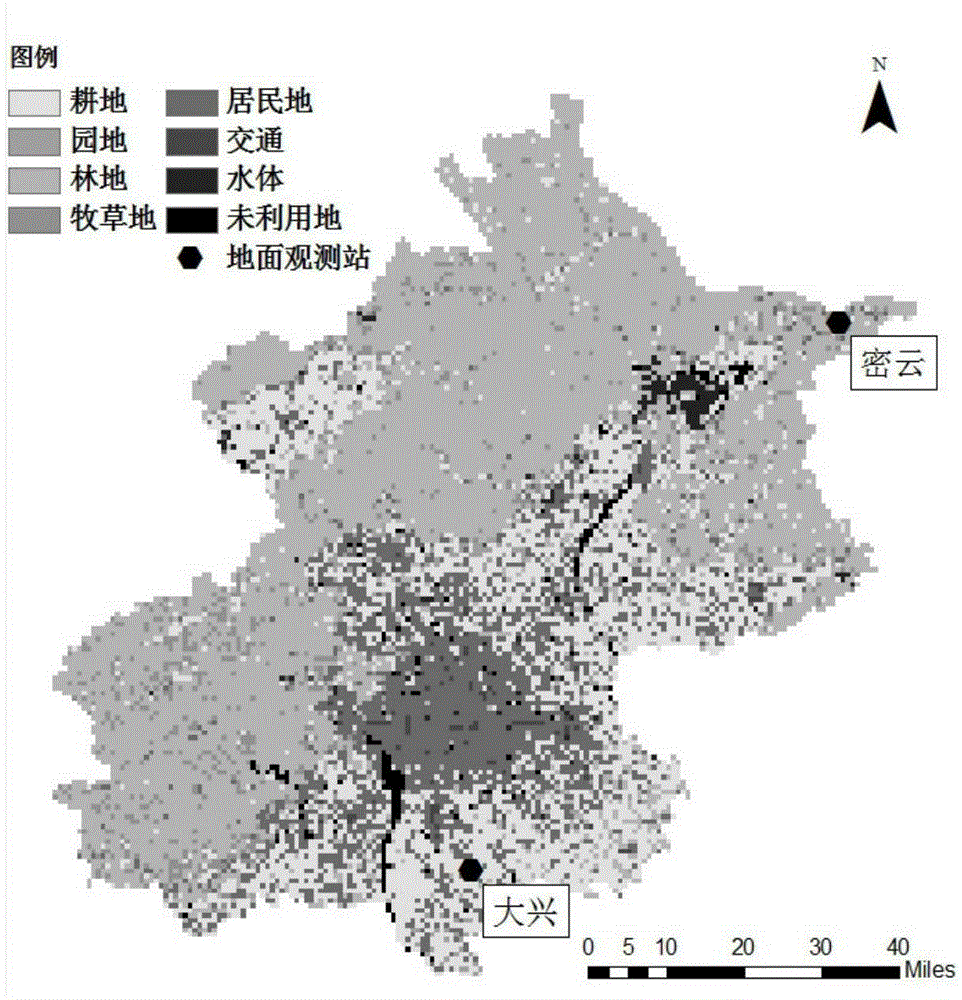
[0153] Beijing is the capital of China, and also the political, economic and cultural center of the country. However, with the deepening contradictions in urban water use, water resources have become a bottleneck restricting the prosperity and development of cities. This algorithm extends the sunny daily evapotranspiration retrieved by the Liu-2007 model to the monthly through the SCE_UA method, and obtains the spatial distribution of annual evapotranspiration. From figure 2 The assimilation method estimation results in (ET_SCEUA) shows that the annual evapotranspiration in the eight urban districts of Beijing is significantly lower than that of the surrounding suburban districts and counties. Small. Among surrounding districts and counties, Huairou and Miyun in the north had higher evapotranspiration than Daxing and Fangshan in the south. This distribution feature of surface evapotranspiration is related to the urban planning of Beijing. There are many real estate projects...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com