Optical coupling bidirectional thyristor element
A technology of silicon components and optical coupling, applied in the direction of electrical components, semiconductor devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of short distance, difficulty in obtaining joint margin, and limitation of pad size, so as to ensure withstand voltage, eliminate bad conditions, and chip zoom out effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
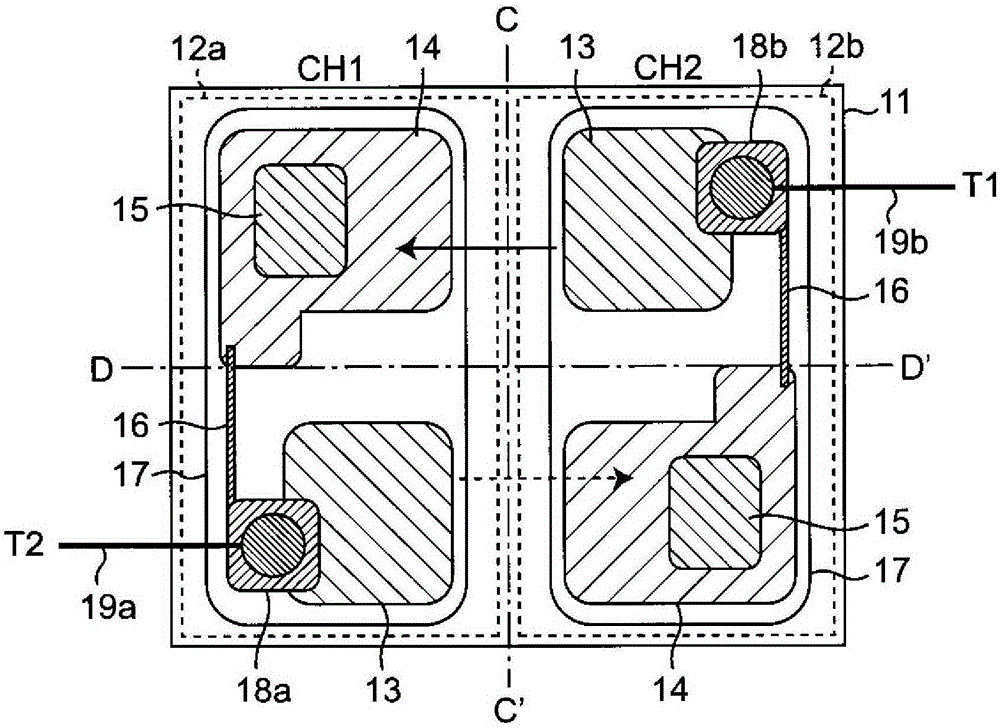
[0061] The optically coupled triac of this embodiment, and Figure 5 The shown optically coupled triac is likewise a point-symmetric optically coupled triac.
[0062] figure 1 A schematic pattern layout of the optically coupled triac of this embodiment is shown. Such as figure 1 As shown, the pattern has 180-degree rotational symmetry with respect to the intersection point of the center line C-C' and the line segment D-D' perpendicular to the center line in plan view, that is, a pattern that is substantially point-symmetrical with respect to the above-mentioned intersection point. Hereinafter, the photothyristor located on the left side of the figure with respect to the center line C-C' is called the photothyristor of CH1, and the photothyristor on the right side is called the photothyristor of CH2.
[0063] This optical coupling triac is composed of the first photothyristor 12 a of CH1 and the second photothyristor 12 b of CH2 formed separately on the surface of the N-typ...
no. 2 approach
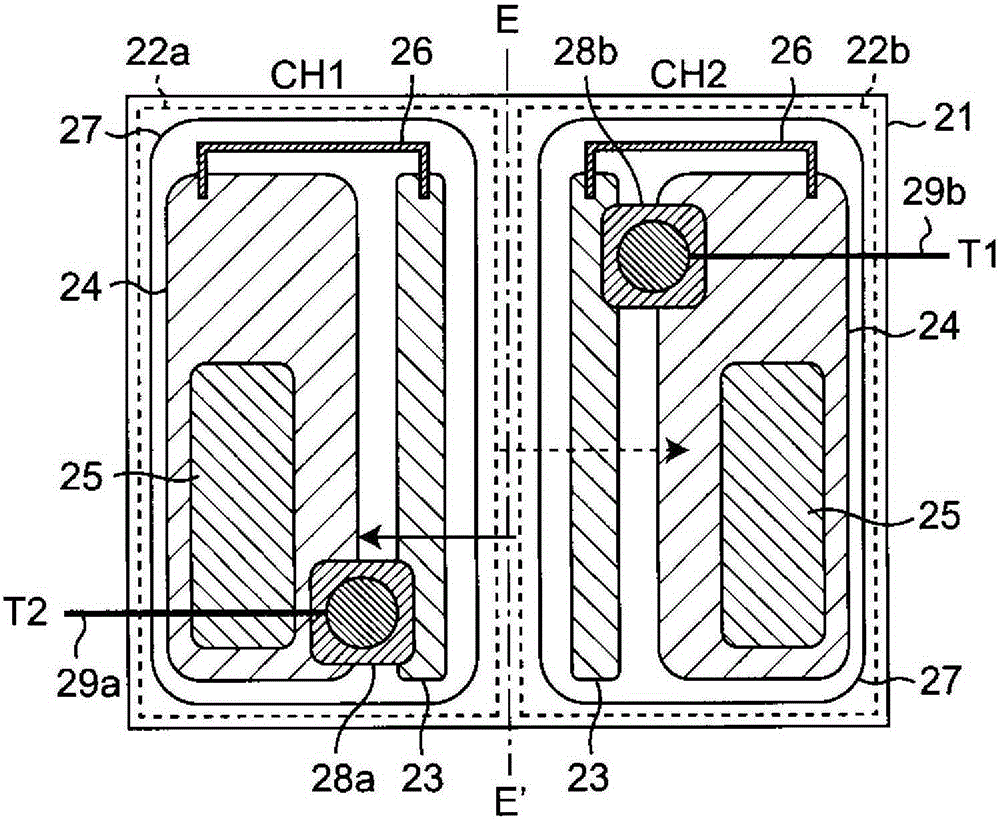
[0077] The optically coupled triac of this embodiment is a line object type optically coupled triac.
