System to increase the in-line power factor of a three-phase brushless DC motor
A power factor and power supply terminal technology, applied in the field of control systems, can solve the problems of power factor reduction and increase, and achieve the effect of low switching loss and low penetration loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
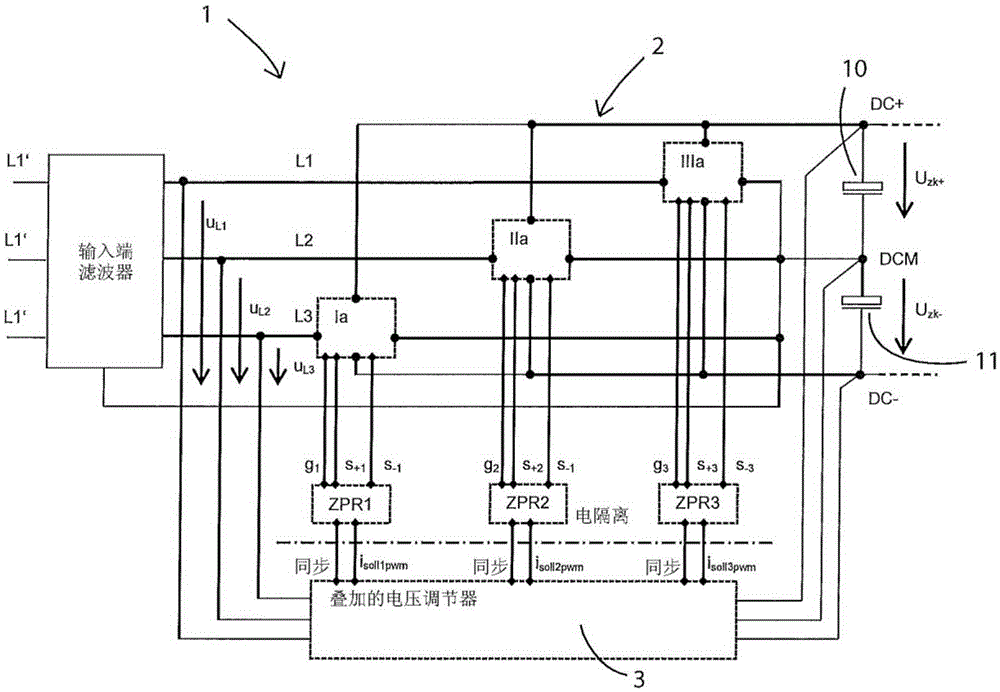
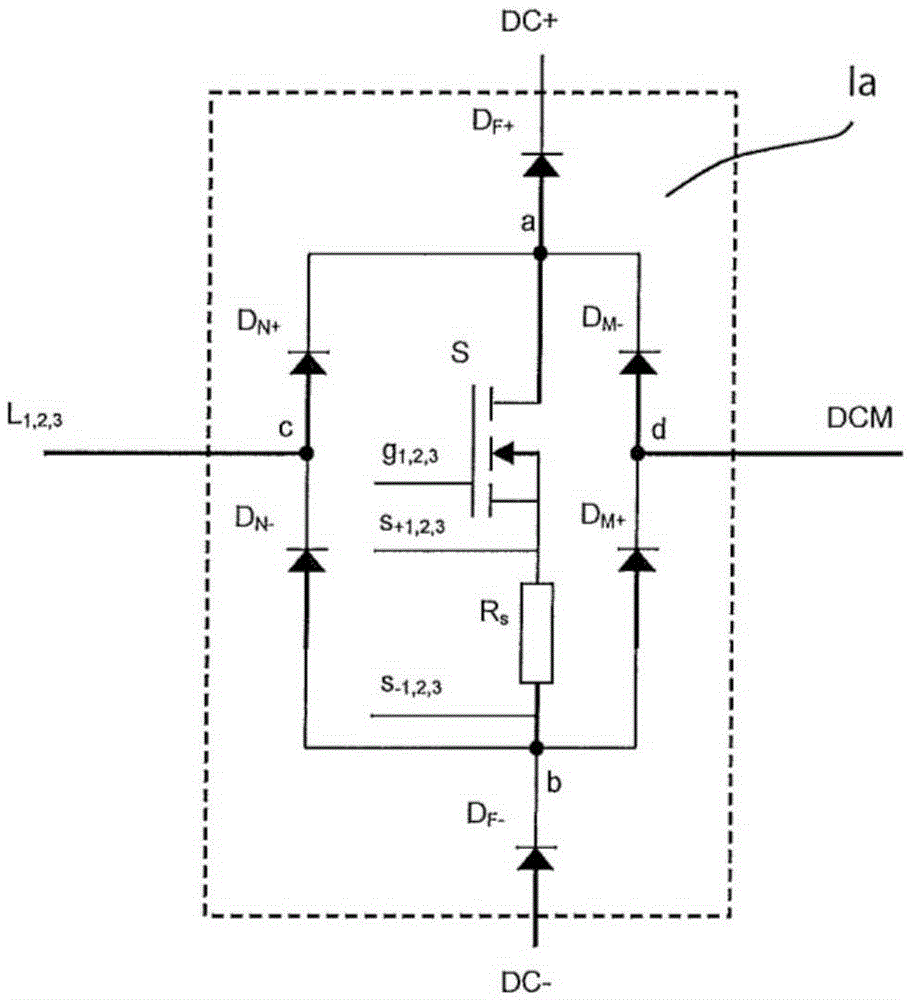
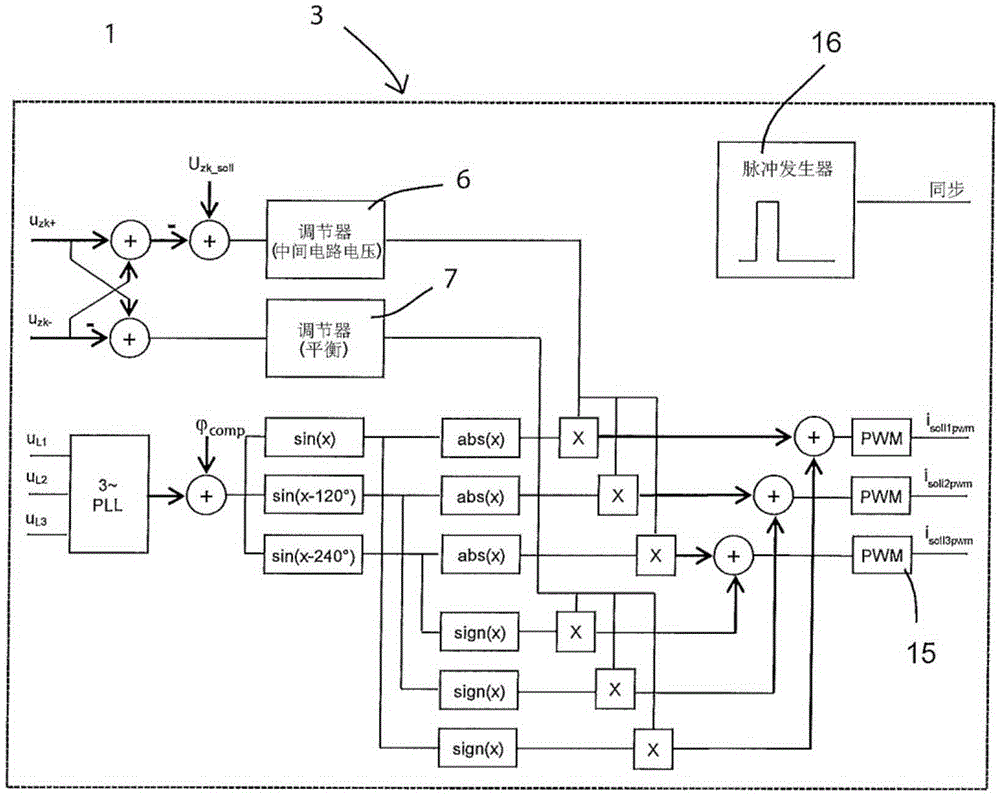
[0033] exist figure 1 An embodiment of a circuit structure with cascade regulation according to the present invention is shown in . It shows a control system 1 for increasing the supply-side power factor λ of a three-phase powered EC motor with a direct voltage intermediate circuit 2 for generating the intermediate circuit positive potential DC+ and negative DC potential and The potential at the intermediate circuit middle section DCM lies between them. The positive intermediate circuit potential DC+ represents the potential at the upper contact of the intermediate circuit capacitor 10 , while the negative intermediate circuit potential DC− represents the potential at the lower contact of the intermediate circuit capacitor 11 . The intermediate circuit voltage share Uzk+ represents the potential difference between the potentials DC+ and DCM, and the intermediate circuit voltage share Uzk− represents the potential difference between the potentials DCM and DC−. The intermediat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com