Polymer-flavonoid conjugates and hydrogels for biomedical applications
A technology for polymers and flavonoids, which can be used in pharmaceutical combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, inactive components of polymer compounds, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability of flavonoids, and no way of preparing stable polymer-flavonoid conjugates. , to achieve the effect of improving bioavailability, improving biological activity, and avoiding the separation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
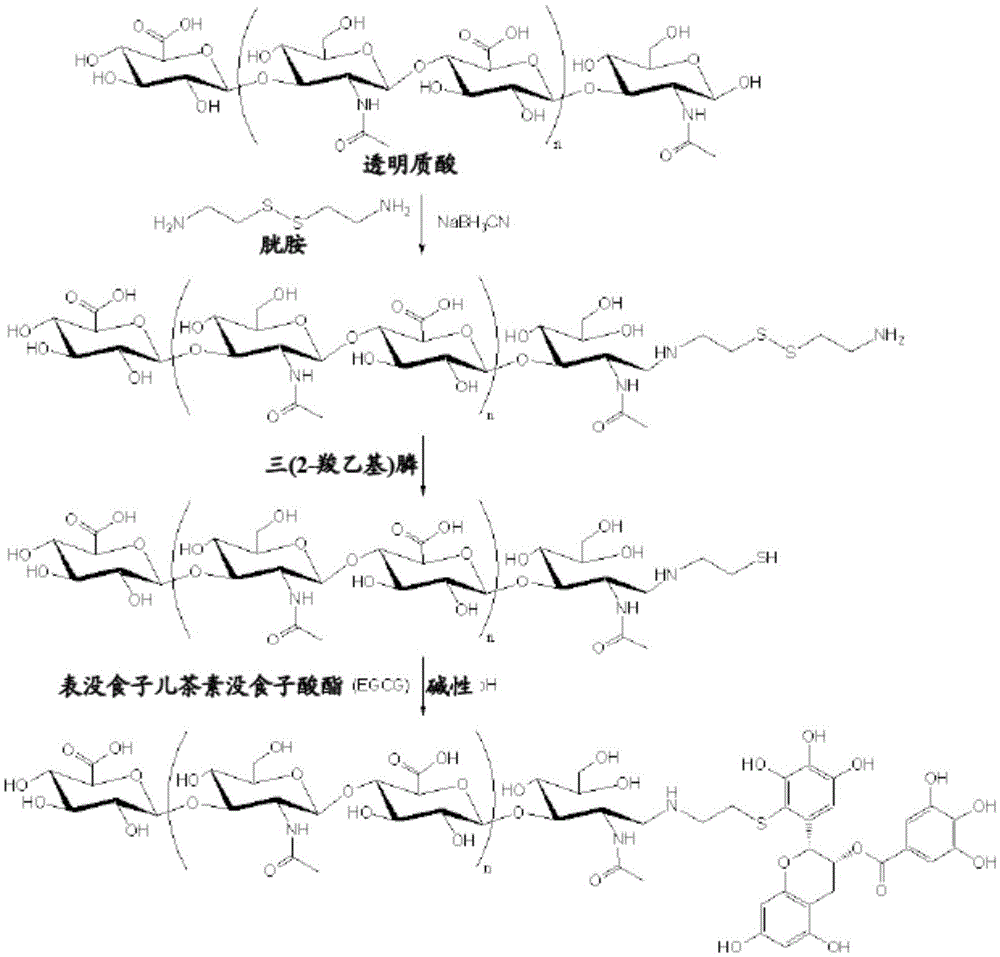
[0057] According to the present invention, the polymer is modified with thiol groups for attachment to flavonoids. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, described method further comprises the following steps:
[0058] (a) linking a thiol- or disulfide-containing compound to the polymer in the presence of a reducing agent; and
[0059] (b) cleaving any disulfide formed at the disulfide bond to form said polymer with terminal thiol groups.
