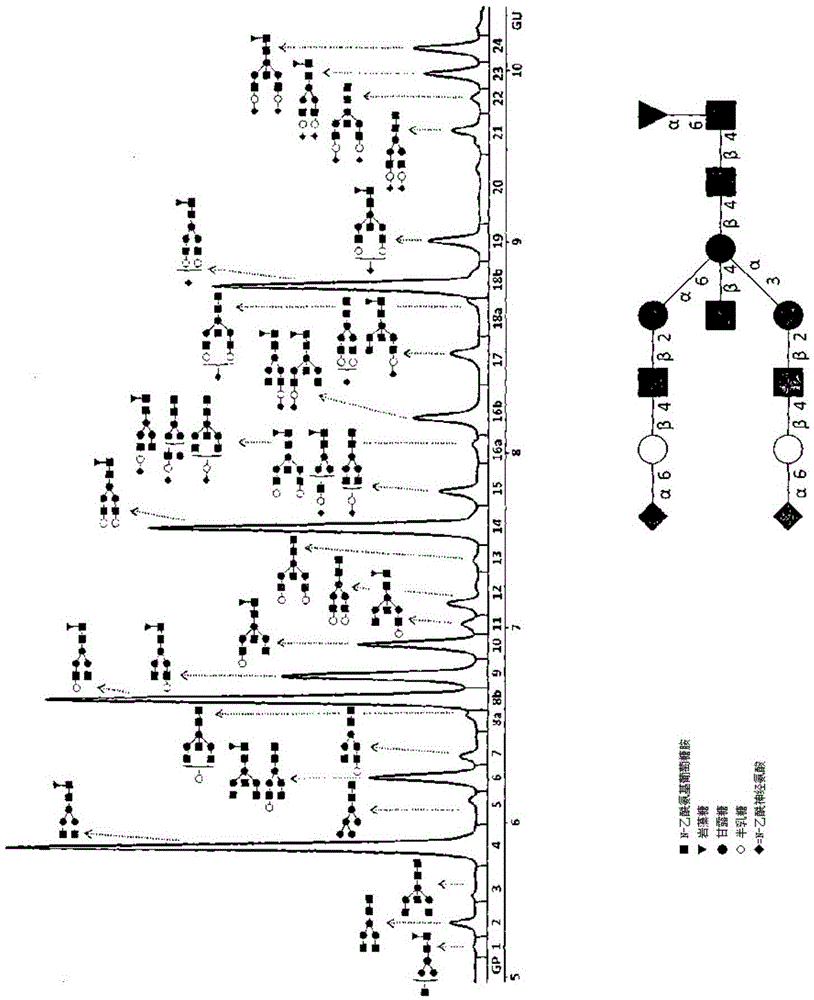
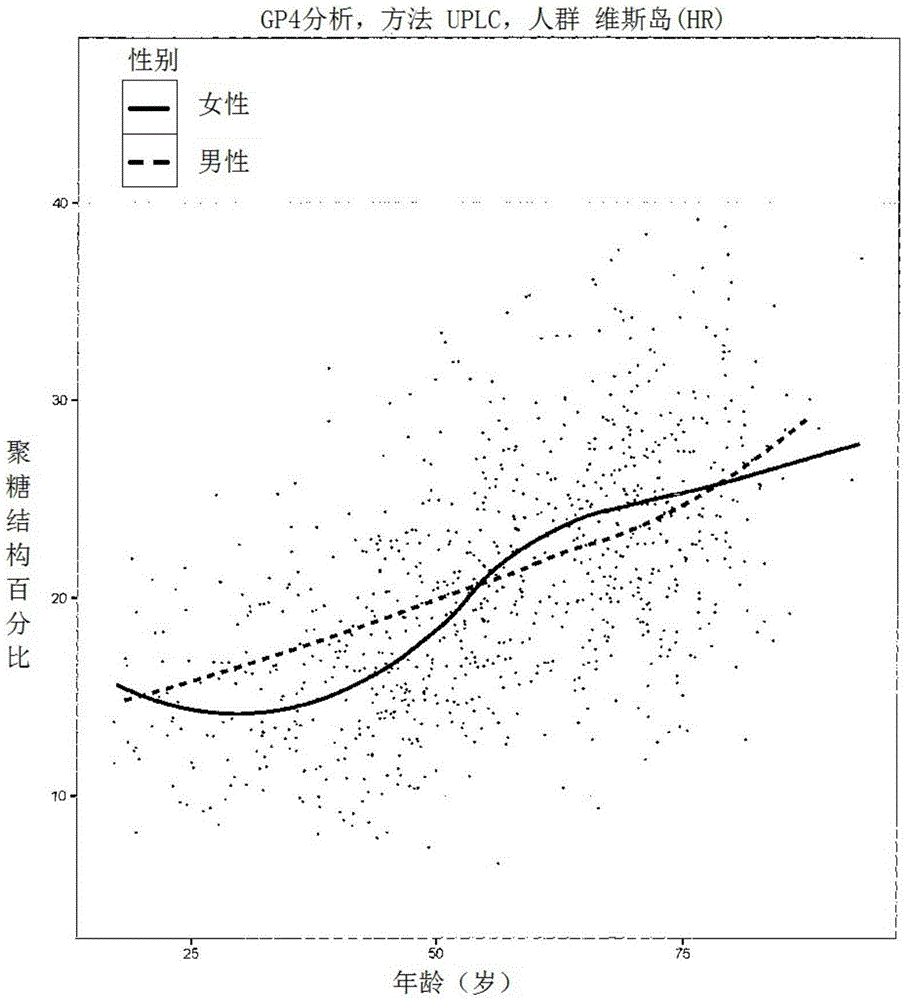
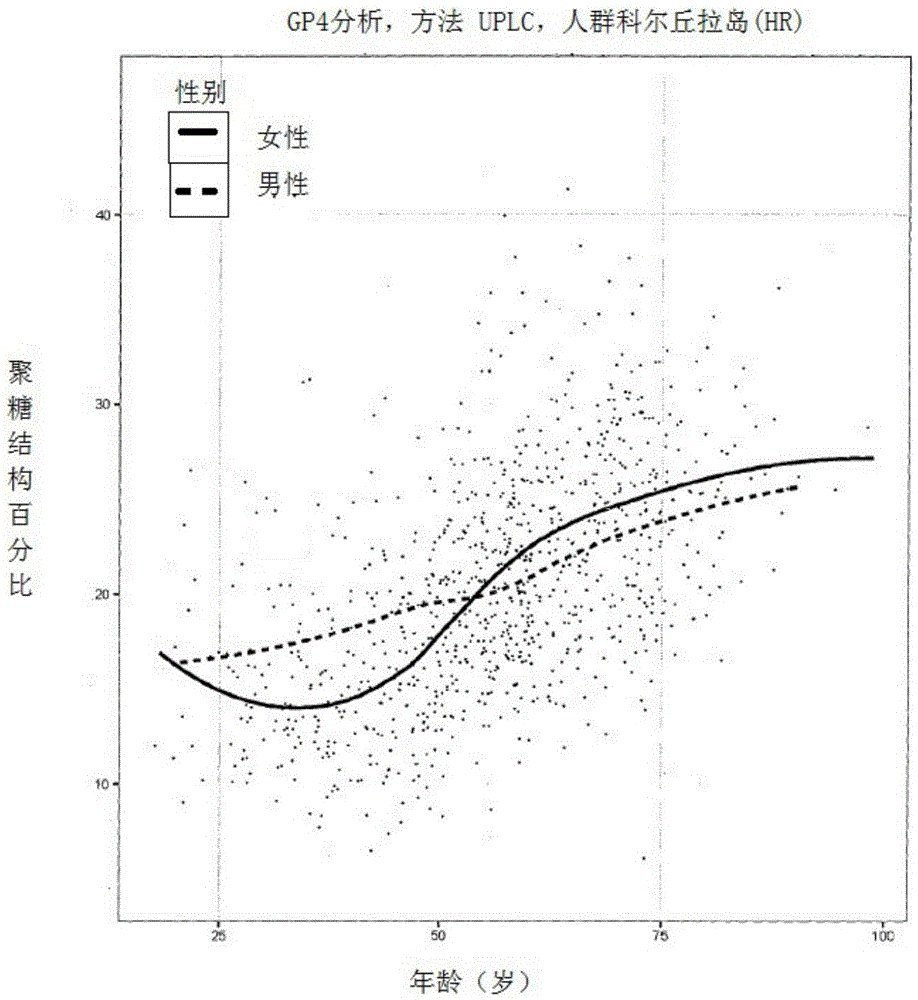
Method for the analysis of N-glycans attached to immunoglobulin G from human blood plasma and its use
一种免疫球蛋白、分析方法的技术,应用在人类血浆中的免疫球蛋白G连接的N-聚糖的分析及其应用领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0179] Example 1 Purification of Immunoglobulin G (IgG) from Plasma
[0180] Immunoglobulin G (IgG) was purified from plasma by affinity chromatography with the aid of protein G bound to a monolithic column in a 96-well microplate (BiaSeparations, Ljubljana, Slovenia). All solutions used in the purification process were prepared with ultrapure water and filtered through 0.2 PES filters. All washing steps through the monolith were accomplished with the aid of a vacuum pump (Pall Corporation, MI, USA). Before use, the chromatographic column was washed with 2 ml of water and activated with 4 ml of binding buffer (lxPBS; pH=7.4). Prior to loading on the monolithic column, 100 ml of plasma was diluted with binding buffer (1:7, V / V) and filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size GHP filter plate. After dilution and loading of filtered plasma, the monolithic chromatography plate was washed 3 times with 2 mL of binding buffer to remove unbound protein. The IgG antibody was eluted fro...
Embodiment 2
[0181] Example 2 Release of Glycans from Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
