Method for suppressing infectious disease in crustaceans
A technology for crustaceans and infectious diseases, applied in the direction of antiviral agents, anti-infective drugs, single-celled algae, etc., can solve problems such as environmental adverse effects, antibiotic residues, and production of resistant bacteria, so as to improve immunity, suppress infectious diseases, The effect of stable supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
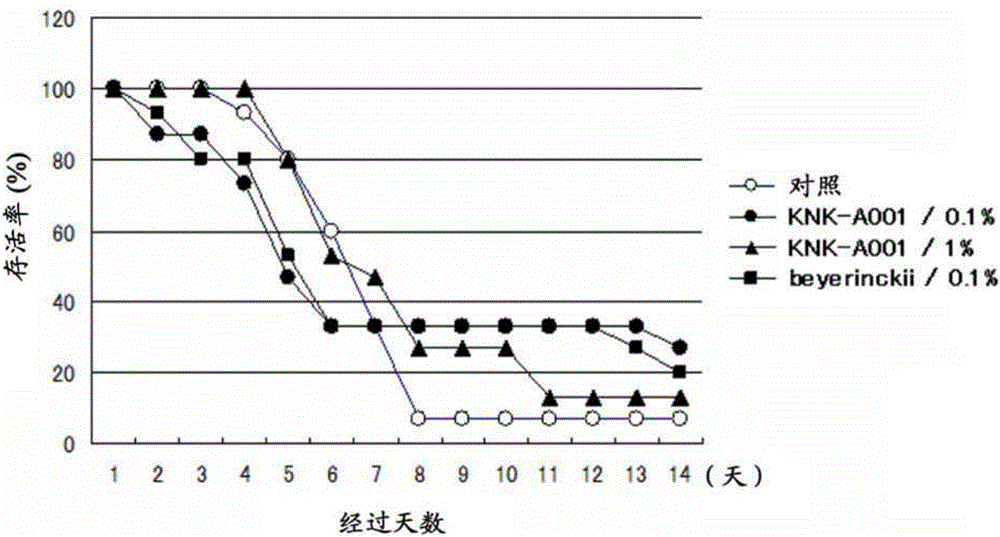
[0085] Embodiment 1: the cultivation experiment of Penaeus japonicus
[0086] (1) Preparation of feed
[0087] The sterilized liquid medium was inoculated with Parachlorella kessleri KNK-A001 strain (Accession No.: FERM BP-22256), shaded with aluminum foil, and then pre-cultivated at 30° C. for 72 hours. Next, add the pre-culture medium to a larger volume of sterilized liquid medium, shield it with aluminum foil, and then cultivate it for 143 hours under the conditions of an internal temperature of 30°C, an aeration rate of 2L / min, a stirring speed of 450rpm, and a pH of 6-7.
[0088] Next, the culture solution was dried with a double-drum dryer, and the obtained dried aggregate was pulverized with a feather mill to obtain a dried cell product of the KNK-A001 strain.
[0089] In addition, as algae of the genus Pseudochlorella, algae of the species Parachlorella beyerinckii (product name "Beyerinckii", available from Mitsui & Co., Ltd.) were used in the same experiment.
[00...
Embodiment 2
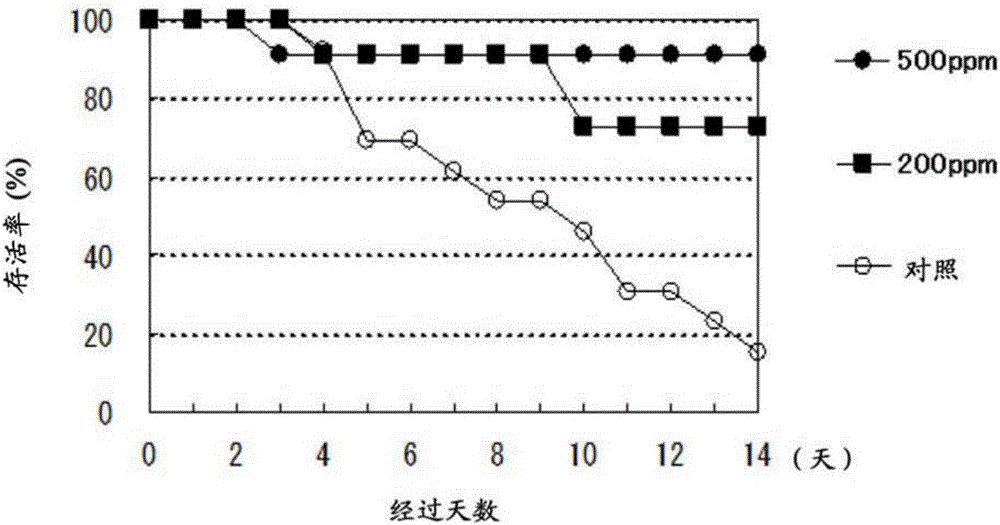
[0095] Embodiment 2: the cultivation experiment of Penaeus japonicus
[0096] Feed containing 0.02% by mass (200 ppm) or 0.05% by mass (500 ppm) of Parachlorella kessleri KNK-A001 strain (Accession No.: FERM BP-22256) was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 (1). In addition, for comparison, only the above-mentioned feed for shrimp was used as a control.
