A Peak-to-Average Ratio Suppression Method of ofdm System Based on Differential Evolution Algorithm
A differential evolution algorithm and peak-to-average ratio suppression technology, applied in the field of communication transmission, can solve problems such as high time complexity, and achieve the effect of low hardware overhead and low time complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
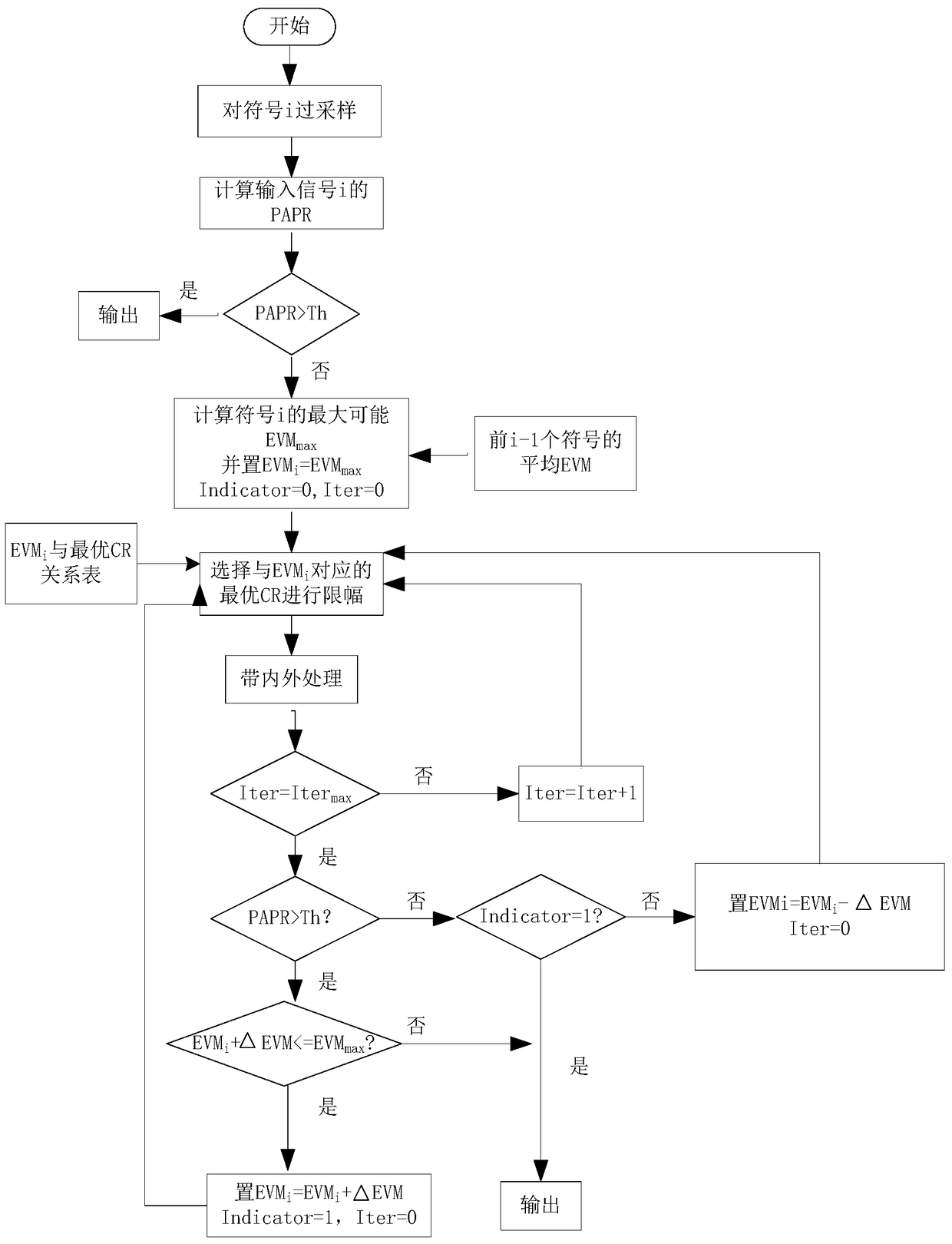
[0105] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
[0106] A peak-to-average ratio suppression method for OFDM systems based on differential evolution algorithm (DEPR),
[0107] S1. Randomly generate the initial population
[0108] The population of DEPR algorithm is N-dimensional noise vector, and the initial noise vector is randomly generated from the whole noise space.
[0109] First you need to define the N-dimensional noise vector e(n)
[0110] e(n)=x(n)-x'(n),
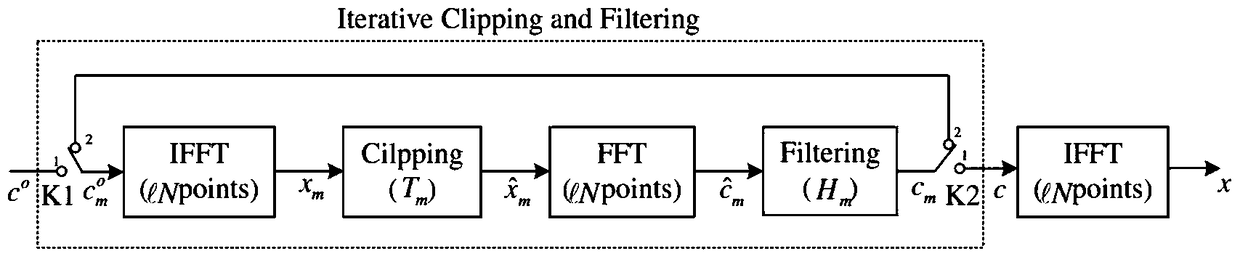
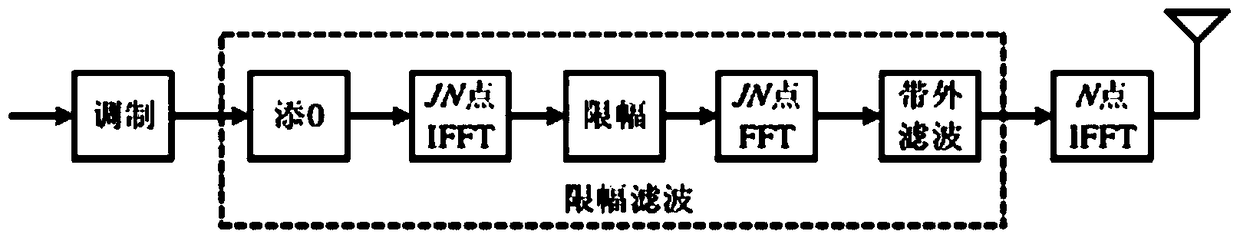
[0111] e(n) is the offset introduced by various methods during the filtering process. Noise can serve the same purpose, but effectively reduces the search space of the signal compared to the original signal. x(n) is the original time-domain signal, and x'(n) is the filtered signal.
[0112] X'(K)=DFT[x'(n)]
[0113] =DFT(x(n)-e(n)) L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com