Method for rapidly detecting content of ATP of plant leaf
A technology of plant leaves and detection methods, applied in the field of spectral detection, can solve the problems of limited experiments, lack of convenient and easy-to-use methods and equipment, etc., and achieves the effects of high work efficiency, simple and fast measurement methods, and reliable detection results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
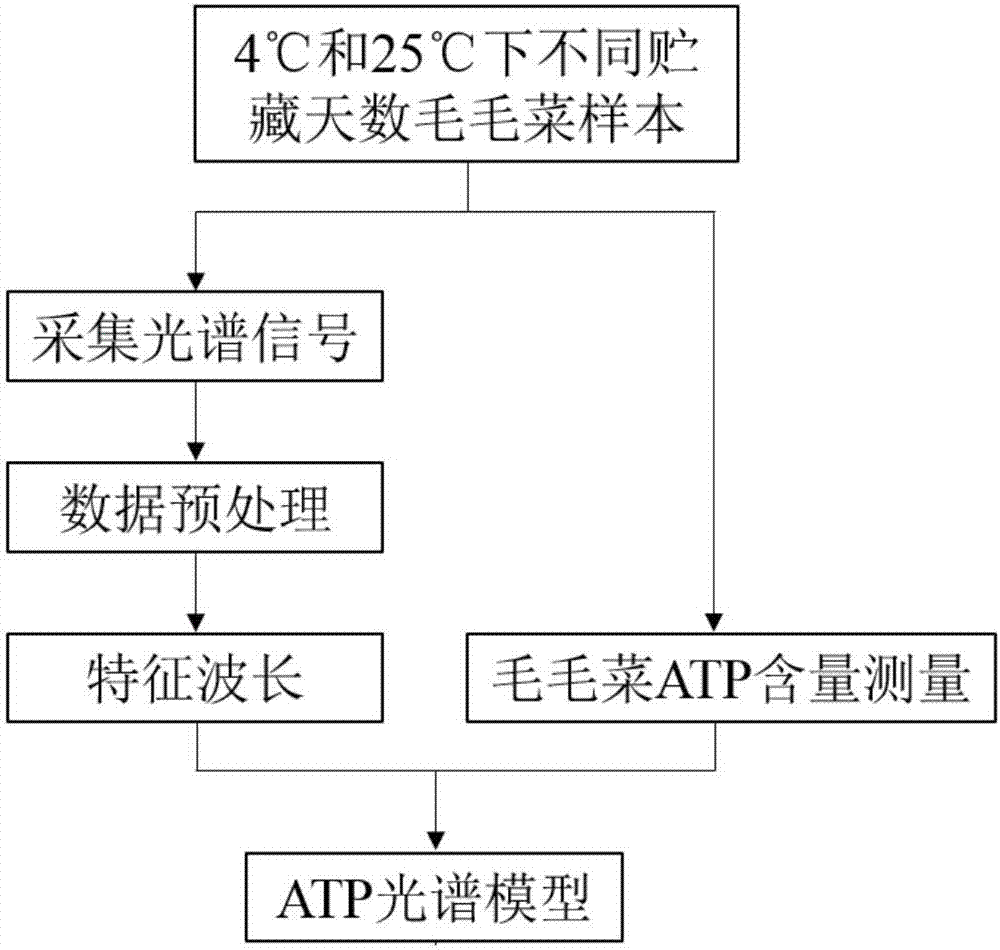
[0037] Take Mao Maocai as an example, such as figure 1 Shown, the rapid detection method of ATP content in plant leaf of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1) Use a spectrometer to separately collect the spectral signal intensity of the 221.99-1019.78nm band of the leaf samples of Prunus edulis at 4°C-25°C for different storage days, and collect the spectral information at 4 different positions for a sample of Prunus edulis leaves;
[0039]Perform averaging and denoising processing on the above spectral signal intensity, and select 15 characteristic wavelengths with continuous projection algorithm, which are 400.21nm, 402.57nm, 404.14nm, 407.29nm, 408.86nm, 410.44nm, 415.94nm, 501.15nm, 526nm , 557.72nm, 647.55nm, 674.22nm, 684.1nm, 693.98nm, 712.16nm;
[0040] (2) Detect the ATP content in the corresponding tomato pulp sample with bioluminescence detection method subsequently, specifically as follows:
[0041] (2-1) Tomato pulp luminescent sample...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com