Recombinant vector vaccine expressing HIV antigen
A recombinant vector and vaccine technology, applied in the field of recombinant vector vaccine and its construction, can solve problems such as unsuitability for application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
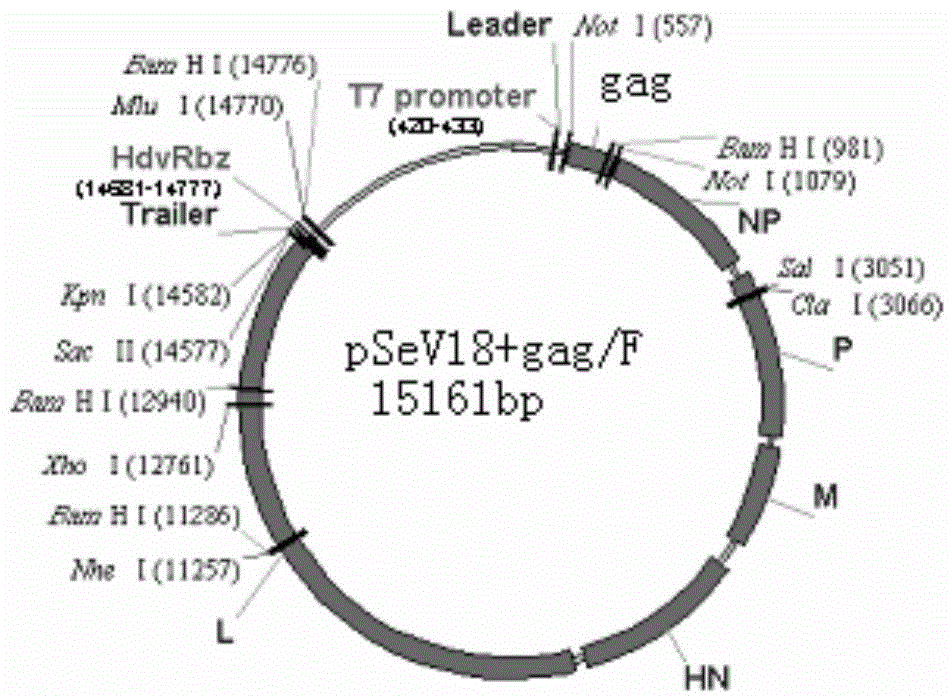
[0039] Construction of non-transmissible Sendai virus vector (SeV / dF) with deletion of F gene
[0040] The present invention obtains the Sendai virus vector with F gene deletion through a series of PCR, enzyme digestion and connection means, and the specific construction process is as follows:
[0041] 1. Clone the full base sequence of the Z strain in Sendai virus to obtain the plasmid pSeV with the full-length cDNA of SeV.
[0042] 2. Digest the plasmid pSeV with restriction endonucleases SphI and KpnI at the same time, recover a 3500bp fragment, and name it pSeV△SK plasmid, and name the excised 14670bp fragment 1, most of which are the genome sequence of Sendai virus.
[0043] 3. Carry out insertion mutation by PCR: insert 18 bp sequence with NotI site at the 119th position of Sendai virus genome sequence, obtain plasmid and pSeV18.
[0044] The primer sequences and methods used are as follows, and the NotI restriction site is underlined.
[0045] OP1,5'-TCTGACACATGCAGCTC...
Embodiment 2
[0060] HIV gag Gene Cloning, Modification and Introduction of Sendai Virus Vector with F Gene Deletion
[0061] 1. Collect venous blood from HIV-positive patients in AIDS-endemic areas in Henan;
[0062] 2. Using Qiagen's QiaAmpBlood kit to extract total cellular DNA from the above venous blood;
[0063] 3. According to the consensus sequence of the gag gene, design primers, use the total DNA in step 2 as a template, amplify the gag gene and connect it to the pMD18-Teasy vector (purchased from Promega) to obtain the plasmid pMD18-T-gag, and transform into DH5α competent Cells (Promega), smeared on a plate, cultured, picked a single clone and cultured, extracted plasmids for enzyme digestion identification;
[0064] 4. Sequencing the correct plasmid identified by enzyme digestion in step 3, and comparing the sequencing results with the gag gene of the B subtype standard strain, the results show that the gene has the sequence characteristics of the B subtype;
[0065] 5. Accordi...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Construction of Particles Expressing Sendai Virus Helper Protein
[0069] 3.1 Construction of plasmid pGEM-NP expressing Sendai virus NP protein:
[0070] 1. Digest pSeV-TDK (from DNADEC) and pGEM11Zf(+) (purchased from Promega) with restriction endonucleases NotI / XhoI respectively, and connect the nucleotide sequence containing the NP protein to pGEM11Zf after digestion (+) on;
[0071] 2. Design the following primers to amplify the nucleotide sequence encoding the NP protein using the product obtained in step 1 as a template:
[0072] forward primer, 5'-CCGGAATTCAACAAATGGCCGGGTTGTTGAGCACCTTCGA-3';
[0073] reverse primer, 5'-CCGGAATTCCTAGATTCCTCCTATCCCAGCTACTGCTGCTCG-3';
[0074] 3. Digest the PCR product with EcoRI and connect it to the vector pGEM11Zf(+) to obtain the pGEM-NP plasmid.
[0075] 3.2 Construction of plasmid pGEM-P expressing Sendai virus P protein:
[0076] 1. Use SeVcDNA as a template to amplify the gene encoding the P protein, and the primer seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com