[0097] Moreover, the cultivation experiment was performed similarly to Example 1 (2). show the result in figure 2 . figure 2 Among them, "*" indicates a significant difference at p<0.05 when the survival rate of Penaeus japonicus on the 14th day since infection with the virus was performed, and "**" indicates a significant difference at p<0.01.
[0098] according to figure 2 The results can prove that in the group fed with the feed compounded with algae of the genus Pseudochlorella, compared with the group fed with common feed, the survival rate was significantly improved, and viral infectious diseases could be...
Embodiment 3
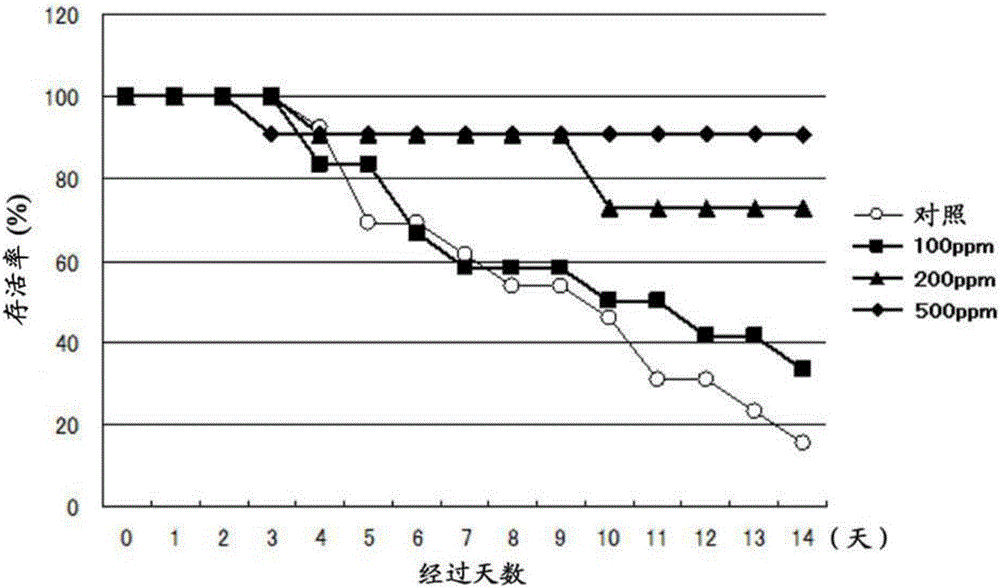
[0099] Embodiment 3: the cultivation experiment of Penaeus japonicus
[0100] In Example 1, the same experiment was carried out using smaller Penaeus japonicus. That is, in the same manner as in Example 1 (1), preparations containing 0.01 mass % (100 ppm), 0.02 mass % (200 ppm) or 0.05 mass % (500ppm) of the feed. In addition, for comparison, only the above-mentioned feed for shrimp was used as a control. And in Example 1 (2), except having used the japonicus of body weight about 1.5g, and the number of the japonicus in each water tank was 25 tails, the cultivation experiment was performed similarly. show the result in image 3 .
[0101] Such as image 3 As shown in the results, even when the amount of inoculated virus liquid relative to the body weight was larger, the survival rate of the three groups fed with the feed containing algae of the genus Pseudochlorella was significantly higher than that fed only with the commercial feed of the control group. It should be n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com