A hollow-slab-bridge hinge joint bearing capacity test piece, a manufacturing method thereof and a test method of the test piece
A technology of hollow slab bridge and bearing capacity, which is applied in the field of bridges, can solve problems such as small size, achieve simple production, clear force, and solve the effects of rapid measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
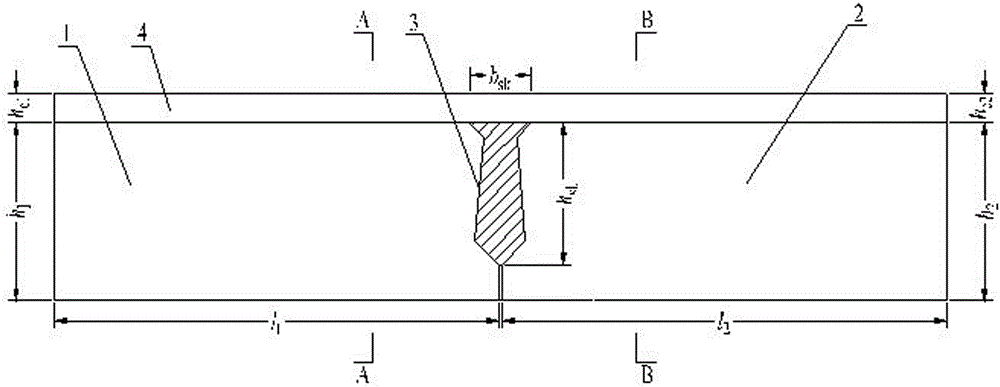
[0066] What this embodiment provides is a 10m hollow slab bridge, and its design is consistent with the new standard of the Ministry of Communications 2008 general set of plans for a simply supported 10m hollow slab bridge Figure 1 Sincerely.
[0067] The specific production includes the following steps:
[0068] (1) Determine the reinforcement of the first concrete beam 1, the second concrete beam 2, the hinge joint 3 and the concrete pavement layer 4 and the strength grade of the concrete.
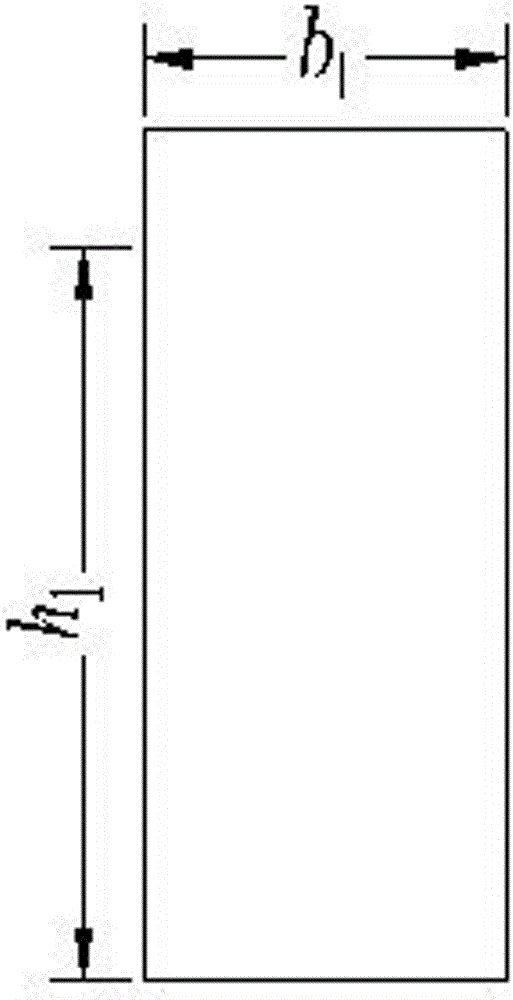
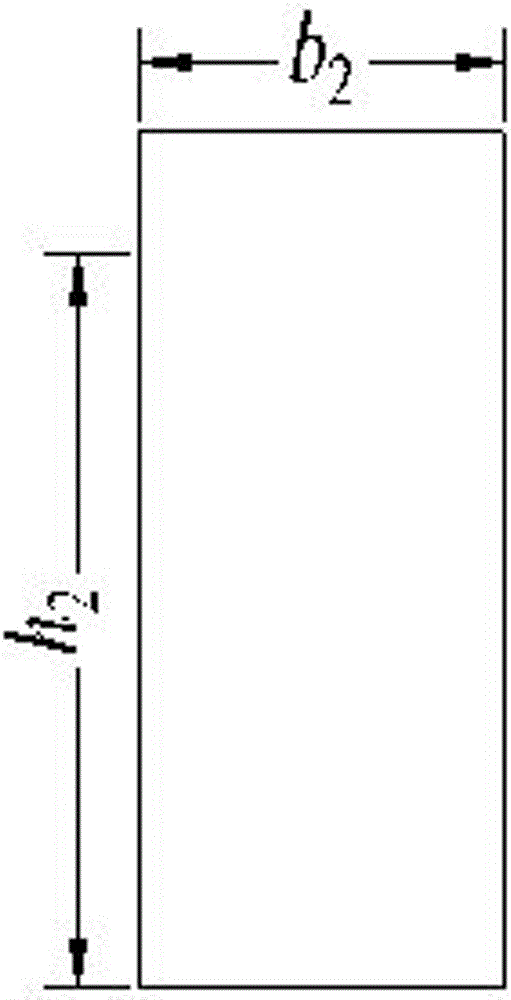
[0069] According to the standard drawing of the first-class simply supported 10m hollow slab girder bridge of the new specification of the Ministry of Communications 2008 general set of drawings, the height h of the first concrete beam 1 1 is 600mm, the width b of the first concrete beam 1 1 is 300mm, the length l of the first concrete beam 1 1 is 1495mm, the height h of the second concrete beam 2 2 is 600mm, the width b of the second concrete beam 2 2 is 300mm, the length l of the...
Embodiment 2
[0088] This embodiment is a widened hollow slab bridge with a span of 10m. It is composed of new and old hollow slab girders with different rigidities. Slab bridge standard Figure 1 , its torsional rigidity is 6.93×10 10 . The hollow slab girder of the old bridge is a double-hole plate Figure 15 , and its torsional stiffness is 4.93×10 10 . The difference from Example 1 is that the torsional rigidity of the new and old hollow slab girders is different, so when testing the bearing capacity of the hinge joint between the old and new hollow slab bridges, the resistance of the first concrete beam 1 and the second concrete beam 2 in the designed test components The bending stiffness is different, and the first concrete beam 1 represents the old hollow slab beam on the side of the hinge joint of the tested hollow slab bridge, and its width b 1 300mm, height h 1 is 943mm; the second concrete beam 2 represents the new hollow slab beam on the other side of the hinge joint of th...
Embodiment 3
[0090] The structure of the hollow slab bridge of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the first embodiment, the difference is that the concentrated load loaded during the test of this embodiment is based on the test methods of pure shear, pure bending or combined bending and shearing. to change the loading position. At the same time, two displacement meters can be arranged on the left side of the bottom surface of the second concrete beam 2 to observe the mechanical performance of the hinge joint under the action of concentrated load and the vertical relative displacement of the beams on both sides of the hinge joint.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com