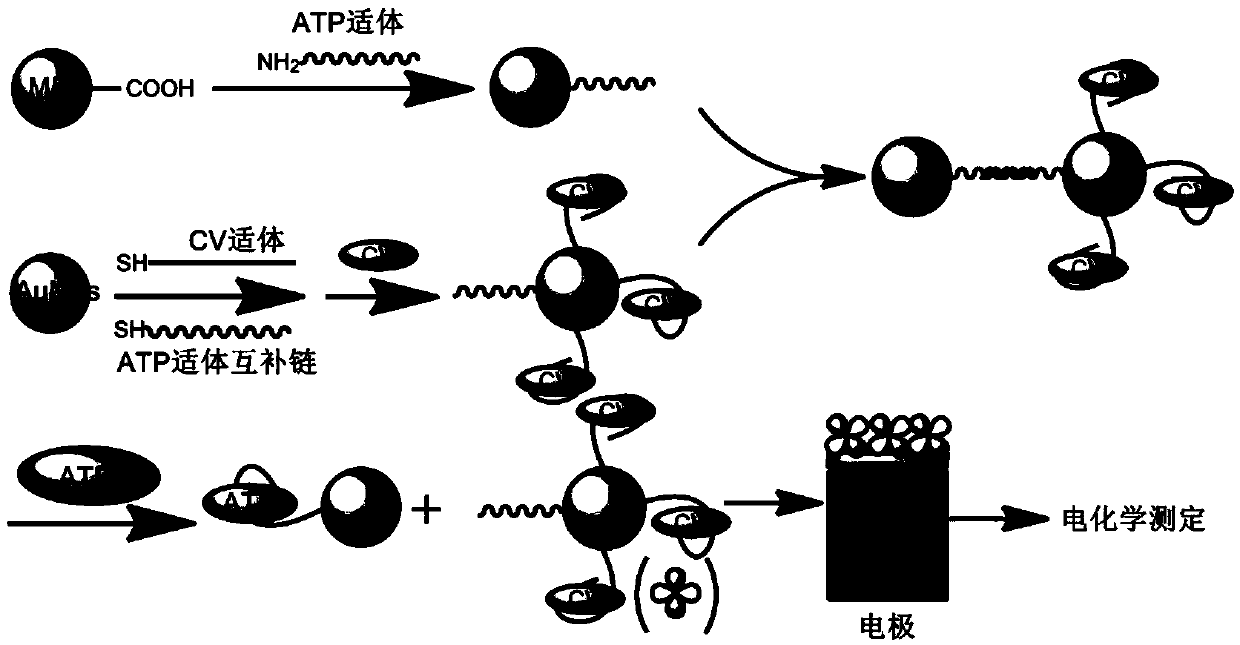
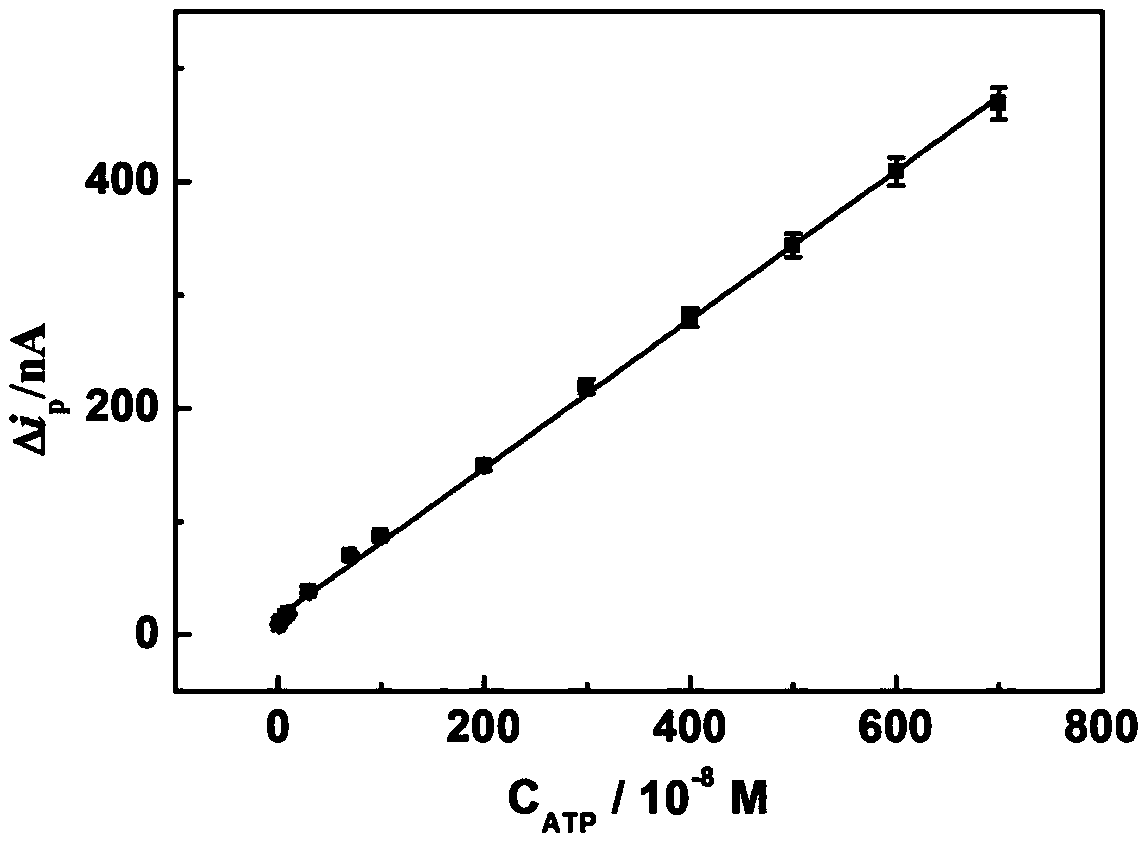
Method for determining ATP content on basis of magnetic bead separation and DNA marker gold nanoparticle probe
A gold nanoparticle and DNA labeling technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, material analysis and material analysis by electromagnetic means
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
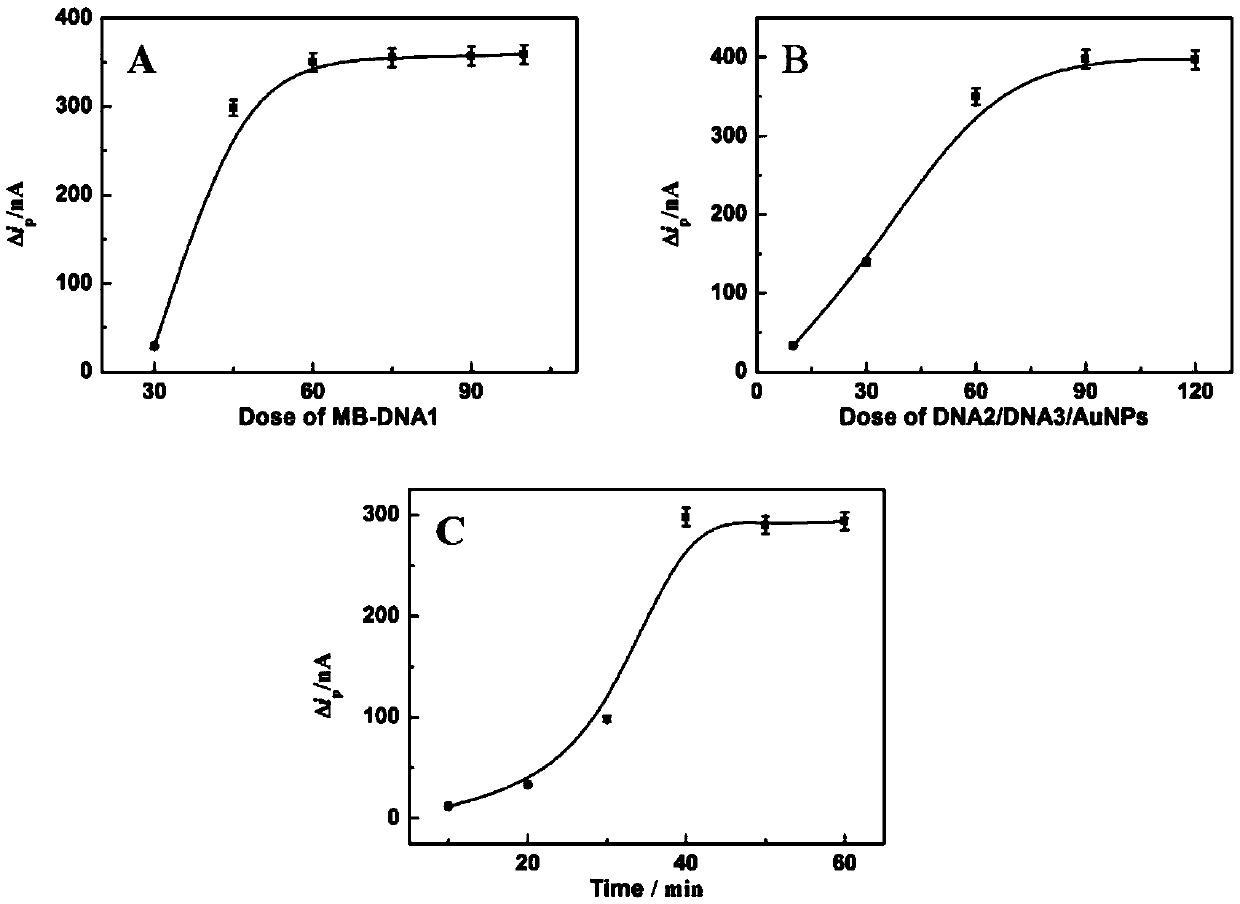
[0031] The impact of the amount of embodiment 1MB-DNA1 on the electrochemical signal
[0032] MB-DNA1 was used as a carrier for immobilizing probes. Firstly, the amount of probe solution was fixed, and the change of detection signal was investigated when the amount of MB-DNA1 solution was changed. The experimental results showed that the detection signal increased with the increase of the amount of MB-DNA1 solution; when the amount was greater than 75 μL, the signal change trend slowed down ( figure 2 (A)). Therefore, 75 μL was selected as the optimal dosage of MB-DNA1 solution in the experiment.
Embodiment 2
[0033] The impact of embodiment 2 probe dosage on electrochemical signal
[0034] When the amount of fixed MB-DNA1 solution was 75 μL, the effect of the amount of probe on the signal intensity was investigated. With the increase of the amount of probe, the detection signal gradually increased. When the amount of probe was 90 μL, the signal was the largest ( figure 2 (B)). Therefore, 90 μL was selected as the optimal amount of probe in the experiment.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Effect of ATP and aptamer binding time on electrochemical signal
[0036] The experiment examined the effect of the binding time of ATP and aptamer on the signal intensity. The signal intensity increased rapidly with the increase of the binding time. The signal intensity reached the maximum at 40 minutes, and then stabilized. It can be seen that 40 minutes is enough for ATP and aptamer. body binding ( figure 2 (C)). Therefore, 40 min was selected as the optimal binding time in the experiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com