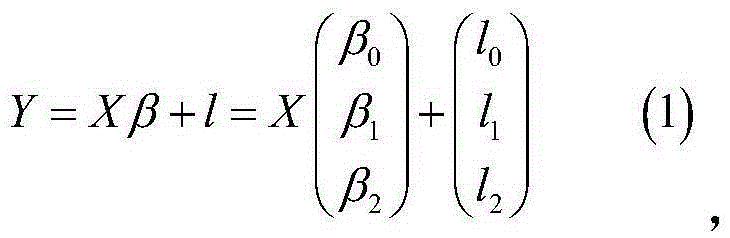Robust-regression-based distributed photovoltaic generating electricity-stealing identification method
A distributed photovoltaic, robust regression technology, applied in the monitoring of photovoltaic power generation, photovoltaic modules, photovoltaic systems, etc., can solve the problems of photovoltaic power calculation error, misjudgment, component matching loss, etc., to improve pertinence and calculation accuracy. High, low impact effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The following examples are only used to illustrate the technical solution of the present invention more clearly, but not to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
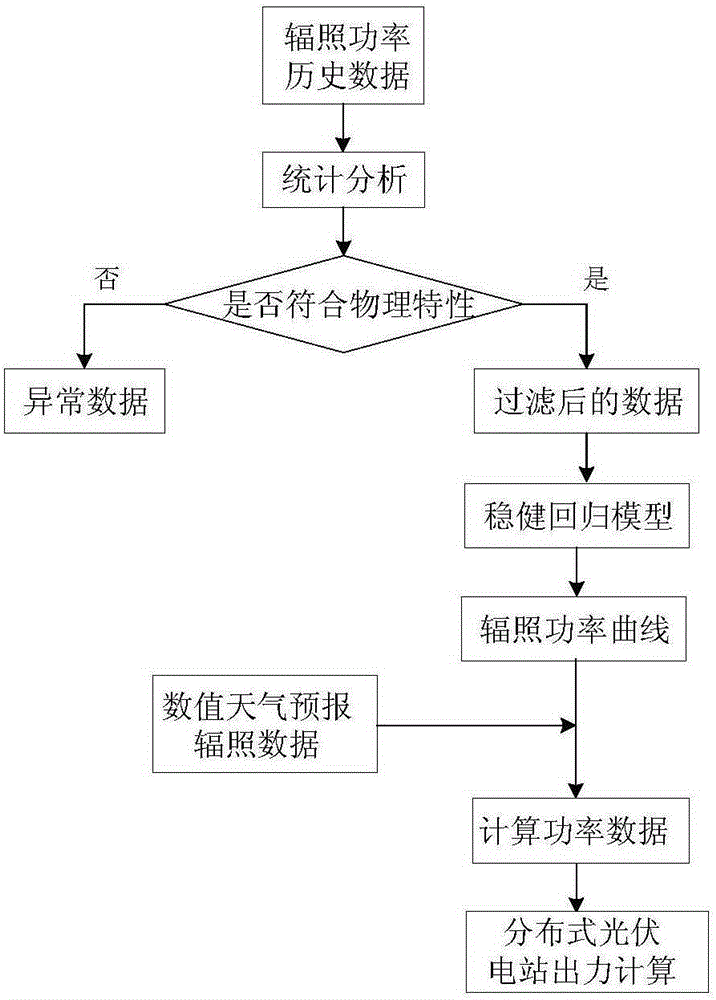
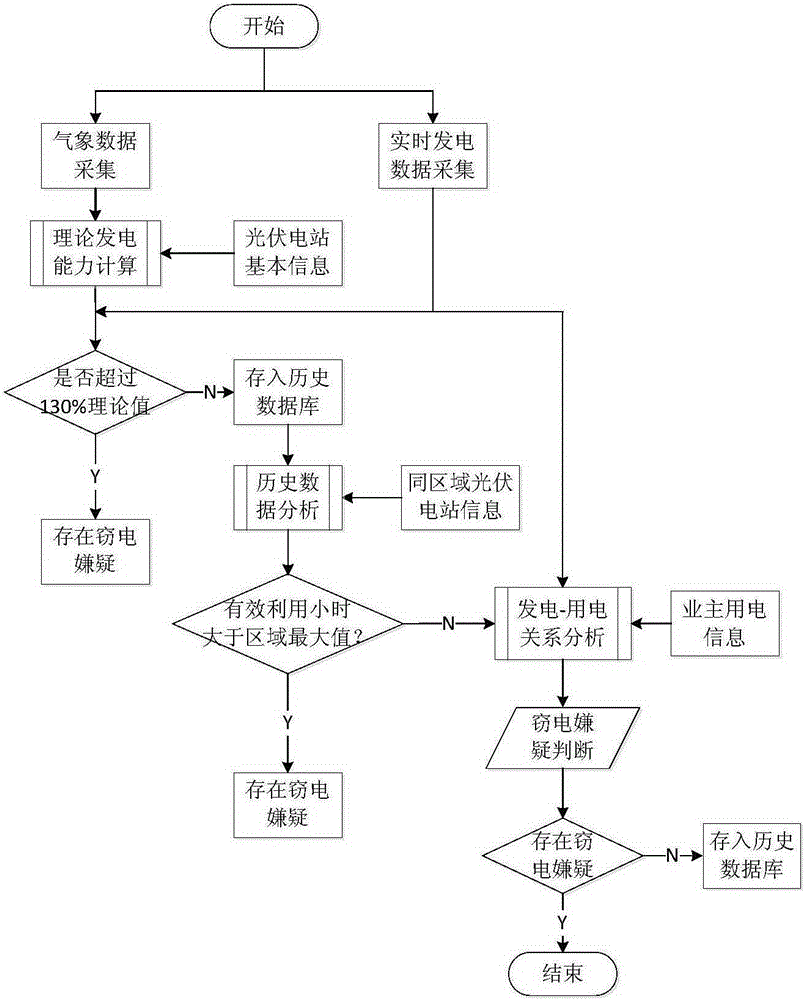
[0022] Aiming at the electricity theft phenomenon existing in the current distributed photovoltaic power generation, the present invention provides a electricity theft identification method based on a robust regression algorithm to judge and analyze distributed photovoltaic owners who are suspected of electricity theft, and provide a theoretical basis for electricity theft inspection.
[0023] The present invention considers that all the energy generated by the photovoltaic power generation system comes from solar radiation, so the intensity of solar radiation received by the photovoltaic cell array directly affects the output of the photovoltaic cell. The greater the radiation intensity, the hig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com