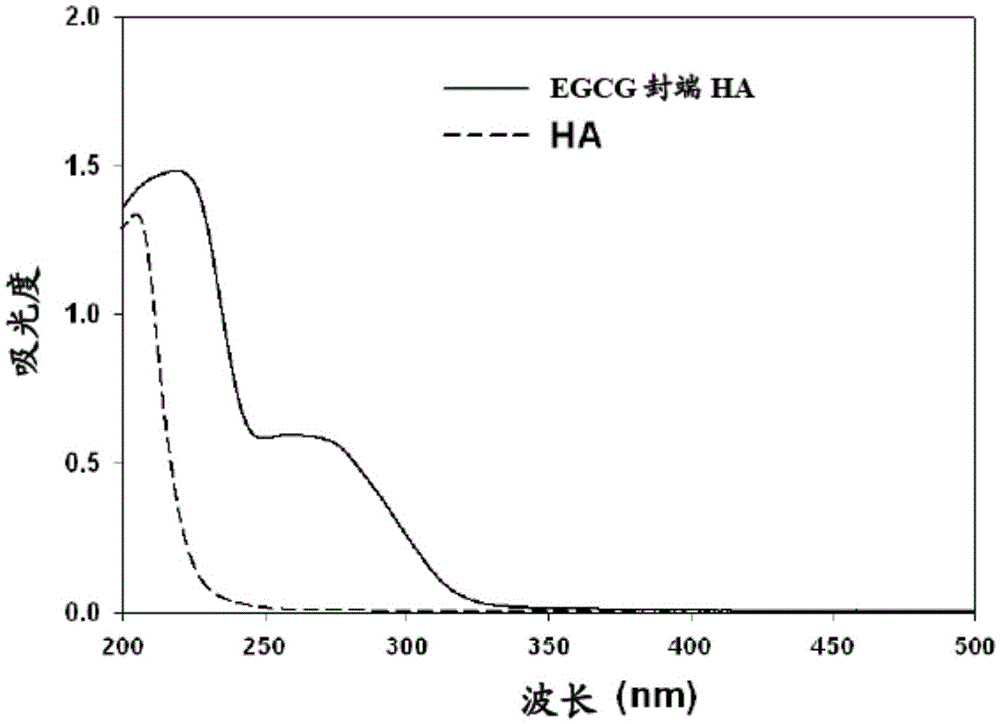
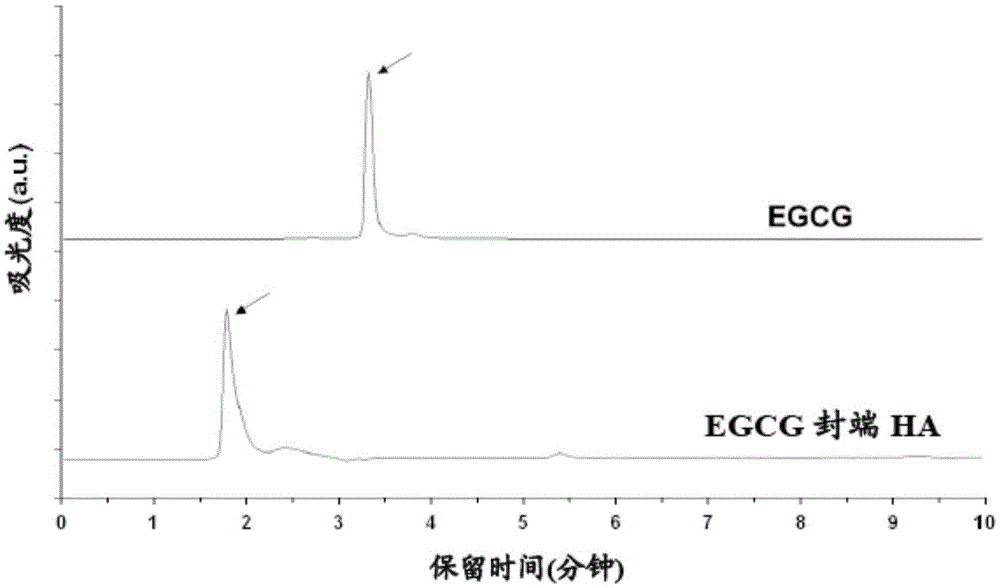
[0060] This method is suitable, for example, for the preparation of flavonoid-terminated polymer conjugates. The conjugate was obtained in high purity and high yield (over 90%). The method is easy to perform and scale up. It is a non-enzymatic method that does not require complex purifications.
[0061] The thiol- or disulfide-containing compound may be, for example, aminoalkylthiol derivatives such as cysteamine hydrochloride and cystamine dihydrochloride.
[0062] According to a preferred embodiment, said linki...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com