[0078] figure 2 A schematic pattern layout of the optically coupled triac of this embodiment is shown. Such as figure 2 As shown in , it has a substantially line-symmetrical pattern with respect to the center line E-E' in plan view. Hereinafter, the photothyristor located on the left side of the figure with respect to the center line E-E' is called the photothyristor of CH1, and the photothyristor on the right side is called the photothyristor of CH2.
[0079] The optical coupling triac is composed of the first photothyristor 22a of CH1 and the second photothyristor 22b of CH2 formed separately on the surface of the N-type silicon substrate 21 .
[0080] The first photosensitive thyristor 22a and the second photosensitive thyristor 22b respectively have: a P-type anode diffusion region 23 formed along the central line EE' on the central line EE' side; The P-type gate di...
no. 3 approach
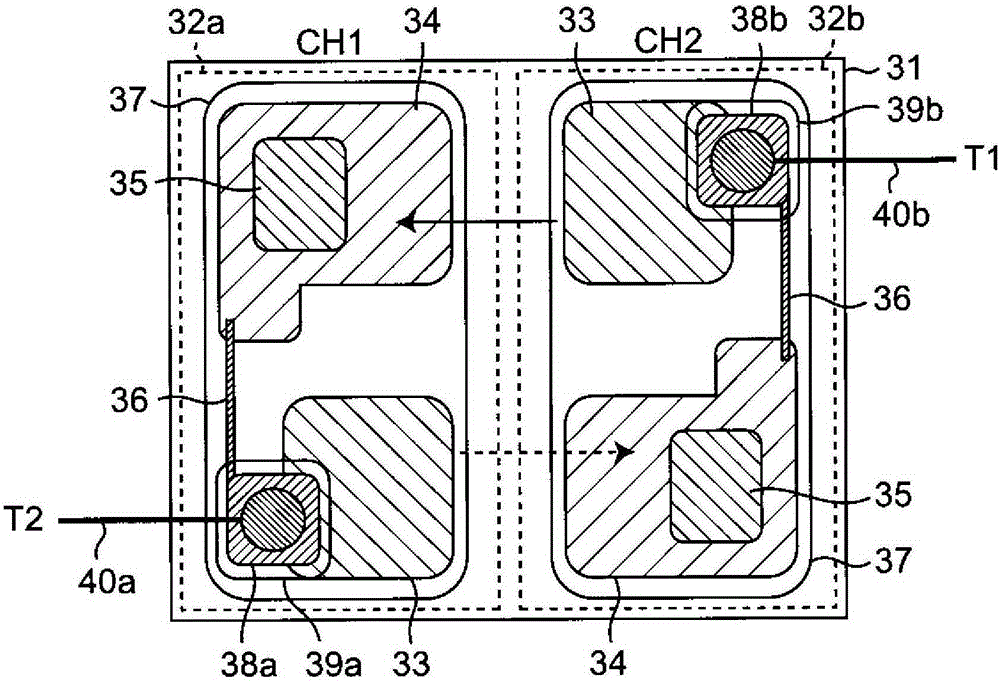
[0089] The optically coupled triac of the present embodiment is a point-symmetrical optically coupled triac similar to that of the above-described first embodiment.
[0090] image 3 The pattern layout of the optical coupling triac of this embodiment is shown. exist image 3 Among them, the N-type silicon substrate 31, the first photothyristor 32a of CH1, the second photothyristor 32b of CH2, the P-type anode diffusion region 33, the P-type gate diffusion region 34, the N-type cathode diffusion region 35, the high-resistance pattern 36. Al electrodes 37, pads 38a, 38b, Au wires 40a, 40b, and the N-type silicon substrate 11 in the first embodiment, the first photothyristor 12a of CH1, the second photothyristor 12b, P of CH2 Type anode diffusion region 13, P-type gate diffusion region 14, N-type cathode diffusion region 15, high resistance pattern 16, Al electrode 17, pads 18a, 18b, Au lines 19a, 19b are identical.
[0091] In addition, the operation of the optically coupled ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com