[0182] An aliquot of purified IgG (app. 100 μg) was dried in a vacuum centrifuge, then resuspended and denatured in 30 μl of 1.33% SDS solution at 65° C. for 10 minutes. Subsequently, 10 μl of 4% NP40, 10 μl of 5-fold PBS and 1.25 mUP PNGazeF (N-glycosidase F, ProZyme, California, USA) were added. The mixture was incubated overnight at 37°C.
Embodiment 3
[0183] Example 3 Labeling IgG Glycans and Removing Excess Fluorescent Labels
[0184] After deglycosylation, add 25 μl of fluorescently labeled mixture to the reaction mixture: a mixture of acetic acid and dimethyl sulfoxide containing 0.48 mg of 2-aminobenzamide (2AB) and 1.12 mg of 2-picoline borane ( 30%:70%, V / V). The mixture was incubated at 65°C for 2 hours. Excess markers were removed by means of microcrystalline cellulose added to 0.45 μm pore size GHP filter plates. Add 200 μl of 0.1 g / mL cellulose aqueous suspension to each well of the filter plate. The cellulose was washed 5 times with 200 μl of water and 3 times with 80% acetonitrile for activation. After labeling, the reaction mixture diluted with 400 μl of acetonitrile was added to the cellulose. Wash the cellulose 7 times with 200 μl of 80% acetonitrile to remove excess marker. Wash the cellulose twice with 100 μl of water to elute the labeled immunoglobulin glycans. The eluate of IgG glycan 2-aminoben...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com